![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
32 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What structures make up the hippocampal formation?
What is the fxn? |
dentate gyrus
hippocampus proper subiculum memory & learning |
|
|
The hippocampus is continuous w/ the ______________ through the subiculum
|
parahipocammpal gyrus
|
|
|
The limbic cortex is typically __________ & ___________
|
paleocortex (3-5 layers) & archicortex
|
|
|
What are the main borders of the hippocampal formation?
|
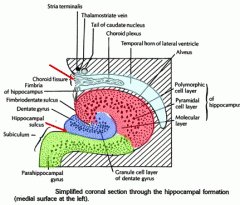
-hippocampal sulcus (grove btwn parahippocampal gyrus/subiculum & dentate gyri)
-choroid fissure -inferior horn of lateral ventricle |
|
|
The hippocampus proper (cornu ammonis, CA) is a 3 layered cortex, divided into 4 regions (CA1-4) based on what?
|
differential sensitivity to oxygen deprivation & corticosteroids
& involvment in memory circuitry |
|
|
The ______________ lies btwn the hippocampus & subiculum & receives major input from entorhinal cortex
|
dentate gyrus
|
|
|
The subiculum forms a transition area btwn the parohippocampal gyrus & the ________________
What originates from the subiculum? |
hippocampus proper CA regions
projections from the hippocampal formation to the mammillary bodies |
|
|
The hippocampal formation has efferent projections to the ____________ via the fornix
The fornix is formed from the _________ as it leaves the hippocampus |
mamillary bodies
fimbria (fimbria = collection of nerve fibers from alveus) |
|
|
The fornix forms 2 major projections from the hippocampus & subiculum to where?
|
precomissural projection to septal area & hypothalamus
& postcomissural projection to mammilary bodies |
|
|
The hippocampal formation has afferent connections from the ______________, ______________, & ____________ (also via fornix)
These afferents work together to incorporate _______ |
etorhinal cortex (olfactory info),
parahippocampal gyrus (visual & sensory info), & basal forebrain (septal area, hypothalamus, amygdala) *MEMORY |
|
|
T/F
Most of the afferent connects TO the hippocampus also recieve efferent info FROM hippocampus |
TRUE
|
|
|
Efferent output from the hippocampus to __________ is associated w/ cortical activation, motivation, & autonomic components of memory & behavior & generation of theta rhythm
|
PREcommisural areas
(septal area, ant hypothalamus, nucleus accumbens, substantia innominata, medial frontal cortex) |
|
|
Efferent output from the hippocampus to the ________________ is associated w/ declarative memory
|
medial mammillary nuc (Papez circuit)-->
POSTcommisural areas |
|
|
Other efferent arise from the subiculum & include ______________ (feeding behavior) & _______________ (memory assoc)
|
ventromedial nuc of hypothalamus (feeding)
lateral dorsal nuc of thalamus (memory assoc w/ cingulate gyrus) |
|
|
Describe the circuit of Papez
|
begins- entorhinal cortex (parahippocampal gyrus)-->
projects tohippocampus (subiculum)--> projects to mammilary bodies--> project to the anterior nuclei of the thalamus--> project to cingulate gyrus (via the internal capsule)--> **cingulate gyrus then projects back to entorhinal area (via cingulum bundle) |
|
|
Cingualte cortex distributes info into & out of ___________
|
Papez’s circuit
|
|
|
Papezis circuit is related to __________
Where does the circuit distribute info? |
behavioral motivation
distributes primarily to prefrontal & premotor areas & visual auditory & somatosenaory association cortex. |
|
|
What is the main descending pathway from Papez's circuit?
|
mammilotegmental fasciculus
(goes to reticular formation & raphe nuc) |
|
|
The ________ is in the anterior medial temporal lobe. It uses visceral & somatic sensory inputs to coordinate emotional responses to pleasurable, fearful & visceral stimuli.
|
amygdaloid complex
(mostly sympathetic autonomic & fear responses) |
|
|
What are the 2 primary nuclear groups of the amygdala?
|
1. corticomedial group- primary connections w/ olfactory bulbs
2. basolateral group- connects w/ broader regions (corticomedial group, entorhinal cortex, septal area) |
|
|
The ___________ group plays a role in autonomic reg of visceral stimuli associated w/ reproduction, feeding, & survival (olfactory funxtion)
|
corticomedial group
(via brainstem, hypothalamus, & thalamus connections) |
|
|
Corticomedial group connects w/ ____________--> rewarding nature of behavior, and w/ ____________--> motor behavior
What is the major connection? |
nucleus accumbens (reward)
caudate & putamen (motor) septal nuclei via stria terminalis |
|
|
The _____________ group plays a role in a wide range of somatosensory, visual, & visceral functions
This group contains ________ neurons |
basolateral group
GABA neurons (GABA agonists reduces anxiety) |
|
|
The basolateral group connects to the hypothalamus, substantia innominata, & septal nuclei via the __________________ pathway
These projections are involved in what? |
ventral amygdalofugal pathway
involved in integration of autonomic & cortical info into the affective aspects of memory & behavior (aggression, fear) |
|
|
The ___________ sends diffuse cholinergic projections to cerebral cortex as part of reticular arousal (emotional stimuli)
|
substantial innominata (basal nucleus, includes Nuc of Meynert))
|
|
|
The substantia innominata also is involved in _________________ via brainstem, locus ceruleus, raphe
|
cortical activation
**degeneration assoc w/ alzheimers |
|
|
What pathway links the septal nuclei w/ the habenular nuclei, interpeduncular nucleus, & brainstem tegmentum autonomic nuclei?
|
stria medullaris thalami
|
|
|
Connections btwn habenular nuclei & globus pallidus linkes the ______________ w/ motor expression of autonomic related behavior (facial expressions, laughing, crying)
|
septal nuclei
|
|
|
The most important function of septal area connections is in regulation of ________ & ________
|
visceral reactions & behaviors
|
|
|
Septal area has cholinergic neurons that project to _____ & _______
what does this contribute to? |
hippocampus & amygdala
theta rhythm & memory formation |
|
|
The ________-
-lies at the jxn of the caudate & putamen -receives input from the amygdala, hippocampus, & dopaminergic nuclei (substantia nigra, ventral tegmental area) -projects to hypothalamus, brainstem & globus pallidus |
nucleus accumbens
|
|
|
What does the nucleus accumbens contribute to? (fxn)
Via what kind of receptors? |
rewarding nature of behaviors (addiction)
endogenous opiod receptors (may be assoc w/ addiction & OCD) |

