![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
20 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Minimal sedation (anxiolysis) |
A drug-induced state during which patients respond normally to verbal commands. Although cognitive function and coordination may be impaired, ventilatory and cardiovascular functions are unaffected. verbal cognitive,coordination ventilatory cardiovsacular |
|
|
Moderate sedation |
(formerly “conscious sedation”): A drug-induced depression of consciousness during which patients respond purposefully to verbal commands, either alone or accompanied by light tactile stimulation. Reflex withdrawal from a painful stimulus is not considered a purposeful response. No interventions are required to maintain a patent airway, and spontaneous ventilation is adequate. Cardiovascular function is usually maintained. |
|
|
Deep sedation: |
A drug-induced depression of consciousness during which patients cannot be easily aroused but respond purposefully following repeated or painful stimulation. The ability to independently maintain ventilatory function may be impaired. Patients may require assistance in maintaining a patent airway and spontaneous ventilation may be inadequate. Cardiovascular function is usually maintained. |
|
|
General anesthesia: |
A drug-induced loss of consciousness during which patients are not arousable, even by painful stimulation. The ability to independently maintain ventilatory function is often impaired. Patients often require assistance in maintaining a patent airway, and positive pressure ventilation may be required because of depressed spontaneous ventilation or -drug-induced depression of neuromuscular function. -Cardiovascular function may be impaired. |
|
|
Dissociative Sedation: |
A trancelike cataleptic state induced by the dissociative agent ketamine characterized by profound analgesia and amnesia, with retention of protective airway reflexes, spontaneous respirations, and cardiopulmonary stability. |
|
|
ASA Classes? |
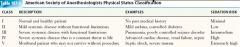
|
|
|
Who should we consult anesthesia for PSA? |
· Difficult airway |
|
|
Ketamine IV Vs IM |
1mg/kg give over 1min peak 1min duration 10min add 0.5
|
|
|
Mechanism of analgesia for ketamine |
Sub-dissociative’ doses (<1mg/kg IV or <2 mg/kg IM) of ketamine provide potent analgesia, due to agonism of mu, delta, and kappa opioid receptors. |
|
|
Mechanism of dissociation |
The dissociative state is a lack of response to external stimuli due to ‘disconnection’ of the thalamoneocortical system from the limbic system, as a result of non-competitive antagonism at NMDA receptors. |
|
|
Epi of emergence with ketamine? |
emergence? |
|
|
Ketmaine in peds? |
dont routinely give atropine(no benefit) or glycol(may harmful) - for hypersaliva dont give <3mo , animal studies NMDA |
|
|
Ketamine - adverse effects and advantages and contra indications |
Hypertension
++++++ Rapid onset
Contraindications include -children younger than 3 months of age, -active pulmonary infection, -cardiovascular disease (angina, heart failure, aneurysm, uncontrolled hypertension), -traumatic brain injury, -CNS mass lesions, -hydrocephalus, -glaucoma, and -acute globe injury. |
|
|
Ketamine Dose, IV,IM,PR,IN,PO? |
IV 1 mg/kg 1 min 15 min IM 5 mg/kg 5 min 15min PR 5 mg/kg 5 min 15min IN 5 mg/kg 5 min PO 5 mg/kg 30–45 min 2–4 hrs
|
|
|
Fentanyl dose,adverse effects, issues? |
2–3 μg/kg 1–2 min 20–30 min
Respiratory depression
Respiratory depression is more pronounced when coadministered with other respiratory depressants. |
|
|
Propofol Dosage, IV/Infusion |
IV 1.0 mg/kg ≤1 min |
|
|
Propofol complications, advantages, issues |
Respiratory depression
Rapid onset
Procedures lasting ≥8–10 min will require repeat boluses or a constant infusion.
|
|
|
Etomidate Dosage IV,PR,PO |
IV 0.1mg/kg <1min 6 min PO 50mg (adult dose) 10min 60min PR 4.5mg/kg 4min 40min |
|
|
Etomidate complications, features? |
Respiratory depression
Rapid onset
Adrenal suppression is not clinically relevant with one-time administration. |
|
|
Ramsey sedation scale |
1. anxious and agitated or restless, or both
2. cooperative, oriented, and calm 3. responsive to commands only 4. exhibiting brisk response to light glabellar tap or loud auditory stimulus 5. exhibiting a sluggish response to light glabellar tap or loud auditory stimulus 6. unresponsive |

