![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
34 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)

|
Temple of Hercules Victor, Forum Boarium
|
• 120 C BCE
• Hercules the winner • Circular temple called Tholos which came from Greek Ideals • Tufa stairs all the way around, door at one part of the temple • Leaves at the top of columns which are fluted are in the Corinthian order • Circular cella • Erected by Lucius Mummius Achaicus o Sack of Corinth in 146 BCE o Dealt with Mummius by leveling the city, took the artwork and valuables back to the city of Rome • Manbail temple, meaning it was paid from the spoils of war Spolia |
|

|
Portrait Statue of Aulus Metellus
|
• Found at bottom of Lake Trasimeno in N Italy
• C 100-90 BCE • Also called the “Orator” • Best ex. Of Roman and Etruscan Influence • Name is in Etruscan Manuscript, but it is a Roman name • Adlocutio pose • Toga and boots are those of a Roman Senator • Realism comes from from, not perfect as opposed to greek it highlights the actual characterisitcs of the person being portrayed • Value system for being old and wise by Aristocrats |
|

|
Model of the Palatine Hill with Iron Age Huts, Rome
|
• 9th/10th BCE
• Built the Huts on the hill and buried the people below in the valley • Postholes in the bedrock for very simple one room circular or round units • Sloping thatched roofs illustrated by the urns shaped like huts • Villanovans called because they are close to Bologna and later called Etruscan |
|

|
Sanctuary of Fortuna at Praeneste (Palestrina), reconstruction drawing
|
o Sanctuary of Fortuna Primigenia, Paeneste C. 80 BCE not RR date in Book
o Fortuna Goddess will give you clues to the future o 82 BCE last of late republic Essentially super generals so rich and power from military basically in Charge o Sulla (2) Always fighting with a guy named Marius (first super general) Pompey (3) Caesar (4) o Sulla goes down to Palestrina to recapture it from Marius’s son His son kills himself Decides to kill 12,000 men women and children enslaved for supporting Palestrina Made Palestrina a military colony Fortuna is adopted by Sulla as his personal goddess o Help up by mortar and stone construction of opus incretum o Oracular temple of Fortuna o Axial symmetry Can fold the thing on top oeach other and it would be the same o Some of the stairways were fake and deceit you 7 levels Tunnels of closed darkness of tunnels, asention spiritually o Sixth level open Likely there was rituals or events here o Seveth level can see rome one clear day o Third level Doric order, fountain houses o Fourth level Series of small spaces of shops and small shrines, Ionic Order o Stepped coffer Steps indentation in the ceiling o 3 columns and two passage ways Double porticos Corinthian order |
|

|
Sanctuary of Fortuna at Praeneste (Palestrina)
|
Begun 2nd century BC, renovated around 80 BC
Takes advantage of hill -- porticos on different levels Symmetrical design Guided perspective Doric Columns |
|

|
Paris/Munich reliefs - detail of Census frieze
|
100 BC
Circus Flaminius o Ceremony of Census (every 5 years) Men collect on campus martius and register as citizens Property is valued Assigned roles in military (based on wealth) Center 2 placed men, 1 wearing toga (civic duty) and 1 in armor • Toga = censor, in charge of taking the census • Armors Man = god of war Mars Sacrificing at altar (not at the temple itself • Lustrum Cemeromy @ end of census o Marked the finale – takes place at temple of mars in Campus Martius o Specific animals Suovetaurilla Bull, pig, and sheep • Roman Soldiers to the right have been counted in the army • Left depic of actual taking of census • Styles Realism Verism Hellenism o Helic style: refers to reliefs Squat, out of proportion Emphasis on hang gestures and faces Little action, quiet scenes • Sacrifice and processions Takes place around neutral background • Earliest example, census |
|

|
Paris/Munich reliefs - detail of Census frieze
|
o Ceremony of Census (every 5 years)
Men collect on campus martius and register as citizens Property is valued Assigned roles in military (based on wealth) Center 2 placed men, 1 wearing toga (civic duty) and 1 in armor • Toga = censor, in charge of taking the census • Armors Man = god of war Mars Sacrificing at altar (not at the temple itself • Lustrum Cemeromy @ end of census o Marked the finale – takes place at temple of mars in Campus Martius o Specific animals Suovetaurilla Bull, pig, and sheep • Roman Soldiers to the right have been counted in the army • Left depic of actual taking of census • Styles Realism Verism Hellenism o Helic style: refers to reliefs Squat, out of proportion Emphasis on hang gestures and faces Little action, quiet scenes • Sacrifice and processions Takes place around neutral background • Earliest example, census |
|

|
Paris/Munich reliefs - detail of Thaiosos frieze
|
Early 1st century BC
Marble Events placed in succession o Mythical depiction of wedding of Neptune and Amphitrite o Contrast italic style Dynamic, action, mythical, masculine o Hellenistic style Drama, energy, complete compositions, details Hellenized • Portiats inspired by images form greek portrait |
|

|
Aemilius Paullus monument, Delphi, fragments of battle frieze
|
168 BC
First relief to depict actual event • Battle of Pydna 168 BCE Aem pail Vs Perseus o Perseus Greek is in Macedonia o Aemulius Paulius – changes original statue, tears down original Equestrian statue • Frieze (round top of a pillar) o Romans armor and dress fighting Macedonians o Torque, energy, dynamic – action overlap Typical of Greek depictions o Roman real subject matter Style was Greek, subject Roman • Oracle says “Who Begins battle will lose” – Riderless Horse o Roman horses runs lose o Perseus thinks Romans started fight, but Perseus started the battle scription at base of pillar monument • Greece losing ground over Roman Conquest, power through appropriation o Does not destroy takes over (spread control and power) • Latin dediacation eenscription at base of Pillar monument Glory of Aem Paulius Few people could read latin in Greece |
|

|
Portrait of Pompey, Copenhagen
|
-55 BCE
-realistic, but not too veristic because not to much signs of aging -hellenized -influnce from greek world is affecting the portrature -Clothes and hair are similar to Alexandar teh great who was kind of a superhero -anastole - calic on the top of teh head -was orignally an honoray statue to Pompey -small pudgy face and eyes make it veristic |
|

|
Temple of Portunus, Forum Boarium
|
Late 2nd century BC
Derived from Etruscan prototype: high podium, deep porch, frontal approach 150-100 BCE o Boarium- cattle market translation, no one knows really, but literature says it’s a religious spot o Square and circle building, next to the river, dieties of water o Portunus Old latin River god o Etruscan, Cella, Porch, Tufa, o Tufa Made the base Etruscan o Travertine Lime stone in Italy, made where you can see it, Super Stucture? Etrustcan o Stucco Cover the limestone with stucco, first from greek influence Changes the color from yucky grey to white, looks like marble Put marble dust in to stucco plaster o Greek Elements Currly cue up (rams horn) on top of columns Signal you are Ionic order Channels down the column shaft called fluting • Optical illusion of making they more delicate and skinny Pseudoperipteral • Half columns around the cella wall • Psudeo=fake, perpeteral go all the way around Engaged • Columns that are attached to the cella wall • No structural just decorative (in greek they were structural) Engaged columns, of the Ionic style |
|

|
Theater of Pompey - model
|
55 BC
Circus Flaminius Great 55 bce When you build a theater you had to build of wood and then afterwards you had to tear it down • A way to control public assemblys from overthrowing and control of the populous • Artistrocrats thought of it as a way to control culture • Law since 200 BCE Pompey decided f the law and I will build a permenate structure • The power of military commanders are influencing the government • Loyality to General not to Rome Pompey went to the Med to fight pirates on the way back he made a victory march through Greece to Rome • He is really impressed with the theaters decide to build one in Rome Difference between Greek and Rome Theaters • Greek, most often built in the side of a hill to make the seats o Roman not, built from ground up Cavea • Seating area, sometimes referred to auditorium • Cunei wedge shaped seating • Praecinctiones o aisle of the seating between the cunei pg 36 in sears • orchestra o the top of the top, bring their own chairs o watching them come in was part of the spectacle of the theater pulpitum • the stage, building behind it was the scaenae frons, doors for the backstage change the scenery, put statues inbetween the columns • postscaenium o storage are behind the scaenae frons to change and hold equipment |
|

|
Portrait of Republican Man, Glyptotek
|
|
|

|
Portrait of Republican Man, New York
|
|
|

|
Tabularium, Forum Romanum
|
78 BCE Quintus Lutatius Catulus
o Records office of the government o Built on top of the remains of the Roman in the 17-18 centurary, midevil walls o Now a museum o The underneath Combo of stone and mortar construction Foundation is large blocks of tufa, bound by mortar As you go up combo of mortar and brick Style should be opus certum, but can’t tell really now because it’s been used so much over time Originally 3 stories, some argue it might be taller than that When you have a arched opening and enclosed by columns stuck to the side • NOT PSUDEOPERIPTAL • Fornix o Becomes really popular, meant for triumph arches Architrave • Shelf on top of the arch in the arch and columns Walls would have been cover with stucco Storage of salt which causes corrosion of stone during the medieval period |
|

|
Temple of Jupiter Optimus Maximus, Capitoline Hill, reconstruction
|
. 550-500 BCE
Etruscans occupied and built temple in the city of Rome Built in the city of Rome Fear of destroying JOM bad things would happen Destroyed when Rome loses because it is filled with valuables and gold Ala (alae in plural) –wings of a bird • Hallways on either side of the cella • Means corridor that doesn’t lead anywhere Collumns down the side of the building comes from the influence of greek Jupiter, juno and Minerva Lucius Tarquinius Priscus vowed this temple while battling with the Sabines |
|
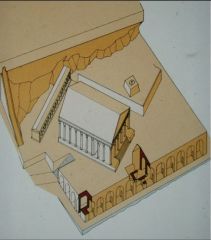
|
Sanctuary of Jupiter Anxur, Terracina, reconstruction drawing
|
Sanctuary of Jupiter Anxur c 80 BCE (anxus the increaser)
Temple not square on the platform • Might be a religious thing Platform was a series of corridors underneath • Used for storage • Cryptoporticus o Crypto hidden o Porticus walkway • Barrel vault o Arch and you stretch it • Portico o Free standing column thing o Storage, get out of the elements o Art weapons, ect Sets of military barrax • To protect sanctuary and passage of the road Off the road of the Opus incertum • Technique for wall facing • Opus wall facing • Incertum random • Form tufa into what looks like ice cream cones • This helps date when thigns are built because wall facing changes Corinthian order Pseudoperipteral • Half fake columns that wrap around -super general sulla, taking $ from conquest, stone and mortor |
|

|
Theater of Pompey, fragments of the Marble Plan
|
AD 193-235
Shows clearly that Pompey disguised his theatre as a sacred precinct to accomplish his immortality |
|
|
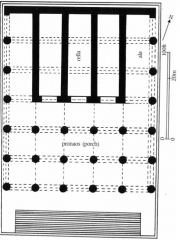
Temple of Jupiter Optimus Maximus, plan
|
|
|

|
Head of Man ("Brutus") from Rome
|
First Century BC
Bronze Establishes virtues associated with distinguished Romans o Heads come off, emphasis is always placed on the head in etrustcan art Distorted to be bigger heads Hands are huge Amazing a bronze casting Paint, insert eyeballs, interest in detail, sometimes cover metal with metal Boy muted as a child “brutus” • Not actually brutus. Just becauase of the nice sculpture named brutus • Head broken off, most likely etrustcan • Military horse, melted down and reused |
|

|
Portrait of Caesar from Tusculum
|
|
|

|
Republican Man from Torlonia
|
|
|

|
Theater of Marcellus, model of interior
|
• Law passed in 18 BCE about the seating of the Theater
Social order seating arrangement in the Theater. Who can sit where Highest ranks orchestra seating bring own chairs • Senators, magistrates, high ranking priests • Soldiers got good seats Middle ranks most of Cavea • Minor priests, magistrates of the surrounding roman towns, Equestrians in the lowest seats • Free born citizens of Rome that were Males Lowest tanks top most seats and standing room • Freedman, foreign visitors, slaves is permitted by their owner then women o Was also interested in getting aristocrats to get married Passes marriage laws financial benefits and if you produce children you get better seats |
|

|
Ara Pacis Augustae, Aeneas Panel
|
Cloak -- acting as priest while assisted with sacrifice
Augustus plays on his dynastic relationship to these heroes |
|
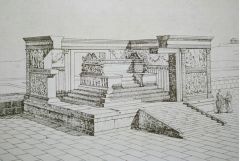
|
Ara Pacis Augustae
|
13-9 BC
Altar of Augustan Peace Product of propaganda program |
|

|
Ara Pacis Augustae, South Frieze
|
Details imperial procession
Each person is different -- very skilled/time consuming |
|

|
Ara Pacis Augustae, Tellus Panel
|
Tellus (Mother Earth) with two babies to emphasize fertility
Augustan peace spreads over the world |
|

|
Augustus Prima Porta
|
Early first century AD 12 AD
Bare feet - hero Cupid, riding dolphin - Julian family was decended from Venus Thinly veiled devine references here Breastplate about propaganda program Figure receiving the standard represents the Romans over Parthians |
|

|
Augustus from the Via Labicana
|
First Century AD
Toga over head - Augustus as a priest (pontifex maximus) most important priest adds to aug self represtentation in his res gestae talks about all of his religios beneficiarys to Rome idealizing Greek style because he he much younger than he is in this picture |
|

|
Forum of Augustus, detail of caryatids
|
-2 women that resembel the women of the Erechtheion temple in greece form 5th cent BCE
-Jupitor head with rams hiorns is named Jupitor Annom -Roman sacrafice in religion -thunder, god of sky -assocaited with the conquest of Eygpt annom toi anum -on the second levle of the porticos in the Forum of Augustus |
|

|
Forum of Augustus, model
|
o Most ambitious and the largest, and changes the layout of the city, roadways
o The first of the imperial fora o Physically attached to the forum of Julius Caesar o Finishes the forum of Caesar and constructs his own attached to it “I am in the son of a God” o Very organized and clear, temples of Mar Ultor is on Augustus o Emperor much more logical symmetrical planning o Temple of Mars Ultor Ultor- the avenger in latin Made a promise to Mars that if he won the battle of Philipi he would dedicate a temple to him in 42 BCE Celebrated the return of the standards • Battle between the Romans and The Parthians • Romes Neminises • Took the units stakes with an eagle as marker for which legion thye are in • When he came ot power wanted to get these back • Sent a bunch of ambassards to Parthia in 20bce Had the standard placed in the cella of the temple o Places a divine traid in the temple with Caesar as a godf o Filled the pediment with sculpture o Marble fluted column shafts, korinthian at the top, singler cella o It is very closed, high porticoes and high back wall that the temple Is backed up against o The back wall A certain kind of tufa that is resistant to fire Shield the forum of ausustus from fires in the city of Rome o Porticoes were two stories tall o Extendions Excedre also hemicycle • Half circular on the sides of temples • Places for statues • Niches were cut into the walls continued the length of the portico for statues o On the second level of porticoes there were statue of a woman on each column and a large round shield with a male bearded face in the middle Women resembled the the porch of the caryatids in Athens temple 5bce Image of Jupiter with rams horns in his head, associated with Egypt Jupiter Amon o Caryatids Erechtheum o Floors made with checker board differnet colors of marbles, yellow and purple, have to be imported distant from far away, symbol for Rome’s power \ o Central nitch is the statues of Aeneas, Trojan who exscaped troy Founder of italy o Across the way the Romules Founder of the city of Rome o Summi viri Great men who lived in the past, who Augustus and Court seemed ot be the best in the past Carsus annorium • Enscruption underneath a statue o Middle of the Forum Hugh statue of Augustus Quadriga- four horse charriet • Peace and prosperity in truimp in victory Pater Patriae • Father of his Homeland • Now made Rome his household • FATE to become a god o Middle Divine Traid Venus, mars and, divus Julius o Political activities were now transferred to the Forum of Augustus instead of the Roman Forum Old republican ideals out and now imperialism |
|

|
Temple of Mars Ultor, Forum of Augustus, drawing
|
- in 42 BCE aug made a promise to mars if he won the battle of philipi he would dedidcate a temple to him
-Gods are a divine triad with Venus, Mars and Julius Ceasar -Archeteure, singluar cella, marble fluted columns, corinthian order, 2 high inclosed porticos back up agianst a special fire proof tufa wall -enclosemant all your lkooking at is the tmeple -put the standards in it in 20bce from Parintians |
|

|
Mausoleum of Augustus
|
• 30-20 BCE. “8th hill of Rome”
• Begun before the battle of Actium, was used as propgranda • Story goes that Antony will was read infront of people and he wanted to be buried in Egypt next to Cleo which was very unroman • Built along Via Flaminia, usually had to have senate approval • Tumulus tomb, fits into landscape, very Etruscan • Opus Reticulatum • Cut out Square columns to hold the remains of his family Marcellus first • Statue on top to symbol him leaving the Romans to the gods • Res Gestae outside of pillars • Placks listing off his accomplishments • Ustrunum, Solarium, Ara Pacis |
|

|
Theater of Marcellus
|
• Theater of Marcellus C 25 13/11 BCE, between the circus Flaminius and forum boarium
• Marcellus was who was thought to take over the Empire after Augustus, was Augustus sisters son • Died in early 20’s in 23 BCE • Augustus wanted to build the theater and was finishing projects that Caesar had started, so he dedicated the theater to Marcellus during construction • Fornix entryways to get up to the seats • Had stacking of the orders, Doric, ionic, Corinthian • First theater to have a semicircular cavea closed by a substantial stage building • Made with travertine and opus reticulatum • Decorated with mythological paintings in the plaster • Fir 12-15k people • Law passed in 18 BCE about the seating of the Theater • Theme- we’ve restored to prosperity because Aug restored the peace |

