![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
87 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the diagnostic criteria for rheumatoid arthritis?
|
Morning stiffness lasting at least 1 hr*
Arthritis in at least 3 joints* Arthritis of hand joints( Symmetric arthritis* Abnormal RF levels Rheumatoid nodules Typical changes in xray of hand/wrist * must last at least 6 weeks |
|
|
What is the stereotypical person who is diagnosed with RA?
|
WOMAN between 35 and 60
|
|
|
What is the impact of RA on finances/work?
|
50% decreased lifetime earning potential
30 days of lost productivity/year |
|
|
Having RA puts you at an increased risk for this?
|
CV disease
|
|
|
What predisposes someone to RA?
|
HLA-DR4 mutations
|
|
|
What are the joints involved in RA?
|
Hands: MCP, PIP joints
Wrists Elbows Shoulders Hips Knees Ankles Feet Cervical spine |
|
|
What part of the body is spared in RA?
|
Thoracic spine
Lumbar spine DIPs |
|
|
What are the typical physical findings of RA?
|
Soft tissue swelling
Warmth Deformities |
|
|
What are the typical findings of RA on a radiograph?
|
Periarticular osteopenia
MARGINAL EROSIONS |
|
|
What are the typical labs found in RA?
|
Increased ESR
RF Anemia Thrombocytosis Hypoalbuminemia |
|
|
What are the different causes of systemic rheumatic disease?
|
SLE
Scleroderma Polymyositis Vasculitis |
|
|
What types of arthritis can involve the TMJ? What don't?
|
Do: RA, Juvenille RA
Rare: Gout |
|
|
What types of arthritis can involve the larynx? What don't?
|
Do: RA
Don't: all others |
|
|
What types of arthritis can involve the elbows/wrists/MCPs? What don't?
|
Do: any synovitis
Don't: OA |
|
|
What types of arthritis can involve the DIPs? What don't?
|
Do: OA, psoriatic arthritis
Don't: RA |
|
|
What types of arthritis can involve the hips? What don't?
|
Do: OA, RA
Doesn't: Gout |
|
|
What types of arthritis can involve the cervical spine? What don't?
|
Do: Everything but gout
Don't: Gout |
|
|
What types of arthritis can involve the thoracolumbar spine? What don't?
|
Do: Spondyloarthropathies, OA
Don't: Gout, RA |
|
|
What kinds of arthritis shows markedly elevated leukocyte counts?
|
Gout
Septic arthritis Juvenille RA RA |
|
|
What kinds of arthritis show a white count that isn't elevated much at all?
|
OA
|
|
|
Where on the bone do you typically see damage happening in RA?
|
ON the side, where there isn't any cartilage to protect the bone from the inflamed synovium
|
|
|
What does the histology of RA look like?
|
Severe inflammation of the synovium
-Immune cells -Hyperplasia -Angiogenesis |
|
|
What are some bacterial triggers of RA?
|
Gram + cocci
Mycobacteria Proteus E. coli Mycoplasma P GINGIVALIS |
|
|
What are some viral triggers of RA?
|
EBV
Parvovirus Retroviruses CMV Rubella HHV6 |
|
|
What dental condition is associated with RA? What bacteria is implicated?
|
Peridontal disease
P. gingivalis |
|
|
What are the genetic risk factors for RA? Environmental?
|
Genetic:
MHC Class Ii alleles (HLA-DR4) Environmental SMOKING!! |
|
|
Why should you counsel someone with a history of RA to stop smoking?
|
IT PUTS THEM AT SIGNIFICANTLY INCREASED RISK FOR RA!!!
|
|
|
What are the different kinds of autoantibodies in RA?
|
RF
anti-citrullinated peptides (anti-CCP) |
|
|
What is the structure of the RF antibody?
|
an IgM antibody against the constant region of IgG
|
|
|
What is the problem with using RF as a test for RA?
|
It's present in a lot of other conditions!!!
Also, if someone doesn't have it, you can't rule out RA: 20% have RA but aren't RF positive |
|
|
What is citrulline? What causes it to be present in the body?
|
It's a derivative of arginine
PADI (peptidyl arginine deaminase) is responsible for it being in the body: arginine ------PADI-----> citrulline |
|
|
Where are citrullinated proteins present in large numbers?
|
They're found in inflamed synovium
|
|
|
What is the effect of smoking on the lung?
|
Aside from catastrophic damage, you cause...
CITRULLINATION OF THE PROTEINS |
|
|
What kind of bacteria expresses PADI?
|
Our dental friend...
P. gingivalis |
|
|
What kinds of immune cells are involved in the pathogenesis of RA?
|
T-cells
|
|
|
What inteleukins are found in RA?
|
IL-17
-Found in arthritis joints -Administering makes the symptoms worse |
|
|
What interleukins induce IL-17 expression?
|
IL-6, IL-1
|
|
|
What causes an undifferentiated helper T cell to differentiate into the differet kinds of T helper cells? What interleukins do the different kinds of T helper cells produce?
|
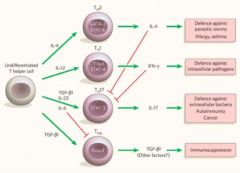
|
|
|
What are the pro-inflammatory cytokines in chronic inflammation?
|
TNF alpha
IL-1 |
|
|
What are some of the antiinflammatory cytokine inhibitors in chronic inflammation?
|
Soluble TNF receptor
IL-10 IL-1 receptor antagonist |
|
|
Where is TNF found? Where does it act?
|
TNF is found on the cell surface of a macrophage or activated T cell
When it gets cleaved off, it goes to different cell types |
|
|
What are the activites of TNF throughout the body?
|
Endothelium: adhesion molecules, angiogenesis via EGF
Macs: cytokine release Hepatocytes: increased CRP Synoviocytes: articular cartilage degeneration via increased MMPs Osteoclast progenitors: RANKL expression-->erosions |
|
|
What do you want to block in RA?
|
TNF-alpha
|
|
|
What are the hematologic manifestations of RA?
|
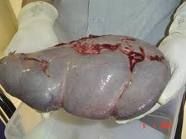
Anemia
Thrombocytosis Frelty's syndrome (uncommon) -Leukopenia -Splenomegaly (see picture!) -+/- infections, leg ulcers |
|
|
What is the composition of the RA nodules? Who is more likely to have them?
|
Pallisading granuloma
More common if someone's RF+ |
|
|
What are some of the "other" complications of RA?
|
Hematologic
Nodules Sjogren's syndrome Secondary amyoiditis Ocular PNS Pulmonary Serositis |
|
|
What are the symptoms of Sjogren's?
|
Dry eyes
Dry mouth |
|
|
What is the cause of Sjogren's syndrome?
|
Lymphocytic infiltrate in salivary, lacrimal glands
|
|
|
What's a serious complication of Sjogren'?
|
LYMPHOMA
|
|
|
If someone has secondary amyloidosis in RA, how do they present?
|
Proteinuria
|
|
|
What vascular problems can RA cause?
|
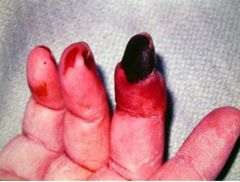
Rheumatoid vascuitis
|
|
|
What are some of the ocular manifestations of RA?
|
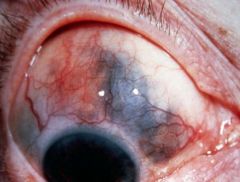
Keratoconjunctivits sicca (dry, inflamed eye)
Episcleritis SCLERITIS (DANGEROUS - SEE PICTURE) |
|
|
What are some of the PNS complications of RA?
|
Peripheral neuropathy
Nerve entrapments Mononeuritis multiplex due to arteritis |
|
|
What are some ofthe pulmonary complications of RA?
|
Interstitial infiltrates
BOOP (bronchiolitis obliterans - organizing pneumonia) |
|
|
What types of serositis can occur during RA?
|
Pleural effusion
Pericardial effusion: can result in tamponade or constriction if serious enough |
|
|
What are the properties of a pleural effusion within RA?
|
Low glucose
Low complement Variable WBC High protein Basically, low glucose in the context of no infection (odd.) |
|
|
What are some of the different classes of drugs used to treat RA?
|
NSAIDS
Corticosteroids DMARDS |
|
|
What is the general principle for medication administration in RA?
|
POlypharmacy - more drugs is better!
You've got to monitor carefully for side effects. |
|
|
When should you use NSAIDS in RA?
|
Short term: analgesic, anti-inflammatory, anti-pyretic effects for a number of reasons
Long term: treatment for chronic inflammatory RA |
|
|
What are different ways that you can use steroids in RA?
|
Flares: inject it in the joints
Low dose, long term: adjunct to the biologics (below 10 mg/day) Higher doses: vasculitis, etc. |
|
|
What should you never, ever do to someone who's been on steroids?
|
Don't let them abruptly stop!!!
|
|
|
What are some example of conventional DMARDS for RA?
|
Anti-malarials
Tetracyclines Sulfasalazine |
|
|
What are some of the cytotoxic/immunosuppressive agents used to treat arthritis/RA?
|
Methotrexate
Azathioprine Leflunomide Cyclosporin |
|
|
What is the mechanism of hydroxychloroquine?
|
Inhibits H transport in lysosomes
|
|
|
What are the side effects of hydroxychloroquine?
|
Ocular toxicity!
Rash GI Rare: hemolytic anemia, neuromopathy Most benign |
|
|
What is the dosing of hydroxychloroquine?
|
200-400 mg/day, 6.5 mg/kg ideal body weight
|
|
|
What are the indications for sulfasalazine?
|
RA
IBD |
|
|
What is the action of sulfasalazine?
|
Unknown.
|
|
|
What are the toxicities associated with sulfasalazine?
|
Indigestion
headache rash Hepatitis Neutropenia |
|
|
What's the dosing of sulfasalazine?
|
Initially 500 mg big
Increase to 1.0-1.5 gm bid |
|
|
What is the mechanism of methotrexate?
|
Folic acid antagonist
|
|
|
What's the dosing of methotrexate?
|
5-20 mg/WEEK given po, im, iv
|
|
|
What are some of the toxicities associated with methotrexate?
|
Nausa/vomiting
Oral ulcrs/stomatitis Bone marrow suppression , esp. in people with bad kidneys Pulmonary toxicity Hepatotoxicity Teratogenesis Infection |
|
|
What is the mechanism of leflunomide?
|
Pyrimidine synthesis inhibitor
|
|
|
What's the dosing of leflunomide?
|
10-20 mg qd
|
|
|
What are the toxicities of leflunomide?
|
Alopecia
Hepatitis Infection |
|
|
How do you get rid of leflunomide toxicity?
|
Washing out with a couple days of cholestryamine, which is a binder of the drug.
|
|
|
What are some of the different kinds of TNF inhibitors used to treat RA?
|
Etanercept
Infliximab Adalimumab Golimumab Certolizamab |
|
|
What kind of a TNF inhibitor comes from Speedy Gonzalez, a mouse?
|

Infliximab
He INFLIX lots of pain on the cat! |
|
|
What is the mechanism of Infliximab?
|
Binds to soluble, membrane-bound TNF with lots of affinity
|
|
|
What is the mechanism of etanercept?
|
Has the TNF receptor on connected to the Fc region of IgG1 --> consumes TNF inside the cell
|
|
|
What are some of the consequences of administering anti-cytokines ?
|
Infection
Malignancy |
|
|
What are some conditions that are containdications to giving TNF inhibitors? Why?
|
Histoplasmosis
TB Many others YOU NEED TO BE ABLE TO FORM GRANULOMAS TO GET RID OF THESE GUYS...IF YOU DON'T HAVE TNF, NO GRANULOMAS! |
|
|
What rheumatic disease can you cause, in a way, by giving TNF inhibitors?
|
SLE
|
|
|
What cell does Rituximab target? What molecule?
|
B cells
anti-CD20 |
|
|
What cells does Abatacept target? What molecule?
|
T cell costimulation through CD28
CTLA-4-Ig |
|
|
What is the target of Tocilizumab?
|
IL-6
|

