![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
26 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Renal diseases: more morbidity or mortality?
|
morbidity
|
|
|
a glomerular syndrome
hematuria (red blood cells in urine), mild to moderate proteinuria, and hypertension; it is the classic presentation of acute poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis. |
Acute nephritic syndrome
|
|
|
syndrome characterized by heavy proteinuria (more than 3.5 gm/day), hypoalbuminemia, severe edema, hyperlipidemia, and lipiduria (lipid in the urine).
|
nephrotic syndrome
|
|
|
Antibody-mediated glomerular injury can result either from the deposition of circulating immune complexes or, more commonly, from in situ formation of complexes exemplified by what 2 diseases?
|
anti-GBM disease or
Heymann nephritis |
|
|
Two patterns of deposition of immune complexes as seen by immunofluorescence microscopy: granular, characteristic of ________ and linear, characteristic of classic ______- disease.
|
granular: circulating and in situ immune complex nephritis
linear: anti-GBM |
|
|
D: granular, characteristic of circulating and in situ immune complex nephritis
E: linear, characteristic of classic anti-GBM disease (E). |
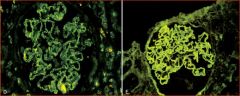
Two patterns of deposition of immune complexes
D? E? |
|
|
Acquired disorders that lead to proteinuria also disrupt the structure or the podocyte foot processes and filtration slits
The foot processes retract and the podocytes make broad flat contacts with the basement membrane, a condition known as ______ effacement |
podocyte
|
|
|
rare, inherited forms of congenital proteinuria occur when genetic mutations disrupt key structural proteins of the ____ diaphragm
|
slit
|
|
|
With the exception of ______-, the benign tumors rarely cause clinical problems
|
oncocytoma
|
|
|
the 3 most common of malignant tumors of the kidneys.
|
1- renal cell carcinoma
2- Wilms tumor 3- urothelial tumors of the calyces and pelves |
|
|
The amounts of proteoglycans in the interstitial tissue of the medulla increase with age and ______.
|
ischemia
|
|
|
the medulla does not have its own arterial blood supply but is dependent on the blood emanating from the glomerular ______ arterioles
|
efferent
|
|
|
to minimize the risk of bleeding during renal biopsy, the biopsy needle should be aimed tangentially through the cortex WHY?
|
Interlobar and arcuate vessels do not extend into the cortex
|
|
|
The glomerulus consists of three components
|
1- glomerular capillaries
2- mesangium 3- podocytes |
|
|
Recall that the parietal layer of the capsule of Bowman is a simple ____ epithelium
|
squamous
|
|
|
What causes thickening of the basement membrane
|
immune complexes
|
|
|
the antigens in the NC1 (of collagen) domain are the targets of antibodies in anti-____ nephritis
|
GBM
|
|
|
Genetic defects in the __-chains underlie some forms of hereditary nephritis
|
α
|
|
|
The _____ porous nature of the GBM determines its permeability characteristics
|
acidic
|
|
|
A chronic condition that develops gradually, IgA nephropathy most often affects young _____
|
men
|
|
|
___ nephropathy is the most common form of primary glomerulonephritis
|
IgA
|
|
|
Signs and symptoms of IgA nephropathy include:
Repeated episodes of __________-colored urine (gross hematuria or blood in the urine), usually during or following an upper respiratory infection |
cola-colored or tea
also: Pain in the side proteinuria Swelling (edema) in hands and feet High blood pressure Low-grade fever |
|
|
IgA nephropathy (______ Disease).
|
Berger’s
|
|
|
Excessive protein reabsorption induces tubular interstitial damage due to up-regulation of ________
|
endothelin
|
|
|
Diffuse Mesangial Sclerosis:
May be associated with Denys-Drash syndrome (nephrotic syndrome, male pseudohermaphroditism, ______ tumor) or be isolated |
Wilms’
|
|
|
Diffuse Mesangial Sclerosis:
Immunofluorescence: mesangial deposits of Ig_?_, C3, C1q |
IgM
|

