![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
32 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
causes of acute monoarthritis |
septic arthritis gout reactive arthritis polyarthropathy presenting as monoarthropathy - osteoarthritis, RA, psoriatic |
|
|
causes of oligoarthritis (1-4 joints) |
Disseminated gonococcal infection Acute pseudogout Reactive arthritis Lyme disease Psoriatic arthritis |
|
|
2010 EULAR classification criteria for RA |
Joint involvement Serology - RF / ACPA Acute Phase bloods - CRP / ESR Duration of symptoms - > 6 weeks score >6 = RA |
|
|
radiological features of RA |
joint space narrowing osteopenia periarticular erosion sparingof the DIP joints subluxation and ulnar deviation at MCP joints |
|
|
radiographic features of OA |
Loss of joint space Osteophytes Subarticular sclerosis Subchondral cysts |
|
|
investigation for gout |
Polarized light microscopy of synovial fluid shows negatively birefringent urate crystals, needle shaped |
|
|
treatment for gout |
1st line = high dose NSAID If NSAIDs contraindicated, (e.g. due to peptic ulcer; heart failure; anticoagulation), colchicine In renal impairment, use steroids |
|
|
side effect of colchicine |
diarrhoea |
|
|
protocol for introduction of allopurinol |
Introduction of allopurinol may trigger an attack so wait until 3 weeks after an acute episode, and cover with regular NSAID (for up to 6 weeks) or colchicine for 6 months |
|
|
tests for pseudogout (Calciumpyrophosphate) |
Polarized light microscopy of synovial fluid shows weakly positively birefringent crystals Rhomboid shape |
|
|
infecting organisms for septic arthritis |
Staph. Aureus Neisseria gonorrhoeae Salmonella |
|
|
causes of osteomalacia |
vitamin D deficiency renal failure drug-induced liver disease |
|
|
radiological features of osteomalacia |
loss of cortical bone Partial fractures without displacement |
|
|
Aetiology of osteoarthritis |
Primary - cause unknown Secondary - to joint disease, haemochromotosis, obesity, occupation |
|
|
extra-articular disease in ankylosing spondylitis |
Anterior uveitis Apical fibrosis Aortic incompetence Achilles tendinopathy |
|
|
radiological features of ankylosing spondylitis |
sacroiliitis vertebral syndesmophytes calcification of ligaments - bamboo spine reactive sclerosis - shiny corner sign |
|
|
nail changes in psoriatic arthritis |
pitting onycholysis |
|
|
ARA criteria for SLE |
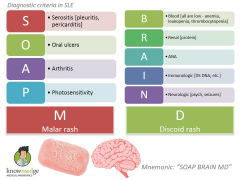
Malar rash Discoid rash Photosensitivity Oral ulcers Arthralgia Serositis Renal - glomerulonephritis Haematological - bone marrow failure Neurological - seizures, psychosis, depression, movement disorders ANA positive Immunological test positive for dsDNA, anti-Sm, or phospholipid antibodies |
|
|
red flags for sinister causes of back pain |

age: <20, >55
acute onset in elderly pain: constant, progressive, nocturnal, worse when supine, thoracic, leg pain Cancer signs: fever, night sweats, weight loss, history of malignancy, abdominal mass Neurological signs: neuro / sphincter disturbance Infective: current/recent infection, immunosuppresion Inflammatory: morning stiffness Spinal stenosis: leg claudication / exercise-related leg weakness/numbness |
|
|
signs of prolapsed disc |
Straight leg raise test - pain between 30-70 degree loss of reflex localized wasting |
|
|
Risk factors for osteoporosis |
↑Age female Family history of fracture BMI < 19 Menopause Smoking Alcohol Steroids use |
|
|
Causes of secondary osteoporosis |
Hyperthyroidism Untreated hypogonadism RA + inflammatory disorders Long-term low calcium - GI surgery, IBD, eating disorders Drugs - Breast cancer treatment, steroids, anti-epileptic treatment |
|
|
Diagnosis of polymyositis |
raised CK |
|
|
causes of raised ANA |
SLE, RA, scleroderma, Sjogren’s and autoimmune hepatitis |
|
|
symptoms of reactive arthritis |
Diarrhoealillness up to one month before arthritis Balanitiscircinata Keratodermablennorhagica conjunctivitis (early) Uveitis (late) Urethritis |
|
|
Markers of osteomalacia |
25hydroxylatedvitamin D decreased Serum calcium slightly low/normal Urinary calcium decreased Serum phosphorus decreased Serum ALP elevated Serum PTH elevated. |
|
|
neurological complications of RA |
Cervicalcord compression (odontoid erosion) Mononeuritis multiplex Compression neuropathy |
|
|
Ocular complications of RA |
episcleritis scleritis kerato-conjunctivitis sicca |
|
|
cardiovascular complications of RA |
Pericarditis Conduction abnormalities Coronary vasculitis Aortitis Increased atherosclerosis Increased risk of MI |
|
|
haematological complications of RA |
Anaemia - due to chronic disease, malnutrition, or drugs Thrombocytosis |
|
|
Pulmonary complications of RA |
Nodules Effusions Fibrosis Caplan's syndrome - severe lung fibrosis |
|
|
signs and symptoms of OA |
1. Localized disease (usually knee or hip): pain on movement and crepitus, worse at end of day; background pain at rest; joint gelling; joint instability. 2. Generalized disease (primary OA): Heberden’s nodes at DIP, Bouchard’s nodes at PIP |

