![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
61 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Obj.
Describe the role of the anatomo-clinical method in the development of the theory of cortical localization of function. |
involved palpating irregularities on the skull to make inferences about the underlying cortical structures and linking these to mental capacities.
|
|
|
Obj.
Name and identify the six layers component layers of neocortex |
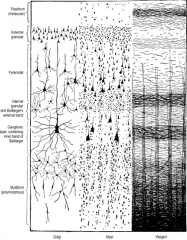
I – Molecular (Plexiform) Layer
II – Outer Granular Layer III – Outer Pyramidal Layer IV – Inner Granular Layer V – Inner Pyramidal Layer VI – Multiform Layer |
|
|
Roughly 90% of the cerebral cortex is ___________
|
neocortex
|
|
|
Obj.
Compare and contrast between heterotypical agranular and granular cortex. |
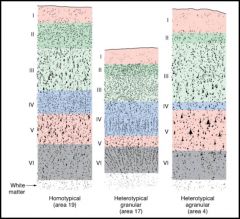
heterotypical agranular:
- primary motor cortex - dominated by pyramidal projection neurons granular cortex: - primary sensory cortex - dominated by smaller cells, stellate cells |
|
|
Pyramidal neurons are present in all molecular layers except _____
|
Layer 1
*Prominent in 2, 3, & 5 |
|
|
__________ dendrites extend toward the molecular layer
|
large apical dendrites
|
|
|
___________ dendrites project horizontally
|
basal dendrites
|
|
|
Giant pyramidal neurons of Betz are only found where?
|
in motor cortex--> in layer 5
|
|
|
pyramidal neurons are the major output pathway of the _______________
|
cerebral cortex
NOTE: fusiform modified pyramidal cells project to thalamus from layer 6 |
|
|
___________ neurons are intrinsic neurons most numerous in layer 4
What type of projections do they receive? |
stellate neurons
thalamocortical projections |
|
|
(spiny/aspiny) stellate cells are only excitatory interneurons (Glu)
|
spiny stellate
|
|
|
Chandelier cells are found in what layer?
w/ dendrites in what layer? |
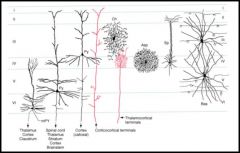
layer 3
dendrites in layer 4 |
|
|
Basket cells are present in what layers w/ dendrites in all layers?
|
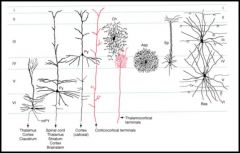
3 & 5
|
|
|
found in deeper layers, multipolar neurons w/ short branching dendrites & an axon that projects into superficial layers
|
Cells of Martinotti
|
|
|
Obj.
Describe the different types of fibers (axons) originating and terminating in cerebral cortex: local intrinsic neurons corticofugal corticopetal |
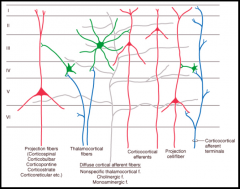
local intrinsic neurons- connect diff layers
corticofugal- go to subcortical areas, brainstem, & spinal cord corticopetal- from the thalamus to layer 5 |
|
|
Noradrenergic, seritonergic, dopaminergic, cholinergic from other subcortical nuclei – diffuse inputs
why type of axons? |
corticopetal
|
|
|
2 types of IntRAhemispheric (association fiibers)
|
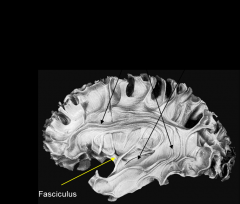
long association= layer 3 & 5 connect lobes together
(pictured above) short association= layer 2 & 3 connect gyri together |
|
|
INtERhemispheric (Callosal fibers) connect the R & L hemisphers (corpus callosum) & temporal poles (anterior commissure).
What layer? |
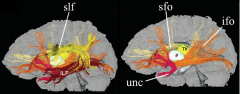
layer 3
|
|
|
Brodmann's areas are cytoarchitectural areas used to describe what?
|
functional areas of the cortex
|
|
|
Primary motor cortex
|
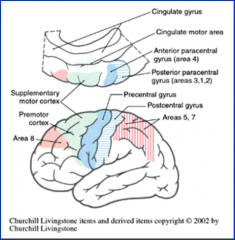
area 4
*precentral gyrus (frontal) = major motor output register to spinal cord & brain |
|
|
premotor cortex & supplementary motor area
|
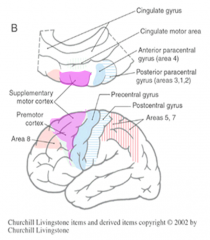
area 6
*front of precental gyrus (frontal) --> pink area ^ = planning of motor activities |
|
|
frontal eye fields
|
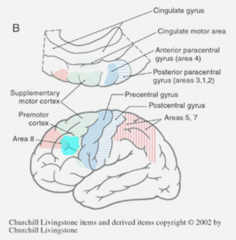
area 8
*anterior to premotor cortex (frontal)--> teal ^ = cortical (conscious) control of eye movements |
|
|
Broca’s area on left (pars triangularis & opercularis of Inferior Frontal Gyrus)
|
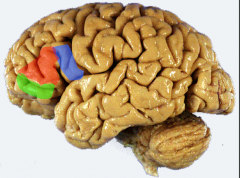
area 44 & 45
*pars trangularis (red) & pars opercularis (blue) (inferior frontal gyrus) = motor area for speech in dominant hemisphere (left usually) |
|
|
Primary somatosensory cortex
|
areas 1, 2, & 3
*postcentral gyrus (purple) (parietal) = response to modality of discriminitive touch, vibration, position, pain, & temp |
|
|
Somatosensory Association areas
|
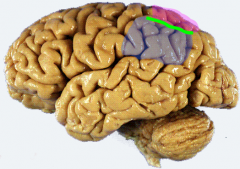
areas 5 & 7
*superior parietal lobule (pink) = understanding spoken & written language (usually L hem) (integration of kinesthetic sense, hand eye coordination) |
|
|
Primary Visual Cortex
|
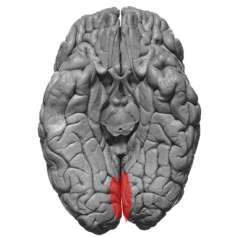
area 17
*on both sides of calcarine sulcus (occipital) |
|
|
Visual Association Cortex
|
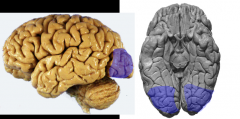
areas 18 & 19
*extrastriate cortex (occipital) = processing of visual data to percieve motion, depth (binocular vision), color, & object position |
|
|
Primary Auditory Cortex
|
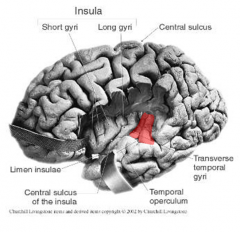
areas 41 & 42
* w/i lateral fissure, transverse temporal gyru (of Heschl) = audition, recieves info from BOTH ears, recognition of sounds= coordinates understanding of spoken language |
|
|
Auditory Association Cortex (left posterior- Wernicke’s area)
|
area 22
* posterior superior temporal gyrus = comprehension of the spoken language = coordinates understanding of spoken language |
|
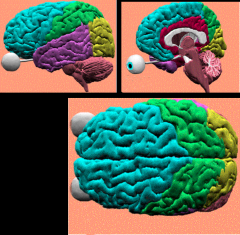
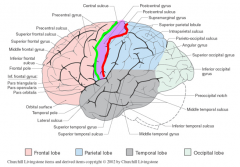
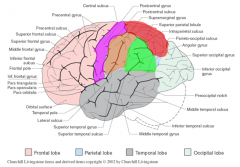
Identify the primary lobes of the brainstem
|
frontal= teal
parietal= green occipital= yellow temporal= purple limbic= red insula= interior to grey |
|
|
Obj.
Describe the anatomical boundaries of the frontal lobe |
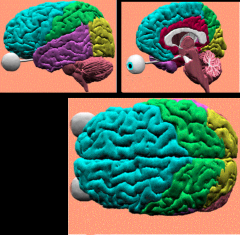
separated from parietal lobe by central sulcus & temporal by lateral fissure
|
|
|
Primary motor cortex.
Supplemental motor areas Frontal eye fields Prefrontal cortex functional components of what lobe? |
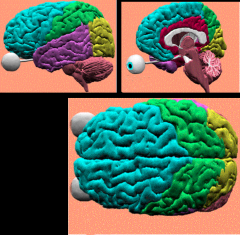
frontal lobe (teal)
|
|
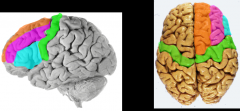
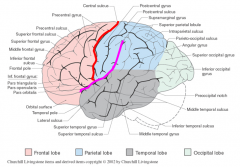
Identify the primary gyri on frontal lobe
|
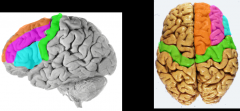
green= precentral gyrus = primary motor cortex
orange= superior frontal gyri pink= middle frontal gyri blue= inferior frontal gyri |
|
|
How is the precentral gyrus of the frontal lobe somatotropically organized?
|

trunk, head, hand, & tongue = lateral & inferior
-tongue near lateral fissure -legs in anterior paracentral gyrus |
|
|
3 primary parts of inferior frontal gyrus (frontal lobe)
|
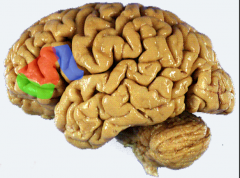
1. pars opercularis (blue)
2. pars trangularis (red) 3. pars orbitalis (green) |
|
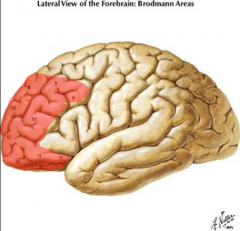
The prefrontal cortex of the frontal lobe is associated w/ what Brodmann areas?
What functions does it participate in? |
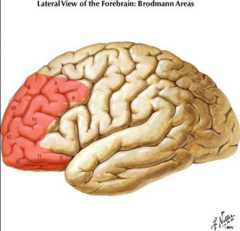
Areas 9, 10, 11, & 12
judgement, foresight, a sense of purpose, responsibility, & socialy propriety |
|
|
The gyri of the frontal lobe are separated by what?
|
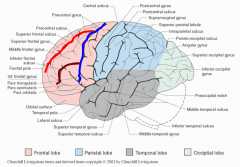
precentral sulcus (blue),
superior frontal sulcus (red), & inferior frontal sulcus (brown) |
|
|
On the medial surface,
the precentral gyrus continues as ______________ & the superior frontal gyrus continues as _____________ |
anterior paracentral gyrus
cingulate sulcus |
|
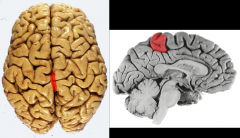
The _____________ contains both the primary motor (anterior) & primary sensory (posterior) functional areas in the frontal lobe.
|
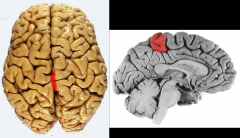
paracentral lobule
(medial extension of pre & post-central gyri) |
|
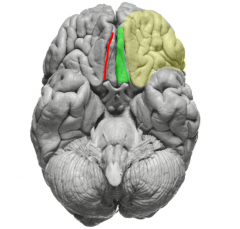
Identify the ventral structures of the frontal lobe
|
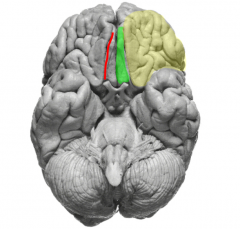
yellow= orbitofrontal gyri (extension of prefrontal area)
red= olfactory sulcus (contains olfactory bulb & tract) (medial boundary of orbitofrontal gyri) green= gyrus rectus (superior frontal gyrus extension) |
|
|
Primary somatosensory cortex & sensory association areas are w/i what lobe?
|
parietal lobe
|
|
|
Obj.
Describe the anatomical boundaries of the parietal lobe |
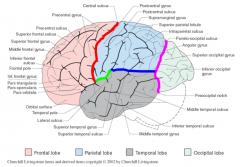
laterally posterior to frontal via central sulcus (red)
above temporal lobe (blue) above lateral fissure (sulcus) (green) anterior to occipital lobe via parieto-occipital sulcus (pink) |
|
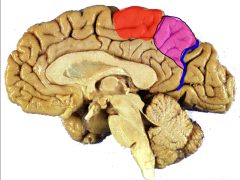
Identify the pink structure of the parietal lobe anterior to the parieto-occipital sulcus (blue) & posterior to paracentral lobule (red)
|
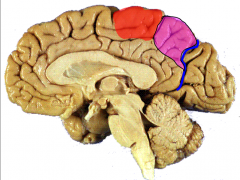
precuneus
|
|
|
Major functional components of the parietal lobe
|
pink= primary somatosensory cortex
red= superior parietal lobule orange= supramarginal gyrus green= angular gyrus (supramarginal gyrus + angular gyrus = inferior parietal lobule) |
|
|
The ________________ lies behind the central sulcus & postcentral sulcus
|
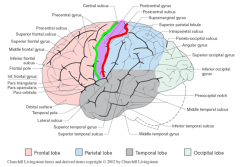
postcentral gyrus (purple)
(central suclus- green, postcentral- red) |
|
|
How is the postcentral gyrus of the parietal lobe somatotopically organized?
|
sensory areas of genitals, foot, leg = medial
tongue= most lateral |
|
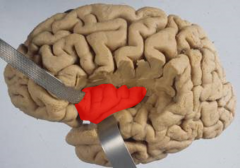
Secondary somatosensory cortex areas from the parietal lobe project to the __________
|
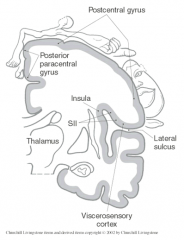
insula
|
|
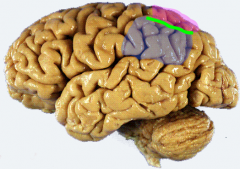
Identify structures of parietal lobe
|
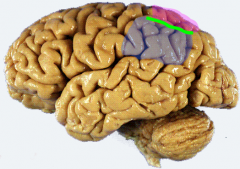
pink= superior parietal lobules
blue= inferior parietal lobules green= intraparietal sulcus |
|
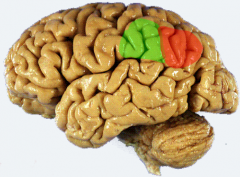
Identify & differentiate btwn the two parts of the inferior parietal lobule
|
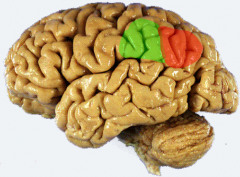
red= angular gyrus = area 39 = comprehension of written language
green= supramarginal gyrus= area 40= comprehension of spoken language (w/ Wernicke's) |
|
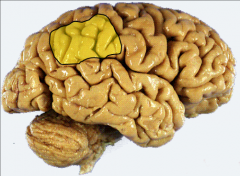
What does the inferior parietal lobule modulate in the nondominant hemisphere?
What syndrome is a lesion in this area associated w/? |
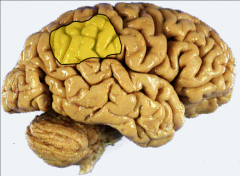
attention to stimuli both on body & visual field= perceptual awareness
hemineglect syndrome= failure to recognize left side of body as self |
|
Identify the primary gyri of the medial occipital lobe
|
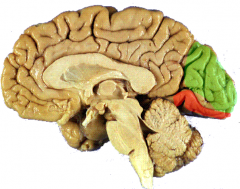
green= cuneus gyrus
orange= lingual gyrus *divided by calcarine sulcus** |
|
|
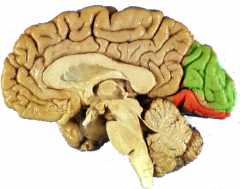
The occipital lobe contains what 2 cortex?
|
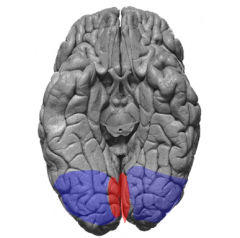
primary visual cortex (orange) & visual association cortex (blue)
|
|
|
How is the retinal surface/visual field represented in the area of the primary visual cortex ?
|
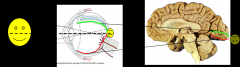
represented in a retinotopic fashion in area around calcarine sulcus
|
|
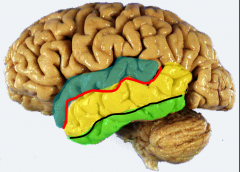
Obj.
Identify the major component structures, e.g., gyri, sulci, etc., of the temporal lobe |
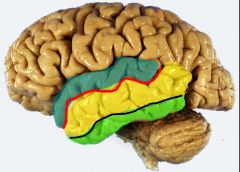
blue= superior temporal gyrus
red= superior temporal sulci yellow= middle temporal gyrus black= inferior temporal sulcus green= inferior temporal gyrus |
|
|
Obj.
Locate and describe the major functional components of each of the temporal lobe |
primary auditory cortex
wernicke's area |
|
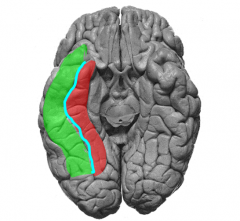
Identify the ventral structures of the temporal lobe
|
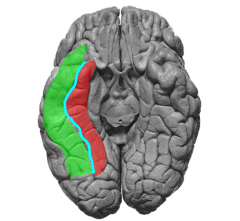
green= lateral occipitotemporal gyrus (fusiform gyrus)
blue= occipitaltemporal sulcus red= medial occipitotemporal gyrus ^involved in recognition of objects & faces** |
|
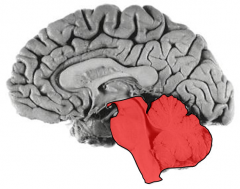
The _____________ is the primary processor of memory & is also involved in emotional behavior, homeostatic responses, motivation, & sexual behavior
|
limbic lobe
|
|
Obj.
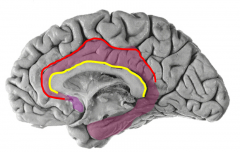
Describe the anatomical boundaries of the limbic lobe |
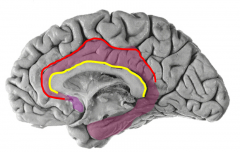
red= cingulate sulcus = anterior / dorsal boundary
yellow= callosal sulcus= separates from corpus callosum |
|
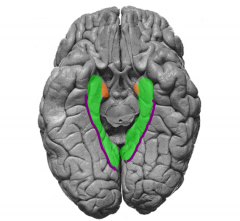
Identify gyrus & sulci of the ventral limbic lobe
|
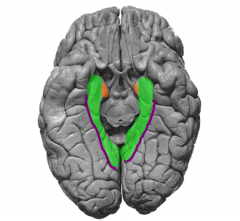
green = parahippocampal gyrus
purple= collateral suclus orange= primary olfactory cortex/ entorhinal piriform cortex (part of parahippocampal) |
|
|
Connections btwn the hippocampal formation, parahippocampal gyrus, & cingulate gyrus are necessary for what?
|
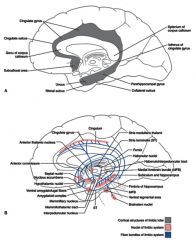
incorporation of short term to long term memory
|
|
|
Obj.
Describe the general functions associated with each of the lobes of the cerebral hemisphere. |
frontal- motor & cognition
parietal- sensory & multimodal associative fxn temporal- integrative sensory, some memory, auditory, & olfactory functions occipital- visual function limbic- primary processor of memory insula- memory of tactile stimuli |

