![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
151 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is sinking? |
Something that receives voltage |
|
|
What is sourcing? |
Something that supplies voltage |
|
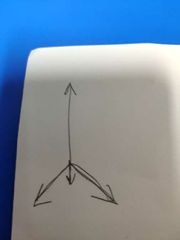
What type of coordinate is this? |
Cartesian |
|

What type of coordinate is this? |

Cylindrical |
|
|
What are the dimensions of the cylindrical coordinate system? |
Elevation, reach, and base rotation. |
|

What is this robots coord system? |
Rectangular. |
|
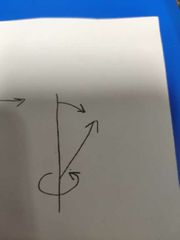
What is this coordinate system? |
Spherical. |
|
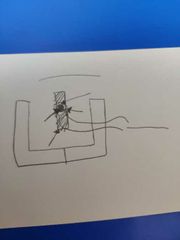
Label. |

|
|
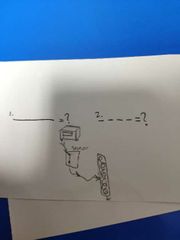
Sinking or sourcing? |

|
|
|
What is a sinking module? |
A module that takes current. |
|
|
What is a sourcing module? |
A module that provides current. |
|
|
What is the purpose of I/o? |
To connect machinery to other machinery. "I'm done" "ok, then I'll start!" |
|
|
What does i/o create? |
Two way communication |
|
|
What are input devices? |
Push buttons, selector switches, limit switches, prox switches, photo switches. |
|
|
What are the methods of operation for switches? |
Physical contact, magnetic or inductive fields, capacitive fields, acoustic fields, light rays, and rf fields. |
|
|
What are push buttons, selector switches, and limit switches made up of? |
Housing, operator, and contacts. |
|
|
How do physical contact operated switches work? |
You have to physically press them and that will change the contacts state. |
|
|
How do magnetic or inductive field operated sensors work? |
They close a switch by bringing the magnet close to the switch or putting magnetic material between the magnet and the switch. This alters the electrical field in the device. |
|
|
How to capacitive field operated sensors work? |
They make use of changes in capacitance in metallic objects and dielectric between plates when detecting non metallic objects. |
|
|
How to acoustic operated sensors work? |
Sound fields are interrupted or detect the reflection of sound from objects. |
|
|
How do light sensors work? |
Same as sound but with light. |
|
|
How do rf field operated sensors work? |
detect the presence of ferrous materials which absorb energy by any currents produced in them |
|
|
Inductive=? |
Metallic |
|
|
Capacitive =? |
Non metallic |
|
|
Do prox sensors have to have physical contact to sense things? |
No. |
|
|
Are prox sensors sensitive to polarity? |
No. |
|
|
How are wires arranged on pros sensors? |
One wire to power supply, one wire to load. |
|
|
What is the distance an object is detected at determined by? |
The diameter of the potentiometer core (varies directly), the size of the object to be sensed (varies directly), the type of metal, circuit sensitivity or design, and voltage and temperature to some degree. |
|
|
What metal is the metal that can be sensed at the greatest distance? |
Iron. |
|
|
What are the parts of a robot? |
The manipulator, the teach pendant, the controller and the main power disconnect. |
|
|
What is the manipulator? |
The arm of the robot. |
|
|
What is the teach pendant? |
The means of programming. |
|
|
What is the controller? |
CPU, power supply, I/O blocks, servo drives, playback panel, break release. |
|
|
What is the power supply? |
Main disconnect with lockout point, 3 phase 220 VAC fused transformer. |
|
|
What is after home? |
Cycle start. |
|
|
What are the types of coordinates? |
Link coordinates, xyz coordinates, cylinder coordinates, tool coordinates, and user coordinates. |
|

Label these. |
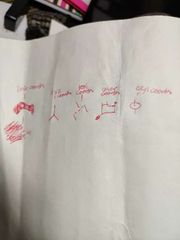
|
|

Label. |
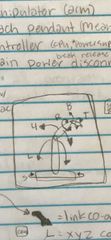
|
|
|
MovJ means? |
That there is no calculated path. Random path. |
|
|
In Movj, velocity can go from what to what? |
. 78 to 100. |
|
|
What does position level mean? |
It's tolerance. How close to the point does the robot have to get? |
|
|
What is MovL? |
Linear motion type. The robot will. Move in a straight line to get from point to point. |
|
|
In MovL, what is the range of velocity? |
0 to 1500 millimeters per minute. |
|
|
What is the tolerance range? |
0 to 4 |
|
|
What is MovC? |
Circular motion type. |
|
|
What is MovS? |
Spline motion type. |
|
|
Encoder counts? |
32, 767. |
|
|
What is OPT? (ope?) |
Pin position. |
|
|
What language is the word robot from, and what does it mean? |
It comes from the Czech word 'robota', which means forced labor. |
|
|
What is hard automation? |
Dedicated machines perform 1 task in an Assembly line. |
|
|
Can machines with hard automation learn a new task? |
No. |
|
|
What happens when a hard automation machine's job is no longer needed? |
They are discarded. |
|
|
When are hard automation machines used? |
When production is high and when the machine is going to be needed for a long time. |
|
|
What is flexible automation? |
Machines with flexible automation can learn new tasks. |
|
|
What category do robots belong in? |
Soft automation. |
|
|
Why is soft automation used? |
Because it saves time and money. |
|
|
Are soft automation machines or bard automation machines more common? |
Soft automation. |
|
|
Are soft automation or hard automation machines more flexible? |
Soft automation. |
|
|
What does the controller of the robot usually consist of? |
A computer chip. |
|
|
What are the three levels of herchal control? |
Actuator control, path control, and main control. |
|
|
Which level of herchal control is intermediate? |
Path control. |
|
|
Which level of herchal control is highest? |
Main control. |
|
|
Which level of herchal control is lowest? |
Actuator control. |
|
|
What is actuator control? |
Actuator is a motor or valve that converts power into robotic movement. |
|
|
In actuator control, what is being controlled? |
The separate movements of the robot. |
|
|
What is path control? |
The movements along the different planes are coordinated into a path. |
|
|
What is main control? |
Programs are interpreted and translated by the controller, broken down into a path, and then into specific movements of each axis. |
|
|
What are non-servo robots often called? |
Pick and place robots. |
|
|
What kind of system do non-servo robots use? |
An open loop system. |
|
|
What does open loop system mean? |
That there is no loop back to the controller to verify the position of the robot. |
|
|
What is an example of a non-servo robot? |
A micro bot. |
|
|
What are servo robots considered? |
They are considered to be intelligent robots. |
|
|
What system do servo robots use? |
Closed loop system. |
|
|
What does having a closed loop system mean for a robot? |
That feedback gets back to the controller to tell it where the robot is, so that it can make corrections. It can determine the positioning of the axes. |
|
|
What is an example of a servo robot? |
A motoman. |
|
|
What is the manipulator made up of? |
Multiple segments jointed together to allow for different types of movement. |
|
|
What types of movement can the manipulator move in? |
Linear actuated movement and rotary actuated movement. |
|
|
What do linear actuators provide? |
Movement along a straight line. |
|
|
What do rotary actuators provide?? |
Rotation in the arc of a circle to the manipulator. |
|
|
What classifies manipulators into configurations? |
The shape of the work envelope they create. |
|
|
What are the types of coordinates systems? |
Rectangular (cartesian), cylindrical, spherical, and revolute (articulated arm). |
|
|
What are manipulators powered by? |
Either electric drive, pneumatic drive, or hydraulic drive. |
|
|
What is electric drive? |
AC or DC servo Motors and stepper Motors. |
|
|
What is an example of something run off of an electric drive? |
A microbot uses stepper Motors. |
|
|
What is a hydraulic drive? |
An electric pump connected to a tank containing hydraulic fluid which is used to control valves and hydraulic actuators. |
|
|
What do pneumatic drives do? |
They use air to control valves and pneumatic actuators. |
|
|
How do stepper Motors move? |
Jerkily, in increments. A square wave shoots a pulse at it. |
|
|
How do servo Motors move? |
Smoothly. |
|
|
Which is more accurate, servo motors or stepper Motors? |
Servo Motors, because of their handy dandy closed loop system! |
|
|
What type of motor do we use today? |
Servo Motors, because they are closed loop and offer more freedom. |
|
|
How many degrees of freedom are there? |
6. |
|
|
For each degree of freedom, what is required? |
A joint to go along with it. |
|
|
What are the 6 degrees of freedom? |
Base, shoulder, elbow, pitch, roll, and yaw. |
|
|
What is a bonus degree of freedom that is sometimes considered? |
Grips. |
|
|
What are the types of input device signals? |
Digital and analog. |
|
|
What are the characteristics of digital input? |
Either on or off. Can be AC or DC. |
|
|
What are the characteristics of analog voltage? |
Varying voltage (a range) and varying current (a range). |
|
|
What are some output devices? |
Lights, solenoid valves, relays, motor starters, Motors, etc. |
|
|
What are electric Motors all about? |
Magnets. |
|
|
What does an electric motor do with a magnet? |
It uses it to create motion. Opposites attract and likes repel. |
|
|
What are the parts of a motor? |
Brushes, communicator, armature, axle, field magnet. |
|
|
What is the armature (or rotor)? |
An electromagnet. |
|
|
What is the field magnet? |
A permanent magnet. (it can also be an electromagnet, but its poles would still remain constant. |
|
|
What do the brushes do? |
Transfer power to the communicator. As the motor spins, they ride on the communicator to switch the electromagnetic poles on the armature. |
|
|
What does the axle do? |
It rides on the bearings that are attached to the motor housing, and transfers the mechanical energy thought the axle shaft to whatever work is to be done. Robb. |
|
|
What are the types of output signals? |
Digital and analog. |
|
|
What are sinking/sourcing modules related to? |
PLCs. |
|
|
What are the terms sinking and sourcing referring to? |
Current that flows in and out of a device. |
|
|
What is the type of current that is sinking or sourcing called? |
Conventional current flow. |
|
|
How does conventional current flow? |
From positive potential to negative potential. |
|
|
What does sinking refer to? |
A device or component that absorbs or receives current. Conventional current flows in. |
|
|
What does sourcing refer to? |
Sourcing refers to a device that or component that provides current. Conventional current flows out of the device. |
|
|
Is PNP sinking or sourcing? |
Sourcing. |
|
|
In NPN sinking or sourcing? |
Sinking. |
|
|
If you have a sinking module, your device has to be what? |
Sourcing. |
|
|
If you have a sourcing module, your device has to be what? |
Sinking. |
|
|
What is a photo switch defined as? |
A sensor that responds to a change in the intensity of the light falling upon it. |
|
|
What are the types of photoelectric switches? |
Remote sensors and self contained sensors. |
|
|
What do remote photoelectric sensors contain? |
Only the optical components of the sensing system. |
|
|
Where are remote photoelectric sensor's power system and output contained? |
At another location, usually a control panel. |
|
|
Which is smaller, self contained sensors or remote sensors? |
Remote sensors. |
|
|
Which is tougher? Remote sensors or self contained sensors? |
Remote sensors. |
|
|
What do self contained sensors actually contain? |
Well, themselves of course! The optics and the electronics. They only require power. |
|
|
What do self contained sensors require? |
Only power. |
|
|
What are the sensing modes? |
Opposed, retro-reflective, diffused, divergent, convergent, and fixed field. |
|
|
In the opposed sensing modes, how are the receiver and emitter placed? |
Opposite one another. |
|
|
How does the opposed sensing mode work? |
Receiver and emitter are opposite each other, light is directly at receiver. When an object is detected, it interrupts the sensing path. |
|
|
What is an example of an opposed sensing mode? |
A light curtain. |
|
|
Can something with an apposed sensing mode be configured? |
Yes. It can be switched between dark and light operating mode. |
|
|
Dark is comparative to what? |
Normally closed. |
|
|
Light is comparative to what? |
Normally open. |
|
|
What is retro-reflective sensing mode? |
Sensor contains both emitter and receiver and a light beam is established between emitter, the beam, the target, and the receiver. The object is sensed when it interrupts the beam. |
|
|
What is an example of a retro-reflective sensor? |
A photo-eye/photosensor. |
|
|
How does a diffused sensing mode work? |
Emitted light strikes the surface of an object at some angle, and the receiver will be at some other angle so that a small portion if diffused light will reach it. |
|
|
What is a divergent type sensor used with? |
Shiny objects. |
|
|
What is the range of a divergent sensor? |
Short. |
|
|
How does a divergent type sensor work? |
It shines a light at a shiny thing. The light reflected must fall with a certain range for it to detect it. |
|
|
Which has a larger beam, a diffused type sensor, or a divergent type sensor? |
Diffused. |
|
|
What are convergent type sensors good for? |
Small objects. |
|
|
How do convergent type sensors work? |
They focus emitted light to an exact point in front of the sensor and focus the receiving element at the same point. |
|
|
Are convergent type sensors precise? |
Yes. Very. |
|
|
What do fixed field type sensors do? |
Ignore objects that lie beyond their sensing range, regardless of how reflective the object is. They compare the amount of reflected light from two receivers, and the target is recognized as long as the amount of light reaching the receiver is equal to or greater than the light reaching the other. Phew. |
|
|
On fixed field sensors, both receivers have to see what to work? |
Some amount of light. |
|
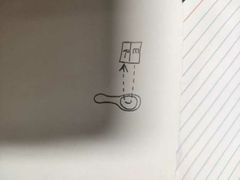
What kind of sensor is this? |
A divergent sensor. |
|
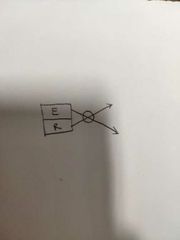
What type of sensor is this? |
A convergent type sensor. |
|
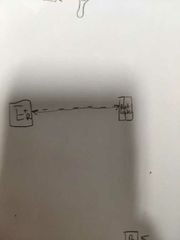
What type of sensor is this? |
A retroreflective sensor. |
|
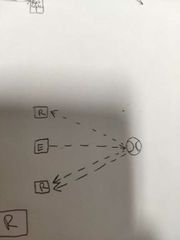
What type of sensor is this? |
A fixed field type sensor. |
|
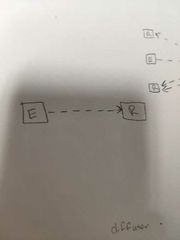
What type of sensor is this? |
Apposed type. |
|
|
What is opposed sensing mode also known as? |
Direct scanning, or beam brick. |
|
|
What is retro reflective type sensor also known as? |
Reflex, or retro sensor. |
|
|
What is the answer to the bonus question? |
Indy 500 |

