![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
40 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Draw granite classification triangle |

|
|
|
Peraluminous equation and type of granite |
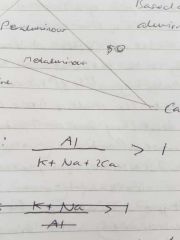
S type |
|
|
S type granites occur from melting from |
Sedimentary rocks |
|
|
S granites contain a greater abundance of |
Al |
|
|
S type granite SiO2 range and Sr87-86 ratio |
64-77% 0.708-0.765 |
|
|
S granitess are confined to regions of and why? |
Highly evolved crust because of the large Si and Al concentrations |
|
|
S type granite example |
Tasman mobile belt, australia |
|
|
High or low K/Na ratio for s granites |
High |
|
|
Characteristic opaque phase of s granite |
Ilmenite |
|
|
Origin of s type granites |
Partial melting of metasedimentary rocks via anatexis or ultrametamorphism |
|
|
Why do s type granites have low Na and Ca concentrations |
Properties based on protolith and its likely the rocks lost Na and ca through weathering to the sea and evaporites |
|
|
Why are s granites more reduced |
Presence of Carbon and sulphur in protolith |
|
|
Typical s granite O18 % |
9.9-10.5 |
|
|
Another reason why s granites are depleted in Na,Ca and Sn? |
Lost when feldspars weather to clays |
|
|
I type granites can be described as |
Metaluminous |
|
|
Metaluminous equation |

|
|
|
Typical Si range in I granite |
55-77% |
|
|
Sr ratiod of I granites |
0.704-0.706 |
|
|
Describe the distribution of sr ratios in i granites and what do they reflect |
They are regualar and reflect homogenous source material |
|
|
O18 isotope % of i type granites |
7.9-9.4% |
|
|
Name for mantle derived granites |
M type |
|
|
Sodic variety in i type felsic and mafic bodies |
Felsic greater than 3.2% Mafic as low as 2.2% |
|
|
Diagram to show the molar proportions in granite types |

|
|
|
P-T diagram of muscovite dehydration |
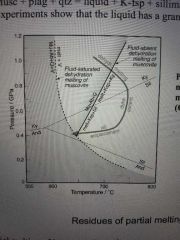
|
|
|
What type of granite are the himalyas |
S type |
|
|
Describe the inducement of melting in the himalayan granites |
Fluid induced thought to be caused by the dehydration of muscovite first and then possible biotite |
|
|
Geothermal gradient of himalayan granites and depth of melting |
25-30/km Depth of 30km |
|
|
Spource rock of hhgs and what this entails |
Mudstone therefore high Al concentration |
|
|
Dehydration reaction of hhg |
Musc + plag + qz = liquid (granite composition) + kfsp + sillimanite |
|
|
What happened to the hhg granites after they formed? |
-Crystallised in situ to form leucosomes -Migrated upwards and formed leucogranites |
|
|
Name 3 I type granite examples |
Sierra nevada plutons Lachlon fold belt AUS Caledonian fold belt |
|
|
Sierra nevada granite compositions |
Tonalitic to granite compositions |
|
|
Trend from east to west of sierra nevada granites |
Tonalite to granite Increasing k fsp Increasing Sr ratios |
|
|
Origin of lachlan fold belt granites |
Major magmatic event 400ma |
|
|
2 origins of M granites |
-Fractionation of basic magma -Partial melting of Si rich continental crust
|
|
|
Process of sierra nevada granite formation |
Partial melting of peridotite Basalt crystallisation Partial melting of basalt Intermediate magma formed Increasing assimilation of continental crust from east to west |
|
|
Describe underplating model 1 for granite genesis |
-Underplating of crust by subduction zone magmas -Mafic magmas melting of underplate crust produces tonalites -Tonalites differentiate and assimilate crust to form granitic magma |
|
|
Describe model 2 MASH model |
-Underplating of the crust by subduction mafics -Fractionation of mafics accompanied by assimilation and melting of the crust -MASH= Melting, assimalation, storage and homogenization |
|
|
Describe model 3 restite model |
-Melting of source gives a granitic melt -Mafic restites persist throughout however -Composition ot magma body varies magma mixing with restites |
|
|
Model 4 magma mixing |
-Melting of crust produces granitic melt -Invasion of mafic magma into granitic magma gives new melt composition |

