![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
37 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back

|
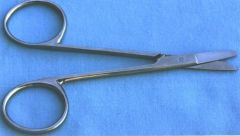
Littauer Suture Removal Scissors; Used to remove stitches following routing surgery, wound repairs etc.; Note hooked portion of scissors for ease of removal of sutures; Length= 4 & 1/2 inches long |
|
|
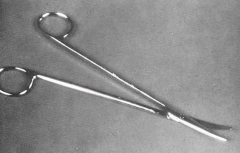
Spencer Suture Removal Scissors; Similar to Littauer but smaller; Typically about 3 & 1/2 inches long; Have hooked portion as well |
|

|
Wire Cutting Scissors; Have short, thick jaws with serrated (etched) edges; Used for cutting wire sutures (jaw fracture repairs) |
|

|
Lister Bandage Scissors; Used for cutting bandage material; Blunt tipped end slides under bandaging |
|

|
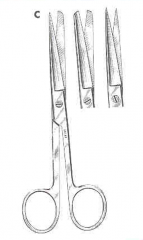
Mayo Dissecting Scissors; Heavy scissors; Blades may be straight or curved; Used for cutting tough tissue such as heavy connective tissue |
|
|
Metzenbaum Scissors; Blade is straight or curved; Used for cutting delicate tissues such as fat or thin muscle |
|
|
Operating Scissors; Sharp-blunt; Blunt-Blunt; Sharp-sharp; Cut through or snip tissue; Separate tissu by inserting tips into the tissue and speading the points; Separate tissue by exerting a steady force of the tips against the tissue until separation is adequate; Cut suture material |
|

|
Mayo-Hegar Needle Drivers; Used to hold curved suture needles; NO built in scissors |
|

|
Olsen-Hegar Needle Drivers; Used to hold curved suture needles (similar to mayo hegar); Scissors built in- advantage dual function for tying sutures and cutting, disadvantage- cutting before you're ready |
|
|
Hemostatic Forceps |
AKA hemostats; Utilized for hemostasis; Clamp and hold blood vessels; Different sizes with straight or curved jaws |
|

|
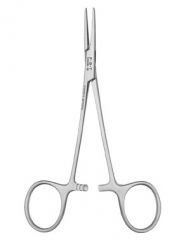
Kelly Hemostatic Forceps; Transverse serrations; Serrations only cover HALF of the jaws; Jaws can be straight or curved |
|
|
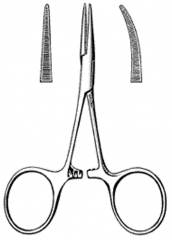
Halsted Mosquito Hemostatic Forceps; Transverse serrations; Serrations cover entire jaw; Smaller, finer jaws than kelly hemostats; Jaws can be straight or curved; Length=5.5 inches |
|
|
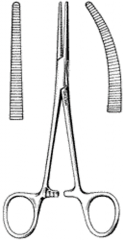
Hartman Mosquito Hemostatic Forceps; Similar to Halsted; Length= 3.5 inches |
|
|
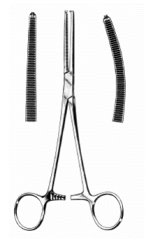
Crile Hemostatic Forceps; Larger than mosquito hemostats; Transverse serrations cover entire jaw; Jaws can be straight or curved; Used on larger blood vessels than mosquito hemostats |
|
|
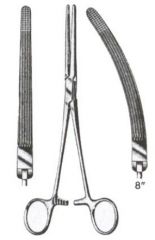
Rochester-Ochsner Forceps; Similar to Rochester-Pean foreceps but have teeth; Used to clamp blood vessels or to grasp tissue; Most commonly used in orthopedic or large animal surgery; May be used to grasp the claw during an onychectomy |
|
|
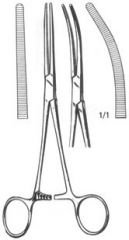
Rochester-Carmalt Forceps; Larger than a Kelly or Crile; Longitudinal serrations; Used for clamping tissue and containing blood vessels; Curved or straight |
|
|
Rochester-Pean Forceps; Large version of Crile forceps; Used for clamping tissue bundles and large blood vessels |
|

|
Brown-Adson Tissue Foreceps; Designed to hold and easily release tissue; Multiple intermeshing teeth of jaws; Often used to grasp delicate tissue |
|

|
Adson Tissue Forceps; Similar to Brown-Adson forceps; Have a single "rat tooth"; Wider area for easier handling; Commonly used to hold skin when suturing |
|

|
Rat Tooth Tissue Forceps; Different series of teeth; Used for grasping skin and fascia |
|

|
DeBakey Vascular Tissue Forceps; Long, narrow jaws with multiple small teeth; Atraumatic forceps used for handling blood vessels; Used for vascular surgery |
|

|
Dressing Forceps; Used for handling dressings; Jaws have no teeth- just transverse serrations |
|

|
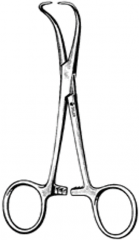
Allis Tissue Forceps; Multiple teeth in the jaws; Used to grasp intestine, fascia and skin; Also used for retraction- can clamp to skin on both sides of the abdominal incision for better access to abdomen |
|
|
Backhaus Towel Clamp/Forceps; Secure drapes or towels to a patient's skin; Sharp pointed jaws; Autoclave in closed position |
|

|
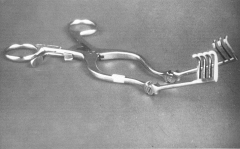
Jones Towel Clamp/Forceps; Same purpose as Backhaus towel clamps; No ratchets- spring motion allows instrument to be opened and closed; Instrument always in closed position |
|
|
Weitlaner Retrators; Self-retaining; Used most commonly for muscle retraction in orthopedic surgeries;
|
|
|
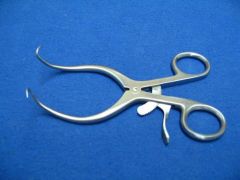
Gelpi Retractors; Self-retaining; Used most commonly for muscle retraction in orthopedic surgeries |
|

|
Balfour Retractors; Self-retaining; Hold abdominal wall open for surgical procedures |
|

|
Army-Navy Retractors; Hand-held- need a surgical assistant to maintain position of these retractors; Used to retract skin, fat or muscle |
|

|
Senn Retractors; Hand-held- Need a surgical assistant to maintain position of these retractors; Used to retract skin, fat or muscle; Looks like back-scratcher |
|
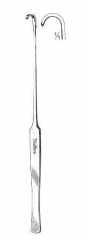
|
Snook Ovariohysterectomy Hook; Used to retrieve each uterine horn during an ovariohysterectomy |
|

|
Scalpel Handle # 3; Used primarily for small animals |
|

|
Scalpel Handle # 4; Used primarily for large animals |
|
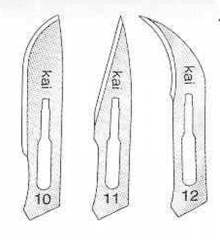
|
Small Animal Scalpel Blades; 10- routine surgeries: castration/ovariohysterectomy; 11- stab incision's: abscesses and creating opening for drains; 12- onychectomies (declaws)
|
|
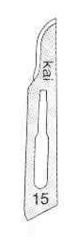
|
Small animal Scalpel Blade: 15- Routine surgeries (small animals- cats and others) |
|
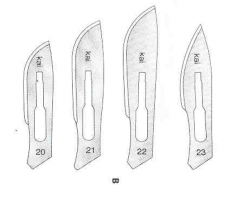
|
Large Animal Scalpel Blades; Most commonly used are sizes 20, 21, 22 and 23; Fit on a #4 scalpel handle |
|
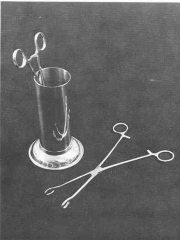
|
Transfer Forceps; Sponge forceps or hemostatic forceps in a weighted cyclinder; Used for transfer items from cold sterilization trays to the sterile field; Forceps sit in "cold sterile" solution |

