![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
43 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What is located superior to the diaphragm on the left at the 5th intercostal space? |
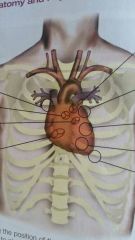
Apex of the Heart |
|
|
|
Pericardium |
Sac surrounding the heart |
|
|
|
Pericardial effusion severe enough to decrease blood flow to the body, compress the heart. If untreated shock & death will occur |
Cardiac tamponade |
|
|
|
Three layers of the Heart wall |
Outer epicardium Middle myocardium Inner endocardium |
|
|
|
Annulus Fibrosus Cordis |
Composing dense connective tissue within the atrioventricular rings, providing support to the 4 chambers and valves of the heart |
|
|
|
The remnant of the fetal foramen ovale.
Where is it located |
Fossa ovalis cordis
Oval depression on the right side of the interatrial septum, between the left and right atrium |
|
|
|
Which 2 chambers do most of the pumping for circulation of blood |
Left and right ventricle |
|
|
|
Left ventricle size and shape |
When looked across anteriorly has the appearance of a sphere 2/3 larger then right |
|
|
|
Describe left atrioventricular aid |
When left ventricle contracts the right ventricle wall is pulled. Due to the right ventricle pocket attachment |
|
|
|
Which 2 arteries arise from the root of the aorta |
Main left and right coronary arteries |
|
|
|
Coronary artery obstruction can lead to tissue ischemia |
Angina Pectoris |
|
|
|
Myocardial Infarction (MI) |
Complete death or obstruction within the coronary artery |
|
|
|
Cardiac muscle ability to initiate spontaneous electrical impulse |
Automaticity |
|
|
|
Extremely high HR decreases blood flow through coronary arteries because |
As diastolic time decreases, increasingly less time is available for coronary artery perfusion that occurs during diastole until coronary blood flow is decreased |
|
|
|
Frank- Sterling law |
The more a cardiac fiber is stretched (up to a point) the greater the tension it generates when contracted |
|
|
|
Aorta on left ventricle and ends @ the right atrium |
Systemic circulation |
|
|
|
Pulmonary circulation |
Starts @ pulmonary artery out of the right ventricle and ends in the left atrium |
|
|
|
What is the goal of the heart and vascular system |
Maintaining adequate perfusion to all tissue according to their METABOLIC needs |
|
|
|
Sympathetic division Of the autonomic nervous system does what |
Primarily the one to Central control of blood flow |
|
|
|
Smooth muscle relaxation & vessel dilatation occur as a result to stimulated by |
Cholinergic or specialized beta- adrenergic receptors |
|
|
|
Formula for cardiac output |
CO= HR x SV |
• over Q |
|
|
Contractility preload and afterload intrinsic control, affect |
SV |
|
|
|
CO changes involves |
Change in SV, change in HR or both |
|
|
|
EDV |
end-diastolic volume |
|
|
|
During resting phase, diastole, the ventricles fill to a what volume |
End-diastolic volume |
|
|
|
70mL |
Normal SV |
|
|
|
Proportion of EDV ejected on each stroke |
64% |
|
|
|
Preload and afterload are which concepts |
Tension or force and filling volume |
|
|
|
Contractility |
The amount of systolic force exerted by the heart muscle @ any given preload |
|
|
|
Stimulation exerting a negative inotropic effect |
Parasympathetic |
|
|
|
A decrease in cardiac contractility and impaired myocardial function are a result of |
Profound hypoxia and acidosis |
|
|
|
Vasoconstrictor area within the medulla being stimulated results in |
Increased vascular resistance and vasoconstriction |
|
|
|
Cardioaccelerator area is a stimulator for |
HR increase by an increase of sympathetic discharge to th SA and AV of the heart |
|
|
|
Name 2 types of peripheral cardiovascular receptors |
Baroreceptor Chemoreceptors |
|
|
|
Responsive to pressure changes |
Baroreceptor |
|
|
|
Chemoreceptors respond |
Blood chemical changes (ABG) |
|
|
|
Vasoconstriction and increased HR are cardiovascular effects from |
Stimulation of the Chemoreceptors |
|
|
|
Amount of time after depolarization ventricles contract |
Few 100th of a second |
|
|
|
S1 sound represents |
Closing of mitral valve 1st. Immediately followed by tricuspid valve closure |
|
|
|
Elastic recoil of the arteries |
Dicrotic notch |
|
|
|
What arises from the aorta |
The main left and right coronary arteries |
|
|
|
Decreased O2 supply |
Ischemia |
|
|
|
Partial coronary artery obstruction Leading to tissue ischemia |
Angina pectoris |
|

