![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
94 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is field of view? |
Imaged area of object under inspection. |
|
|
What is working distance? |
Distance from front of dense to object. |
|
|
What is focal length? |
Distance from center of lens to image sensor. |
|
|
What is the aperture range? |
The amount of light that the diaphragm can let inside the camera to reach the sensor. |
|
|
What is F#? |
Aperture size #. |
|
|
What is depth of focus? |
Maximum object depth that can be maintained entirely in focus. |
|
|
What is contrast? |
How well black can be distinguished from white at a given resolution in an object. |
|
|
What is macro for? |
High magnification applications. Size of image = size of object 1:1 |
|
|
What is a telecentric lense? |
It optically corrects for perspective distortion. |
|
|
What lense always has the same field of view? |
Telecentric. |
|
|
What does specular mean? |
Smooth and glossy. |
|
|
What does diffuse mean? |
Rough and dull. |
|
|
What is collimated light? |
Doesn't spread out quickly. |
|
|
What does an opaque object do? |
It doesn't let light through. |
|
|
What does transparent material do? |
Lets light through without altering it |
|
|
What does translucent material do? |
Lets some light through, but alters it. |
|
|
What does diverging light mean? |
The beams are going away from one another. Outward. |
|
|
What does convergent mean? |
The beams are going towards one another. Inward. |
|
|
What does a condenser lense do? |
Converts scattered light rays into collimated rays. |
|
|
What is fluorescence? |
When an object absorbs a short wavelength light and puts out a longer wavelength light. |
|
|
What is infrared? |
Infrared light is in the range above 700 nanometers. Negates all color. 700nm to 1mm |
|
|
What is UV light? What's the range? |
Ultraviolet is below 400 nm. From 10nm to 400nm |
|
|
What is the range of visible color? |
400nm to 700nm |
|
|
What is refraction? |
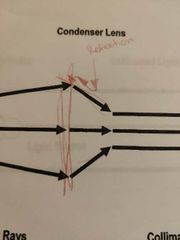
|
|
|
What is a parabolic mirror? |
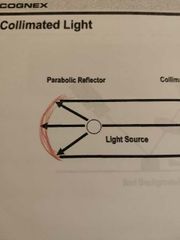
|
|
|
Beam splitter definition? |
Shine a light on it and it splits the beam. |
|
|
What us quantum efficiency? |
The measure of effectiveness of an imager to produce electronic charge from incident photons. |
|
|
What is a black light? |
It emits ultraviolet light. |
|
|
Shorter focal length equals what in relation to field of view? |
Wider field of view. |
|
|
Longer focal lengths require what, and why? |
Short exposure times. To minimize blurring caused by vibration. |
|
|
5.8mm to 17.4mm is what sort of zoom? |
3x. Because 17.4=3x5.8 |
|
|
Smaller focal length equals what in terms of magnification? |
Smaller equals more magnification. |
|

Which has a higher F#? |
Right one. |
|
|
Smaller F# means what? |
Bigger Diameter, more light. |
|
|
Smaller focal length equals what in way of distortion? |
More distortion. Perspective error. |
|
|
What is a pro and a con for halogen light source? |
Pro, very bright. Con, lots of heat. |
|
|
Can halogen lights be strobed? |
No. |
|
|
What is a pro and a con for fluorescent lighting? |
Pro, produces even lighting, con, flickers. |
|
|
Can fluorescent lighting be strobed? |
No. |
|
|
What are the pros and cons of lasers as lighting? |
Pros: highly collimated, can be used for structured lighting. Cons: safety. |
|
|
What is a good/bad thing about lasers? |
Monochromatic. |
|
|
Can lasers be strobed? |
Yes. |
|
|
What is a pro and a con about incandescent lighting? |
Pro: cheap, con: changes over time. |
|
|
Can incandescent lighting be strobed? |
No. |
|
|
Are incandescent bulbs common? |
No. |
|
|
Are LEDs common? |
Yes. |
|
|
What are the pros and cons of LEDs? |
Pros: long lasting, monochromatic or white light. Con: not capable if very high/intense light. |
|
|
Can LEDs be strobed? |
Yes. |
|
|
Should you touch the bulb of a xenon flash? |
No. |
|
|
What is a pro and a con of the xenon flash bulb? |
Pro: can produce a very bright and intense light. Con: has gas under pressure, more dangerous. |
|
|
How does bright field work? |
Light strikes down on flat part and then back up to camera. Any intentions make the light bounce away, which creates a dark edge. |
|
|
What is bright field useful for? |
Diffuse surfaces are dark, polished surfaces are bright, used to emphasize height changes. |
|

What is his an example of? |
Bright field. |
|
|
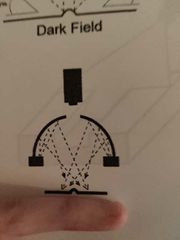
What is dark field? |
Light strikes away from smooth and at camera for rough. |
|

What is this? |
Dark field. |
|

What is this? |
Bright field. |
|
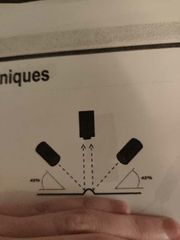
What is this? |
Dark field. |
|

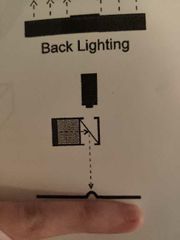
What is this? |
Back lighting. |
|
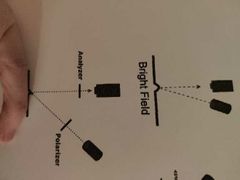
What is this? |
Polarized. |
|
What is this? |
Diffuse off axis |
|
What is this? |
Diffuse on axis |
|
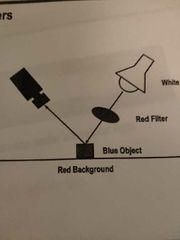
What is this? |
Color filters. |
|
|
What is a good and a bad thing about spacers? |
They're cheaper than a lense, but reduce quality of the image. |
|
|
What is a wide angle lense? |
It has a smaller focal length and a wider depth of field. Closer focusing distance. |
|
|
What is a telephoto lense? |
Larger image, used for small or distant objects. Narrower, greater magnification. Longer working distance. |
|
|
What is a standard lense? |
50mm focal length. |
|
|
What are color filters used for? |
To eliminate certain colors and make other colors more apparent. |
|
|
What do you use like color families to do? |
To lighten. |
|
|
What do you use opposite colors to do? |
Darken. |
|
|
What are polarizers used for? |
To reduce glare or hot spots, enhance contrast, or perform stress evaluations. |
|
|
What are the two primary categories of filters? |
Colored glass filters and coated filters. |
|

This is a polarizer |
Good girl. |
|
|
What is diffuse off axis used for? |
Avoids hot spots and glares. Gets rid of shadows. Good for locating defects on shiny, non-flat surfaces. |
|
|
What is diffuse on axis used for? |
Creates a bright effect, camera is normal to the part, detects flaws on flat, shiny surfaces. |
|
|
What are the applications and advantages of structured light? |
(grid) inexpensive for measuring height/depth, shows surface profile on low contrast. Application: very low contrast part, gauging continuous features. |
|
|
What are the advantages and applications of backlight? |
Maximum contrast, simplifies image by making a silhouette of part. Applications: measuring dimensions, specifically holes. (transparent) |
|
|
How do you calculate the resolution of sensors? |
Length of FOV divided by pixels in length of sensor. |
|
|
Camera sensor QE vs light spectrum? |
Different sensors have different sensitivities across the color spectrum. |
|
|
Light output spectrum intensity? |
Different light sources put out differently across the color spectrum. |
|
|
What is C-Mount? |
Standardized adapter for optical lenses on CCD. 1 inch diameter, 32 threads per inch mounting thread. |
|
|
What is CS-Mount? |
Same as C-mount, but focal length is 5mm shorter. 1inch diameter, 32 threads per inch. |
|
|
Will a CS-mount lense work on a C-mount camera? |
No. |
|
|
What is an S-mount lense? |
A standard lense. Sometimes called an M12. |
|
|
What is the specular reflection law? |
Angle of incidence equals angle of reflection. |
|
|
What are the seven imaging problems? |
Rotation, blur, scale changes, poor contrast, uneven lighting, overlapping parts and process variations. |
|
|
What is a cause of rotation? |
No/loose part fixturing. |
|
|
What is a cause of blur? |
Part is in motion, camera lense is out of focus. |
|
|
What is a cause of scale changes? |
Distance between camera and part varies slightly. |
|
|
What is a cause of poor contrast? |
Part blends into background. |
|
|
What is a cause of uneven lighting? |
Light changes over time. |
|
|
What is a cause of overlapping parts? |
Multiple, unfixtured parts moving down the line. |
|
|
What is a cause of process variation? |
Inconsistencies in the manufacturing process |
|
|
Where does a ring light go? |
Around the camera lense. |
|
|
When calculating the sensor resolution, what is the number you get? |
The theoretical ideal. |

