![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
24 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the overall mortality of GI bleeding?
|
10%
|
|
|
What anatomic landmark divides GI bleeding into upper and lower GI bleed?
|
- Ligament of Trietz (4th duodenal segment)
|
|
|
List etologies of UGI/LGI bleeding in adults in decreasing frequency. Box 23-1.
|

|
|
|
List etiologies of UGI and LGI bleeding in pediatrics. Box 23-2.
|

|
|
|
What is the most common cause of massive LGI bleeding in children < 2 years old?
|
- Meckle’s diverticulum
|
|
|
What must be considered in patients with aortic grafts and rectal bleeding?
|
aortoenteric fistula
|
|
|
List causes of false positive hemoccult testing.
|
- Ingestion of red fruit or red meat
- Methyline blue - Chlorophyll - Iodide - Cupuric acid - Bromide |
|
|
List causes of false negative hemoccult testing.
|
- Magnesium containing antacids
- Ascorbic acid-vit c |
|
|
What else can cause black stool?
- |
Bismuth (pepto-bismol)
|
|
|
In what % of patients with UGI bleeding will endoscopy identify a bleeding source?
|
- 78-95%
|
|
|
In what % of patients with active ongoing lower GI bleeding with angiography identify the site of bleeding?
|
- 40-60%
|
|
|
What is the indication for PPIs?
|
- Documented high risk peptic ulcer disease at endoscopy (Reduced rebleeding and surgery)
- ?Undifferentiated UGI bleeding prior to endoscopy (Reduced stigmata of recent bleeding) |
|
|
Evidence PPI and bleeding and peptic ulcer after endoscopy
|
- Omeprazole infusion started after endoscopic therapy for high risk ulcers reduces the risk of 30 day rebleeding vs. placebo, with most of the benefit seen in the first 3 – 5 days (HR 2.9)
LAU NEJM 2000 - omeprazole (80mg bolus, 8mg/hr infusion for 72h) NNT 6 |
|
|
PPIs FOR PEPTOIC ULCER DISEASE BLEEDING COCHRANE 2006?
|
Plain Language Summary: In people with a bleeding ulcer in the stomach or duodenum there is no evidence of a difference in the risk of death if they are treated with a proton pump inhibitor, or and H2-receptor antagonist, or if they are given no specific drug treatments. However, proton pump inhibitors do reduce the risk of bleeding and the need for surgery
|
|
|
PPI before endoscopy?
|
Lau 2007 NEJM - b4 endoscopy
o Infusion of high dose omeprazole before endoscopy accelerated the resolution of signs of bleeding ulcers and reduced the need for endoscopic therapy - No Significant difference in need for blood transfusions, rebleeding, need for surgery or death |
|
|
What is the indication for octreotide?
|
documented esophageal varices
cochrane 2005 Plain Language Summary: Treating bleeding in the esophagus with somatoststin analogues does not appear to reduce deaths, but may lessen the need for blood transfusions 50 mcg bolus f/b 25 to 50 mcg/hr |
|
|
What are additional therapies for bleeding varicies?
|
- Vasopressin and nitroglycerin
- Sengstaken-Blakemore Tube - Endoscopy o Banding o Ligation o Sclerotherapy - Surgery |
|
|
What are very low risk criteria for patients complaining of GI bleeding who can be discharged home? Box 23-3
|

|
|
|
How are patients initial risk stratification in the ED in low, moderate, or high risk categoiries. Table 23-1
|
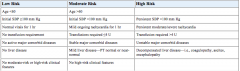
age,BP,abnormal vitals, transfusion,comorbid,liver,high risk features
|
|
|
Provide a table outlining disposition of GI bleed patients by their clinical and endoscoping risk stratification. Table 23-2
|
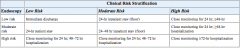
|
|
|
What are general rules of thumb for indications for surgery for GI bleeding?
|
- Hemodynamically unstable and unresponsive to resuscitation
- >5U PRBCs in 4-6hours - >2U PRBCs/4hours |
|
|
What are the treatments for UGIB
|
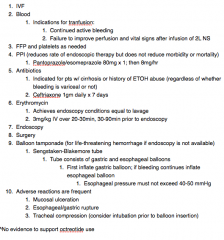
|
|
|
indications for blood transfusion?
|
1. Continued active bleeding
2. Failure to improve perfusion and vital signs after infusion of 2L NS |
|
|
Who should receive antibiotics?
|
1. Antibiotics
1. Indicated for pts w/ cirrhosis or history of ETOH abuse (regardless of whether bleeding is variceal or not) 2. Ceftriaxone 1gm daily x 7 days 2. Erythromycin 1. Achieves endoscopy conditions equal to lavage 2. 3mg/kg IV over 20-30min, 30-90min prior to endoscopy |

