![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
49 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
11 Organ Systems |
Muscular Urinary Reproductive Digestive Endocrine Respiratory Lymphatic Integumentary Nervous Cardiovascular Skeletal |
|
|
Components and Functions of Muscular System |
Skeletal Muscles Functions: -movement & manipulation of external environment -posture -facial expressions -produces heat |
|
|
Components and Functions of Urinary System |
Kidneys, Ureter, Urinary Bladder, Urethra Functions: -eliminates nitrogenous wastes -regulates water, electrolytes, acid-base balance of blodd |
|
|
Components and Functions of Reproduction System |
Female: Mammary Glands, Ovaries, Uterine Tube, Uterus, Vagina -site of fertilisation and development of fetus -Mammary: produces milk -Ovaries: produces oocytes and sex hormones Male: prostate gland, scrotum, testes, vas deferens, penis -testes: produces sperm and sex hormones -ducts & glands: delivery of sperm |
|
|
Components and Functions of Endocrine System |
Pineal, Pituitary, Thyroid, Thymus, Pancreas, Ovaries, Testes Function: -secretion of hormones that regulate processes - growth, reproduction, metabolism |
|
|
Components and Functions of Respiratory System |
Nasal Cavity, Pharynx, Larynx, Brochi, Trachea, Bronchi, Lungs Function: -supplies blood with oxygen and removes carbon dioxide |
|
|
Components and Functions of the Lymphatic System |
Red Bone Marrow, Thymus, Lymphatic Vessels, Spleen, Thoracic Duct, Lymph nodes Function: -returns leaked fluid from blood vessels -disposes of debris in lymphatic fluid -houses white blood cells -immune response - attack foreign substances |
|
|
Components and Functions of the Integumentary System
|
Skin, Hair, Nails Function -external body covering -protects internal organs -synthesises vitamin D -houses cutaneous receptors, sweat glands and oil glands |
|
|
Components and Functions of the Nervous System |
Brain, Spinal Cord, Nerves Function: -control system -responds to internal and external changes by activating muscles/glands |
|
|
Components and Functions of the Cardiovascular System |
Heart, Blood Vessels Function: -Pump blood -Transport of blood - contains oxygen, carbon dioxide, nutrients and wastes |
|
|
Components and Functions of the Skeletal System |
Bones, Joints Function: -Levers for movement -Protection of internal organs -Blood cell formation -Storage of minerals |
|
|
Essential Functions of Life |
Maintaining Boundaries Responsiveness Growth Excretion Reproduction Movement Metabolism Digestion |
|
|
Generic Components of a Homeostatic Mechanism |
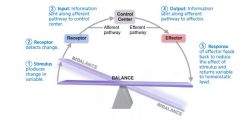
Stimulus, Receptor, Input, Output, Response |
|
|
Sagittal |
divides the left and right |
|
|
Coronal, Frontal |
divides the anterior and posterior parts of the body |
|
|
Transverse/Horizontal |
divides the superior and inferior parts of the body |
|
|
Supination |
facing upwards |
|
|
Pronation |
facing downwards |
|
|
Superior/Cranial |
towards the head |
|
|
Inferior/Caudal |
away from the head |
|
|
Ventral/Anterior |
toward/at the front |
|
|
Dorsal/Posterior |
toward/at the back |
|
|
Medial |
toward the midline |
|
|
Lateral |
away from the midline |
|
|
Intermediate |
between a more medial and lateral structure |
|
|
Proximal |
closer to the origin of a body part |
|
|
Distal |
further from the origin of a body part |
|
|
Superficial |
toward/at the body surface |
|
|
Deep |
away from the body surface
|
|
|
Central tenants of cell theory |
-Cells are the basic structural and functional unit of life -Activities of an organism depend upon the individual and collective activity of cells -Biochemical activities of cells depend upon their specific sub-cellular structures -Continuity of life has a cellular basis |
|
|
Carbohydrates -units -bond -function |
-Monosaccharides, Disaccharides, Polysaccharides -Glycosidic bonds -Functions: energy source, structural, cell id |
|
|
Lipids -units -function |
-Fatty acids -Functions: energy source, membrane barrier (phospholipids), signalling (hormones) |
|
|
Proteins -units -bond -function |
-Amino acids -Peptide bond -Functions: structural, transport, enzyme, defence, storage, signalling, receptors |
|
|
Nucleic acids -units -bonds -function |
-Nucleotides: sugar, base, phosphate -Phosophodiester -Fuctions: genetic material, aid in protein synthesis, carry chemicla energy, form co-enzymes |
|
|
Mitochondria |
ATP production - cellular respiration |
|
|
Ribosomes |
Protein synthesis -free ribosomes: proteins for the cytosol and other organelles -bound ribosomes: proteins for the membrane, lysosomes or exporting |
|
|
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum |
Aid in protein synthesis for membranes, lysosomes or exportation |
|
|
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum |
-Lipid biosynthesis -Detoxify drugs, pesticides and chemicals -Break down stored glycogen |
|
|
Golgi Apparatus |
modify, concentrate and package proteins |
|
|
Peroxisomes |
detoxification |
|
|
Lysosomes |
digests particles, non-useful organelles, non-useful tissues aid in glycogen breakdown |
|
|
Nucleus |
gene containing control centre |
|
|
Totipotent |
cells of the trophoblast which can give rise to all body cells and extraembryonic cells (placenta, umbilical cord) |
|
|
Pluripotent |
stem cells that can give rise to any body cells (cells of the inner cell mass in the blastocyst) |
|
|
Multipotent |
can develop into more than one type of cell |
|
|
Unipotent |
can only develop into one type of cell |
|
|
Ectoderm - gives rise to |
-all nerve tissue -epidermis and epidermal derivatives (e.g. hair) -cornea and lens of eye -epithelium of oral, nasal and anal canals -tooth enamel -epithelium of pineal and pituitary glands, and adrenal medulla -melanocytes -some cranial bones and brachial cartilage |
|
|
Mesoderm - gives rise to |
-skeletal, smooth and cardiac muscle -cartilage, bones and other connective tissues -blood, bone marrow and lymphoid tissues -endothelium of blood vessels and lymphatics -serosum -tunics of eye -synovial membranes -organs of urogenital system |
|
|
Endoderm - gives rise to |
-epithelium of digestive tract -glandular derivatives of the digestive tract (pancreas, liver) -epithelium of respiratory tract, auditory tube and tonsils -thyroid, parathyroid and thymus -epithelium of reproductive ducts and glands -epithelium of urethra and bladder |

