![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
26 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Image summarising conversion from digital to analog image.
|
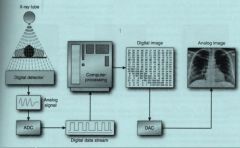
summary
|
|
|
Digital image processing simply means, operate
upon _______ using computer |
pictorial information
|
|
|
What constitute a digital image?
|
An image that has been discretized into coordinates and brightness from a continuous image.
|
|
|
a digital image is represented by ________
|
Represented by 2D integer array or a series of 2D
arrays for each colour band. |
|
|
Monochromatic image has no colour but only ______.
|
shades of
grey. |
|
|
Colour image is represented by ________ or indexed.
|
red, green and blue
components |
|
|
Often the brightness values of a digital image range from _______
|
0 (black)
to 255 (white). |
|
|
waht are the 3 Types of Digital Image?
|
Binary image, Grayscale, True Colour
|
|
|
what is a binary image?
|
Each pixel are either just black or white
|
|
|
what is Grayscale image?
|
Each pixel is a shade of grey, from 0 to 255
|
|
|
What is a True Colour image?
|
Each pixel has a particular colour
|
|
|
Binary Image
|
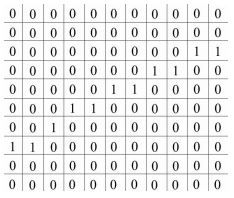
Needs only 1 bit
a binary digit - 0 or 1 1 bit digital representation - black and white |
|
|
Grayscale [each pixel is 1 byte(8 bits)]. for what type of images u use it for?
|
Used in X-rays, MRI, CT
|
|
|
i pixel for true colour image have ___ bits
|
24
8 bits for each of the 3 colour band (red, green blue). Thus, each pixels is 24 bits. |
|
|
true colour images can give how many colours?
|
Each component is 0 to 255; gives 2553 or 16,777,216
different colours. |
|
|
true colour component not used in ______ (modalities) as the devices are unable to detect colours.
|
X-Ray, MRI or CT
|
|
|
what does lightness refer to?
|
Refers to the Intensity value
i.e. Brightness of the colour |
|
|
what does hue refer to?
|
Refers to the colour
i.e. Green, Blue, Orange, etc |
|
|
what does saturation refer to?
|
Saturation
Refers to the measure of how white is in the colour. i.e. pink is more white, so it is less saturated than pure red |
|
|
Eg of analog image, digital sampling, pixel quantisation
|
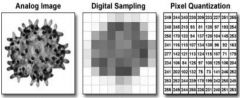
eg
|
|
|
What is the ADC (Analogue-to-Digital) converter for?
|
Vital in converting an analogue signal into digital
data for input into a computer for processing Consists of several components that divide the analogue signal into equal parts |
|
|
Spatial Frequency Domain
|
The rate at which brightness cycle is the spatial frequency.
The higher the cycle rate, the higher the spatial frequency |
|
|
How does the number of bits per pixel impact the image ?
|

Number of bits per pixel determines how many colours or
shades of gray to be displayed |
|
|
How does the Matrix Size affect the image quality?
|
As matrix size increase for the same FOV, picture
quality improves; that is the images become sharper |
|
|
Spatial density?
|
is a measure of the number of pixels in a digital image
|
|
|
Optical resolution
|
is a measure of the capability of how well the entire
physical imaging system can resolve the spatial details of an original scene relates to the quality of imaging system’s optics, photosensor and electronics |

