![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
26 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Alliteration |

Repetition of consonant sounds |
|
|
Anadiplosis |

Figureof repetition that occurs when the last word or terms in one sentence, clause,or phrase is/are repeated at or very near the beginning of the next sentence,clause, or phrase. |
|
|
Anaphora |

Figure of repetition that occurs when the firstword or set of words in one sentence, clause, or phrase is/are repeated at thebeginning of successive sentences, clauses, or phrases; repetition of theinitial word(s) over successive phrases or clauses. |
|
|
Epanalepsis |

repeats the beginning word of a clause orsentence at the end. The beginning and the end are the two positions ofstrongest emphasis in a sentence, so by having the same word in both places,you call special attention to it |
|
|
Epistrophe |

Figureof repetition that occurs when the last word or set of words in one sentence,clause, or phrase is repeated one or more times at the end of successivesentences, clauses, or phrases. |
|
|
Polysyndeton |

Figureof addition and emphasis which intentionally employs a series of conjunctions(and, or, but, for, nor, so, yet) not normally found in successive words,phrases, or clauses; the deliberate and excessive use of conjunctions insuccessive words or clauses. |
|
|
Asyndeton |

Figureof omission in which normally occurring conjunctions (and, or, but, for, nor,so, yet) are intentionally omitted in successive phrases, or clauses; a stringof words not separated by normally occurring conjunctions. |
|
|
Tri-colon |

a sentence with three clearly defined parts of equal length, usually independent clauses and of increasing power. Example: "A happy life is one spent in learning, earning, and yearning." |
|
|
Allusion |

A direct or indirect reference to something which is presumably commonly known, such as an event, book, myth, place, or work of art. Allusions can be historical, literary, religious, topical, or mythical. There are many more possibilities |
|
|
Foreshadowing |

A narrative device that hints at coming events; often builds suspense or anxiety in the reader. |
|
|
Imagery |
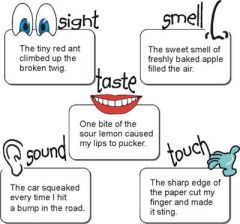
Description that appeals to the senses (sight, sound, smell, touch, taste) |
|
|
Personification |

A figure of speech in which an object or animal is given human feelings, thoughts, or attitudes |
|
|
Simile |

A comparison using "like" or "as" |
|
|
Verbal irony |

A figure of speech in which what is said is the opposite of what is meant |
|
|
Metaphor |

A comparison without using like or as |
|
|
Hyperbole |

A figure of speech that uses exaggeration to express strong emotion, make a point, or evoke humor |
|
|
Analogy |

A kind of extended metaphor or long simile inwhich an explicit comparison is made between two things (events, ideas, people,etc) for the purpose of furthering a line of reasoning or drawing an inference;a form of reasoning employing comparative or parallel cases. |
|
|
Antithesis |
Figure of balance in which two contrasting ideas are intentionally juxtaposed,usually through parallel structure; a contrasting of opposing ideas in adjacentphrases, clauses, or sentences. |
|
|
Chiasmus |

do not repeat the same words and phrases, but invert a sentence's grammaticalstructure or ideas. |
|
|
Ethos |

is the speaker well-informed of good will, goodsense, and good moral character; citations or quotes of respected authorities |
|
|
Pathos |

An emotional appeal; draws upon theaudiences’ feelings and sentimentality |
|
|
Logos |
A logical appeal; draws upon theaudiences’ sense of reason using facts, statistics, evidence |
|
|
Litotes |

understatement, for intensification, bydenying the contrary of the thing being affirmed. (Sometimes used synonymouslywith meiosis |
|
|
Parallelism |

Figureof balance identified by a similarity in the syntactical structure of a set ofwords in successive phrases, clauses, sentences; successive words, phrases,clauses with the same or very similar grammatical structure. parallelism of words:She tried to make herpastry fluffy, sweet, and delicate. parallelism of phrases:Singing a song orwriting a poem is joyous. parallelism of clauses:Perch areinexpensive; cod are cheap; trout are abundant; but salmon are best |
|
|
Rhetorical fragment |

sentence fragment used to deliberately for a persuasive purpose or to create a desired effect |
|
|
Rhetorical question |

asked just for effect or to lay emphasis on some point discussed when no real answer is expected |

