![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
27 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
TEMPLATE |
Signaling System: Drug Target: MOA: Therapeutic Use: |
|
|
KETAMINE |
Signaling System: GLUTAMATE. Drug Target: NMDA R. MOA: Non-competitive Antagonist. Therapeutic Use: Anesthetic, Pain (can be drug of abuse "Special K". 'Trick': Special 'K' = 'K'etamine blocking sensation. |
|
|
PHENCYCLIDINE (PCP) |
Signaling System: GLUTAMATE. Drug Target: NMDA R. MOA: Non-competitive Antagonist. Therapeutic Use: Drug of abuse "angel dust". |
|
|
DIAZEPAM |
Signaling System: GABA (BENZODIAZEPINE). Drug Target: GABA-A R Modulator (*WIDE RANGE OF SUBTYPES*). MOA: Bind to Rs at *SEPARATE SITE* to GABA, allosteric modulation *INCREASING HYPERPOL.*. Safer than BARBITURATES (no effect w/o GABA present). Therapeutic Use: Anxiolytic, epilepsy (*ER*), agitation, insomnia, muscle spasm, pre-anesthesia. |
|
|
MIDAZOLAM |
Signaling System: GABA (BENZODIAZEPINE). Drug Target: GABA-A R Modulator (*WIDE RANGE OF SUBTYPES*). MOA: Bind to Rs at *SEPARATE SITE* to GABA, allosteric modulation *INCREASING HYPERPOL.*. Safer than BARBITURATES (no effect w/o GABA present). Therapeutic Use: Anxiolytic, epilepsy, agitation, insomnia, muscle spasm, pre-anesthesia. |
|
|
ZOLPIDEM |
Signaling System: GABA ('technically' not a BENZO). Drug Target: GABA-A R Modulator (*NARROW RANGE OF SUBTYPES*). MOA: Bind to Rs at *SEPARATE SITE* to GABA, allosteric modulation *INCREASING HYPERPOL.*. Safer than BARBITURATES (no effect w/o GABA present). Therapeutic Use: Insomnia. |
|
|
ESZOPICLONE |
Signaling System: GABA ('technically' not a BENZO). Drug Target: GABA-A R Modulator (*NARROW RANGE OF SUBTYPES*). MOA: Bind to Rs at *SEPARATE SITE* to GABA, allosteric modulation *INCREASING HYPERPOL.*. Safer than BARBITURATES (no effect w/o GABA present). Therapeutic Use: Insomnia. |
|
|
BACLOFEN |
Signaling System: GABA. Drug Target: GABA-B R. MOA: Agonist. Therapeutic Use: Treat *SPASICITY*. |
|
|
L-DOPA |
Signaling System: DOPAMINE. Drug Target: Substrate for DOPAMINE SYNTHESIS. MOA: DOPA Synthesis, *CROSSES BBB* Therapeutic Use: |
|
|
AMPHETAMINE |
Signaling System: DOPAMINE. Drug Target: Presynaptic Vesicle Release. MOA: Increases vesicular DOPA release. Therapeutic Use: |
|
|
HALOPERIDOL |
Signaling System: DOPAMINE. Drug Target: Dopamine D2 R Competitive Antagonist w/ limited "off target" effects H1 & M1 ACh Rs (reduced sedation), and competetive antagonist of ALPHA-1 adr. & 5-HT. MOA: Leads to extrapyramidal effects. Therapeutic Use: Antipsychotic. |
|
|
COCAINE |
Signaling System: DOPAMINE. Drug Target: Dopamine Transporter (DAT). MOA: DOPA reuptake inhibitor. Therapeutic Use: Drug of abuse. |
|
|
FLUOXETINE (Prozac) |
Signaling System: SEROTONIN. Drug Target: SEROTONIN TRANSPORTER. MOA: SEROTONIN reuptake inhibitor. Therapeutic Use: |
|
|
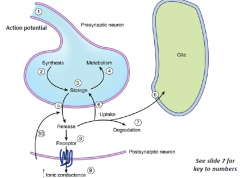
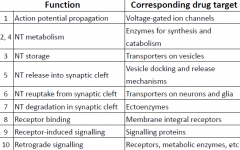
Molecular Targets (6 w/ tubule locations) |
-G-protein (*METABOTROPIC Rs) w/ 2nd messengers (i.e. MACh Rs). -L-G Ion Channel (*IONOTROPIC Rs) w/ multi-subunits, homo-/hetero-complexes (i.e. NACh Rs). -V-G Ion Channel (i.e. L-type Ca2+ channel). -Transporters (integral to PM for cell uptake [neurons/glia] or integral to vesic.M). -Vesicle Docking Machinery (i.e. SNAP-25). -Enzymes (membranes/cytoplasm, i.e. tyrosine hydroxylase [synth.], MAO [catab.]). |
|
|
CLONIDINE |
Signaling System: NE. Drug Target: ALPHA-2 Adrenoreceptor. MOA: Agonist. Therapeutic Use: Anxiety, depressive d/o, stress-related d/o, pain, inflammation, *USED IN OPIATE WITHDRAWAL (dampens NE tone)*. |
|
|
NICOTINE |
Signaling System: ACh. Drug Target: NACh R. MOA: Agonist. Therapeutic Use: Drug of abuse. |
|
|
CARBAMAZEPINE |
Signaling System: V-G Ion Channels. Drug Target: Use-dependent V-G Na+ channel Blocker. MOA: Binds to *INACTIVATED V-G Na+ Channel*, slows recovery from inactivation (inhibits repetitive neuronal firing), *USE-DEPENDENT BLOCK (blocks APs after initial APs began)*. Therapeutic Use: Anticonvulsant. |
|
|
|
|
|
Key NTs (w/ & w/o NT pathways) |
"Dan's GGG" - * w/o pathways -Glutamate* -GABA* -Glycine* (ONLY IONOTROPIC, GABA-A Rs, mutation can cause HYPEREKPLEXIA) -DOPA (ONLY METABOTROPIC) -Serotonin -NE -ACh |
|
|
Glutamate R Subtypes |
-IONOTROPIC (Both Na+ & Ca2+: NMDA, AMPA; Just Na+: KAINATE). -METABOTROPIC (CLASS I [inc. IP3, Ca2+], II [dec. cAMP], & III [mixed]). |
|
|
NMDA vs. AMPA Rs |
-NMDA: GLUTAMATE w/ GLYCINE (co-agonist). Mg2+ is, also, bound and prevents opening of channel until potential reaches near threshold (kicks off Mg2+ so channel can open). -AMPA: Same as NMDA w/o GLYCINE (co-agonist) or Mg2+ modulation. |
|
|
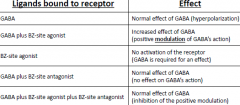
GABA R Types & Agents That Act on Them |
-GABA is found at ~30% of synapses: -GABA-A Rs: *IONOTROPIC*, Cl- influx leading to HYPERPOLARIZATION (mutations cause *EPILEPSY*). -GABA-B Rs: *METABOTROPIC*, reduces NT release via modulation of K+ or Ca2+ channels. -Agents: GABA Agonists/Antagonists, Benzodiazepines, Barbiturates, Neurosteroids, General Anesthetics, EtOH (*ALLOSTERIC INTERACTION*). |
|
|
GABA-A R Modulators |
|
|
|
Dopamine Rs |
-5 Families w/ 2 Main: -D1-like Family: G(s), INC. cAMP. -D2-like Family: G(i), DEC. cAMP (supress Ca2+ and activate K+ channels). -Dopamine used to treat Neurodegen. d/o (Parkinson's), Neurodevel. d/o (Schizophrenia, ADD), and plays a role in REWARD CENTER. |
|
|
Serotonin Rs |
-Seven families, some excitatory, some inhibitory. -Metabotropic 5-HT(1,2,4-7) inc. cAMP, dec. cAMP, inc. PLC. -Ionotripic 5-HT(3), Na+, K+, Ca2+. |
|
|
Serotonin Drug Targets |
-Catabolic enzyme (MAO) -Serotonin Transport (tricyclic antidep., SSRIs) -Receptors (agonists & antagonists) |
|
|
ACh NT |
-CNS: cortical activation, synaptic plasticity, cognitive fx, REM sleep, motor coordination. -Alzheimer's (loss of central MCh neuron). -Addiction (nicotine). Targets: -M1 Rs, AChesterase (cross BBB increasing ACh in Alzheimer's Pts). -Nerve gas AChesterase inhibitors. |

