![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
43 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the 5 step process of gathering information about each rhythm strip? |
-Rhythm -Rate -P wave configuration -PR interval -QRS duration and configuration |
|
|
How do you evaluate the rhythm of atrial contraction? |
assessing the regularity or irregularity of the occurrence of the P waves |
|
|
How do you evaluate the rhythm of the ventricular contractions? |
assessing the regularity or irregularity of the QRS complex |
|
|
What interval in the ECG rhythm strip should be evaluated first? |
P-P Interval |
|
|
What can you do if the QRS complex does not exhibit an R-wave? |
use the point of the Q and S wave junction as an easy point of evaluation |
|
|
The P-P wave intervals measure this |
the atrial rate |
|
|
The R-R wave intervals measure this |
the ventricular rate |
|
|
Tachycardia |
A fast heart rate, usually greater than 100 beats per minute |
|
|
Bradycardia |
A slow heart rate, usually less than 60 beats per minute |
|
|
Used to determine the number of small boxes or duration of time |
The caliper interval of P-P and R-R measure |
|
|
This is what the relationship between P wave and QRS complex provides |
information regarding the coordination between atrial and ventricular contractions |
|
|
Questions you should ask when analyzing P-waves |
-Are the shapes and wave forms all the same? -Does each P-wave have a QRS complex following it?
|
|
|
What does the PR interval measure? |
this interval measures the length of time it takes the electrical current to be initiated at the sinoatrial node and travel through the electrical current pathway to cause a ventricular contraction |
|
|
How is the PR interval determined? |
This interval is determined by measuring the form the beginning of the P wave, or its up slope, to the beginning of the QRS complex |
|
|
Normal range of PR interval |
0.12-0.20 |
|
|
What does the QRS complex measure? |
the duration of time it takes for the ventricles to depolarize or contract |
|
|
What does a normal QRS complex indicate? |
if the QRS complex is within normal limits of 0.06 to 0.10 second, current has traveled through the normal ventricular conduction pathways to activate the ventricles to contract |
|
|
The J Point |
This point is located where the S wave stop and the ST segment is initiated |
|
|
the QRS duration is measured from where to where |
Measures the duration from the beginning of the QRS complex to the J point |
|
|
The criteria for classification |
-Rhythm: The intervals between the two P and two R waves will occur in a consistent pattern.
-Rate: Both the atrial and ventricular rate will be within 60 and 100 beats per minute
-P wave configuration: The P waves will have the same shape and are usually upright in deflection on the rhythm strip. A P wave will appear in front of every QRS complex
-PR interval: The measurement will be between 0.12 and 0.20 second, which is within normal limits. Each PR interval will b e the same, without variations
-QRS duration and configuration: The QRS duration and configuration measurement will be between 0.06 and 0.10 seconds, which is within normal limits. EACH should be the same without variations |
|
|
Normal Sinus Rhythm |
Sinus rhythm is the only rhythm for which all five steps are within normal limits
Desired rhythm. Patients with this rhythm should have normal cardiac output |
|
|
Cardiac Output |
Observation guidelines used to assess the blood supply to the vital organs of the body to maintain normal function |
|
|
Signs and symptoms of normal cardiac output |
alert and oriented patient with no difficulty breathing, no chest pain or pressure, and a stable blood pressure |
|
|
ECG rhythm is included in what documents and includes what information |
included in the patients medical records. The patients name, date, and time plus the initials of the person performing the ECG must be identified on each rhythm strip. Documentation of the ECG rhythm and the patients response help support the reason for medical treatments |
|
|
Criteria for Normal Sinus Rhythm |
Rhythm: Normal/Regular Rate: 60-100 P wave configuration: upright, positive deflection PR interval: 0.12-0.20 QRS duration and configuration: 0.06-0.10 |
|
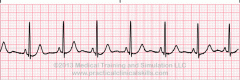
What does this rhythm resemble? |
EKG strip resembles normal sinus rhythm |
|
|
Criteria for Sinus Bradycardia |
Rhythm: Normal/Regular Rate: equal or less than 60 beats per minute P wave configuration: upright/positive deflection PR interval: 0.12-0.20 QRS duration and configuration: 0.06-0.10 |
|
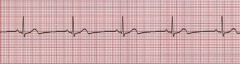
What does this rhythm resemble? |
Sinus Bradycardia |
|
|
Symptoms of Sinus Bradycardia |
The patient with this rhythm may or may not experience signs of low cardiac output |
|
|
Criteria for Sinus Tachycardia |
Rhythm: Normal/Regular Rate: 100-150 beats per minute P wave configuration: upright/positive deflection PR interval: 0.12-0.20 QRS duration and configuration: 0.06-0.10 |
|
|
Symptoms of Sinus Tachycardia |
Patients with this rhythm will complain of palpitations or "heart fluttering" with faster rates |
|
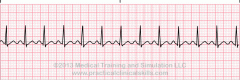
What does this rhythm resemble? |
Sinus Tachycardia |
|
|
Vagal tone |
Condition in which impulses over the vagus nerve exert a continuous inhibitory effect upon the heart and cause a decrease in heart rate |
|
|
Sinus Dysrhythmia (sinus arrhythmia) |
a condition in which the heart rate remains within normal limits but is influenced by the respiratory cycle and variations of vagal tone, causing the rhythm to be irregular |
|
|
Criteria for Sinus Dysrhythmia |
Rhythm: Irregular Rate: 60-100 beats per minute P wave configuration: upright/positive deflection PR interval: 0.12-0.20 seconds QRS duration and configuration: 0.06-0.10 |
|
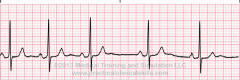
What does this rhythm resemble? |
Sinus dysrhythmia (sinus arrhythmia) |
|
|
Sinus Arrest |
occurs when the SA node stops firing, causing a pause in electrical activity |
|
|
Criteria for Sinus Arrest |
Rhythm: Regular Before and after sinus pause (irregular) Rate: Rate will vary P wave configuration: upright/positive deflection PR interval: 0.12-0.20 seconds QRS duration and configuration: 0.06-0.10 Length of pause: has to be measured |
|
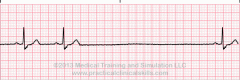
What does this rhythm resemble? |
Sinus Arrest |
|
|
When is sinus arrest a code blue situation? |
When it sinus arrest exceeds 6 seconds, it is considered a medical emergency. Code blue procedures must be intiated |
|
|
Symptoms of Sinus Arrest |
A patient with this rhythm will experience signs and symptoms of decreased cardiac output if the pause is 2 seconds long and occurs on a frequent basis. The pause may include periods of ischemia, hypotension, dizziness, and syncope |
|
|
Ischemia |
lack of blood supply to an area of tissue due to a blockage in the circulation to that area |
|
|
Hypotension |
low blood pressure |

