![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
44 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
The glands are formed of mucous neck cells located at the top, p_______ cells located in the middle and c____ cells located at the bottom.
|
The glands are formed of mucous neck cells located at the top, parietal cells located in the middle and chief cells located at the bottom.
|
|
|
Mucous neck cells produce _____ which coats the surface epithelium.
Parietal cells produce ____________ ____ Chief cells produce p_________ |
Mucous neck cells produce mucus which coats the surface epithelium.
Parietal cells produce hydrochloric acid Chief cells produce pepsinogen |
|
|
Gastric areas (mam________ areas). Close visual inspection shows that the mucosa is divided by furrows into small irregular elevations, 1-6 microm in diameter. These are the gastric areas
|
Gastric areas (mammillated areas). Close visual inspection shows that the mucosa is divided by furrows into small irregular elevations, 1-6 microm in diameter. These are the gastric areas
|
|
|
Gastric pits (_____lae). Inspection of the stomach mucosa with a magnifying glass shows the surface of each gastric area to be studded with minute depressions, the gastric pits. In the pylorus, the pits extend downward to about one-half the thickness of the mucosa; in the cardia, corpus and fundus, the pits occupy only one-fourth the thickness of the mucosa
|
Gastric pits (foveolae). Inspection of the stomach mucosa with a magnifying glass shows the surface of each gastric area to be studded with minute depressions, the gastric pits. In the pylorus, the pits extend downward to about one-half the thickness of the mucosa; in the cardia, corpus and fundus, the pits occupy only one-fourth the thickness of the mucosa
|
|
|
Surface epithelium and epithelium of gastric pits. The __________ ____ epithelium, which lines the luminal surface of the stomach, also extends down to line the gastric pits.
|
Surface epithelium and epithelium of gastric pits. The simple columnar epithelium, which lines the luminal surface of the stomach, also extends down to line the gastric pits.
|
|
|
3 types of pit in the stomach
|
Cardiac
Gastric (fundic) Pyloric |
|
|
The most abundant epithelial cells are ______ cells, which cover the entire lumenal surface and extend down into the glands as "mucous neck cells"
|
The most abundant epithelial cells are mucous cells, which cover the entire lumenal surface and extend down into the glands as "mucous neck cells"
|
|
|
Mucous cells secrete a ___________-rich mucus that coats and lubricates the gastric surface, and serves an important role in protecting the epithelium from acid and other chemical insults.
|
Mucous cells secrete a bicarbonate-rich mucus that coats and lubricates the gastric surface, and serves an important role in protecting the epithelium from acid and other chemical insults.
|
|
|
Hydrochloric acid is secreted from parietal cells into the lumen where it establishes an extremely acidic environment. This acid is important for activation of __________ and inactivation of ingested microorganisms such as bacteria
|
Hydrochloric acid is secreted from parietal cells into the lumen where it establishes an extremely acidic environment. This acid is important for activation of pepsinogen and inactivation of ingested microorganisms such as bacteria
|
|
|
Once secreted, pepsinogen is activated by stomach acid into the active p_______ pepsin, which is largely responsible for the stomach's ability to initiate digestion of proteins
|
Once secreted, pepsinogen is activated by stomach acid into the active protease pepsin, which is largely responsible for the stomach's ability to initiate digestion of proteins
|
|
|
The principle hormone secreted from the gastric epithelium is _______, a peptide that is important in control of acid secretion and gastric motility
|
The principle hormone secreted from the gastric epithelium is gastrin, a peptide that is important in control of acid secretion and gastric motility
|
|
|
The structure and cellular composition of the surface epithelium (simple, tall ________) does not change throughout the stomach
|
The structure and cellular composition of the surface epithelium (simple, tall columnar) does not change throughout the stomach
|
|
|
The surface epithelium is renewed approximately every _____ day
|
The surface epithelium is renewed approximately every third day
|
|
|
The source of the new surface epithelium cells is the i______, i.e. the upper part of the neck, of the gastric glands, where cells divide and then migrate towards the surface epithelium and differentiate into mature epithelial cells
|
The source of the new surface epithelium cells is the isthmus, i.e. the upper part of the neck, of the gastric glands, where cells divide and then migrate towards the surface epithelium and differentiate into mature epithelial cells
|
|
|
(1) the surface mucous cells lining the pit
(2) the mucous neck cells located at the opening of the gastric gland into the pit Both cells produce m_____, glycoproteins with high molecular mass |
(1) the surface mucous cells lining the pit
(2) the mucous neck cells located at the opening of the gastric gland into the pit Both cells produce mucins, glycoproteins with high molecular mass |
|
|
Parietal cells produce the hydrochloric acid of the gastric juice and i________ factor, a glycoprotein that binds to vitamin ___
|
Parietal cells produce the hydrochloric acid of the gastric juice and intrinsic factor, a glycoprotein that binds to vitamin B12
|
|
|
Vitamin B12 binds in the stomach to the transporting binding protein i________ factor
|
Vitamin B12 binds in the stomach to the transporting binding protein intrinsic factor
|
|
|
In the small intestine, the vitamin B12-intrinsic factor complex binds to intrinsic factor receptor on the surface of e___________ in the ileum and is transported to the liver through the portal circulation
|
In the small intestine, the vitamin B12-intrinsic factor complex binds to intrinsic factor receptor on the surface of enterocytes in the ileum and is transported to the liver through the portal circulation
|
|
|
The parasympathetic mediator a_____________ and the peptide g______, produced by enteroendocrine cells of the pyloric antrum, stimulate parietal cells to secrete HCl
|
The parasympathetic mediator acetylcholine and the peptide gastrin, produced by enteroendocrine cells of the pyloric antrum, stimulate parietal cells to secrete HCl
|
|
|
Acetylcholine also stimulates the release of g______
|
Acetylcholine also stimulates the release of gastrin
|
|
|
_________ potentiates the effects of acetylcholine and gastrin on parietal cell secretion after binding to the histamine H2 receptor
|
Histamine potentiates the effects of acetylcholine and gastrin on parietal cell secretion after binding to the histamine H2 receptor
|
|
|
Histamine is produced by e_______________-____ _____ cells within the lamina propria surrounding the gastric glands
|
Histamine is produced by enterochromaffin-like (ECL) cells within the lamina propria surrounding the gastric glands
|
|
|
C_________ is an H2 receptor antagonist that inhibits histamine-dependent acid secretion
|
Cimetidine is an H2 receptor antagonist that inhibits histamine-dependent acid secretion
|
|
|
O_________ with binding affinity to H+,K+-dependent ATPase, inactivates acid secretion and is an effective agent in the treatment of peptic ulcer
|
Omeprazole with binding affinity to H+,K+-dependent ATPase, inactivates acid secretion and is an effective agent in the treatment of peptic ulcer
|
|
|
Peptide hormones are synthesized by g_____e_____e________ cells dispersed throughout the mucosa from the stomach through the colon
|
Peptide hormones are synthesized by gastroenteroendocrine cells dispersed throughout the mucosa from the stomach through the colon
|
|
|
The population of g____________________ cells is so large that the gastrointestinal segment is regarded as the largest endocrine organ in the body
|
The population of gastroenteroendocrine cells is so large that the gastrointestinal segment is regarded as the largest endocrine organ in the body
|
|
|
Auto______ _____itis is caused by autoantibodies to H+,K+-dependent ATPase, a parietal cell antigen, and intrinsic factor
|
Autoimmune gastritis is caused by autoantibodies to H+,K+-dependent ATPase, a parietal cell antigen, and intrinsic factor
|
|
|
Destruction of parietal cells causes a reduction in hydrochloric acid in the gastric juice (a___________) and a lack of synthesis of intrinsic factor
|
Destruction of parietal cells causes a reduction in hydrochloric acid in the gastric juice (achlorhydria) and a lack of synthesis of intrinsic factor
|
|
|
The resulting vitamin B12 deficiency disrupts the formation of red blood cells in the bone marrow, leading to a condition known as pernicious anemia, identified by examination of peripheral blood as _____________ anemia characterized by macrocytic red blood cells and hyper_________ large neutrophils
|
The resulting vitamin B12 deficiency disrupts the formation of red blood cells in the bone marrow, leading to a condition known as pernicious anemia, identified by examination of peripheral blood as megaloblastic anemia characterized by macrocytic red blood cells and hypersegmented large neutrophils
|
|
|
Chief cells predominate in the _____ third of the gastric gland
Chief cells are not present in c______ glands and are seldom found in the pyloric a_____ |
Chief cells predominate in the lower third of the gastric gland
Chief cells are not present in cardiac glands and are seldom found in the pyloric antrum |
|
|
Chief cells have a structural similarity to the zymogenic cells of the exocrine p________: the basal region of the cytoplasm contains an extensive rough endoplasmic reticulum.
|
Chief cells have a structural similarity to the zymogenic cells of the exocrine pancreas: the basal region of the cytoplasm contains an extensive rough endoplasmic reticulum.
|
|
|
Pepsinogen, a proenzyme stored in the z______ granules, is released into the lumen of the gland and converted in the acid environment of the stomach to pepsin, a proteolytic enzyme capable of digesting most p_______
|
Pepsinogen, a proenzyme stored in the zymogen granules, is released into the lumen of the gland and converted in the acid environment of the stomach to pepsin, a proteolytic enzyme capable of digesting most proteins
|
|
|
by far the most numerous type of gastric gland is the f_____ gland
They produce the bulk of secretions in the stomach |
by far the most numerous type of gastric gland is the fundic gland
They produce the bulk of secretions in the stomach |
|
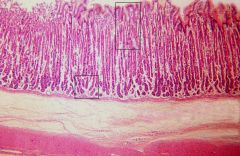
-
|
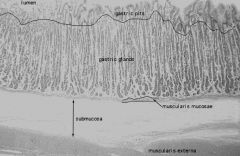
-
|
|

-
|
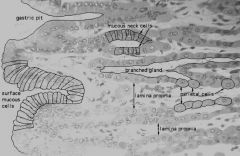
-
|
|

-
|

-
|
|
|
Pyloric glands differ from the cardiac and
gastric glands in the following layers: (1) the gastric pits, or foveolae, are deeper and extend halfway through the depth of the ______ (2) ______ glands have a larger lumen and are highly branched |
Pyloric glands differ from the cardiac and
gastric glands in the following layers: (1) the gastric pits, or foveolae, are deeper and extend halfway through the depth of the mucosa (2) pyloric glands have a larger lumen and are highly branched |
|
|
The predominant epithelial cell type of the _______ gland is a mucus-secreting cell that resembles the mucous neck cells of the gastric glands
|
The predominant epithelial cell type of the pyloric gland is a mucus-secreting cell that resembles the mucous neck cells of the gastric glands
|
|
|
The predominant epithelial cell type of the pyloric gland is a mucus-secreting cell that resembles the mucous neck cells of the gastric glands
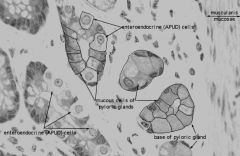
Most of the cell contains large and pale secretory mucus and secretory granules containing l_______, a bacterial lytic enzyme Occasionally, parietal cells can be found in the pyloric glands Enteroendocrine cells, g______-secreting _ cells in particular, are abundant in the antrum pyloric region L_______ nodules can be seen in the lamina propria. |
The predominant epithelial cell type of the pyloric gland is a mucus-secreting cell that resembles the mucous neck cells of the gastric glands
Most of the cell contains large and pale secretory mucus and secretory granules containing lysozyme, a bacterial lytic enzyme Occasionally, parietal cells can be found in the pyloric glands Enteroendocrine cells, gastrin-secreting G cells in particular, are abundant in the antrum pyloric region Lymphoid nodules can be seen in the lamina propria. |
|
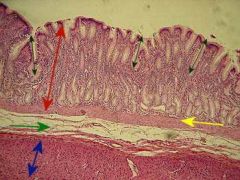
Here is an image of the Pyloric Stomach. The red arrow is pointing to it's ______, the green arrow is pointing to the _________, the yellow arrow is pointing to the M_________ ______, and the blue arrow is pointing to the Muscularis _______. The black arrows are pointing to the characteristic of the pyloric stomach that is an important hint at identifying it, and that is the ____ Gastric ____.
|
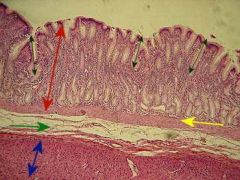
Here is an image of the Pyloric Stomach. The red arrow is pointing to it's Mucosa, the green arrow is pointing to the Submucosa, the yellow arrow is pointing to the Muscularis Mucosa, and the blue arrow is pointing to the Muscularis Externa. The black arrows are pointing to the characteristic of the pyloric stomach that is an important hint at identifying it, and that is the Deep Gastric Pits.
|
|

This is a closer look at the Gastric ____ of the pyloric stomach, indicated by the blue arrows. Notice how ____ they go, compared to the other two sections of the stomach we have seen. This is the clue to identify the _______ stomach
|
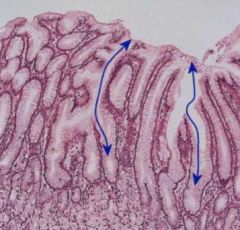
This is a closer look at the Gastric Pits of the pyloric stomach, indicated by the blue arrows. Notice how deep they go, compared to the other two sections of the stomach we have seen. This is the clue to identify the pyloric stomach
|
|

-
|
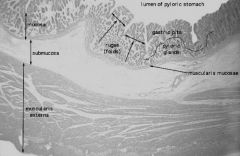
-
|
|
-
|

-
|
|

-
|
-
|

