![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
78 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
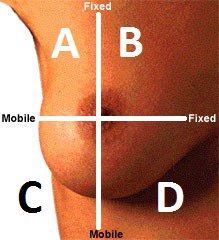
Name region A
|
Upper Outer Quadrant (UOQ)
|
|
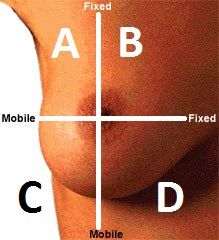
Name region B
|
Upper Inner Quadrant (UIQ)
|
|
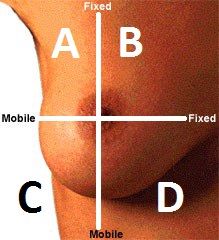
Name region C
|
Lower Outer Quadrant (LOQ)
|
|
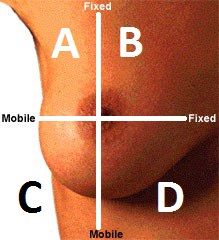
Name region D
|
Lower Inner Quadrant (LIQ)
|
|
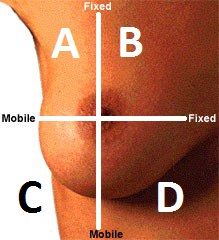
Which quadrant has the highest incidence of malignancy ?
|
Quadrant A. Upper Outer Quadrant (UOQ) : 15%
|
|
|
Name the two benign tumours of the breast
|
Fibroadenoma and Papilloma
|
|
|
Describe 3 Characteristics of Fibroadenoma
|
1. associated with younger women
2. single or multiple nodules within the breast 3. nodules become increasingly dense & sclerotic |
|
|
Describe 4 Characteristics of Papilloma
|
1. occur as single lesions in main duct of breast
2. distend duct and causes breast enlargement 3. may be a discharge of blood from nipple 4. may be accompanied by cystic formation |
|
|
Name the 3 main types of risk factors of breast carcinoma
|
1. personal risk factors
2. non-hormonal risk factors 3. hormonal risk factors |
|
|
State the 5 types of PERSONAL risk factors of breast carcinoma
|
1. age
2. genetics 3. family history 4. history of breast cancer 5. parity |
|
|
state the 4 NON-HORMONAL risk factors of breast carcinoma
|
1. Ionising radiation
2. Amount & Duration of alcohol assumption 3. Smoking 4. Diet |
|
|
which risk factor has the greatest risk for non-hereditary breast cancer ?
|
Age
|
|
|
Which age range has a greater risk of breast carcinoma ?
|
women aged 50 and above
|
|
|
what percentage of breast carcinoma is genetic ?
|
10%
|
|
|
if a patient has a sister who has breast carcinoma, what are the chances the patient will get breast carcinoma ?
|
2 times increased risk
|
|
|
if a patient has a mother who has breast carcinoma, what are the chances the patient will get breast carcinoma ?
|
2 times the increased risk
|
|
|
if a patient has a cousin who has breast carcinoma, what are the chances the patient will get breast carcinoma ?
|
increased risk
|
|
|
if a patient has a grandmother who has breast carcinoma, what are the chances the patient will get breast carcinoma ?
|
increased risk
|
|
|
if a patient has a history of breast carcinoma, what are the chances the patient will get breast carcinoma again ?
|
3-4 times increased risk of getting breast carcinoma on the affected side or the contralateral side
|
|
|
what does it mean if a patient is nulliparous ?
|
she has never given birth before/no children
|
|
|
Women who have had children has a _____________ risk than women who have no children
|
lower
|
|
|
the __________ the number of pregnancies, the lower the risk
|
greater
|
|
|
the greater the number of pregnancies, the ___________ the risk
|
lower
|
|
|
the ______________ the number of pregnancies, the higher the risk
|
lower
|
|
|
the lower the number of pregnancies, the _______________ the risk
|
greater
|
|
|
infertile women has a ______________ risk than fertile women
|
greater
|
|
|
increasing the amount and duration of alcohol assumption, increases _____________
|
serum oestradiol
|
|
|
________ fat diet, increase risk of breast carcinoma
|
high
|
|
|
______ calorie diet, increase risk of breast carcinoma
|
high
|
|
|
low vitamin diet, _________ risk of getting breast carcinoma
|
increase
|
|
|
which hormone is directly associated with risk of breast cancer
|
oestrogen
|
|
|
if a patient started her menstruation at an early age, she has a _______________ risk of getting breast cancer
|
greater
|
|
|
if a patient had her menopause at a later age, she has a _________________ risk of getting breast cancer
|
greater
|
|
|
why do obese women have greater risk of getting breast cancer ?
|
due to the conversion of androstenedione to oestrone in adipose tissues
|
|
|
2 locations where breast cancer manifests
|
1. breast ducts
2. breast lobules |
|
|
2 types of breast cancer
|
1. non-invasive
2. invasive |
|
|
another term for non-invasive
|
carcinoma in situ
|
|
|
another term for invasive
|
carcinoma
|
|
|
what does it mean when a cancer is non-invasive
|
1. confined to the site of origin
2. does not penetrate the membrane |
|
|
what does it mean when a cancer is invasive
|
1. infiltrating
2. spreading 3. penetrate the membrane |
|
|
a non-invasive cancer in the breast lobule is called
|
lobular carcinoma in situ (LCIS)
|
|
|
a non-invasive cancer in the breast ducts is called
|
ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS)
|
|
|
invasive cancer in the breast lobules is called
|
invasive lobular carcinoma (ILC)
|
|
|
invasive cancer in the breast ducts is called
|
invasive ductal carcinoma (IDC)
|
|
|
which is the most common type of non-invasive breast cancer
|
ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS)
|
|
|
which is the most common type of invasive breast cancer
|
invasive ductal carcinoma (IDC)
|
|
|
which type of cancer is called a stage 0 cancer
|
ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS)
|
|
|
which types of breast cancer appears in the milk glands
|
1. lobular carcinoma in situ (LCIS)
2. invasive lobular carcinoma (ILC) |
|
|
which type of breast cancer, occurs in the milk glands but is not cancerous
|
lobular carcinoma in situ (LCIS)
|
|
|
which type of breast cancers originates from the milk glands and spreads to other parts of the body
|
invasive lobular carcinoma (ILC)
|
|
|
how do cancer cells of the breast spread to other parts of the body
|
through the lymph channels to the lymph nodes under the arm
|
|
|
what is the most common breast lesion
|
mammary dysplasia
|
|
|
how is mammary dysplasia affected
|
cyclical changes of the ovary
|
|
|
how does the changes in the breasts seen
|
1. ducts within the breast become enlarged and form cysts
2. adenosis - increase in amount of connective tissue which leads to distortion of the normal breast pattern |
|
|
an increase amount of connective tissue which leads to distortion of normal breast pattern is called
|
adenosis
|
|
|
adenosis of the breast can cause
|
1. retracted nipple
2. skin dimpling |
|
|
what are the indications for a mammogram
|
1. assessment of palpable lumps
2. high risk group e.g family history of breast cancer 3. as a screening procedure |
|
|
what is the most common female cancer in Singapore
|
breast cancer
|
|
|
which cancer is the leading cause of cancer deaths in Singapore women
|
breast cancer
|
|
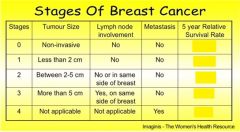
what is the survival rate for Stage 0 patients if the cancer does not relapse within 5 years after treating the cancer ?
|
100%
|
|
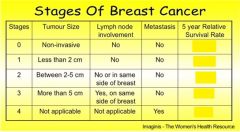
what is the survival rate for Stage 1 patients if the cancer does not relapse within 5 years after treating the cancer ?
|
100%
|
|
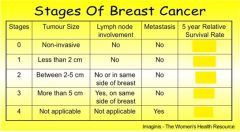
what is the survival rate for Stage 2 patients if the cancer does not relapse within 5 years after treating the cancer ?
|
86%
|
|
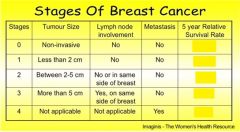
what is the survival rate for Stage 3 patients if the cancer does not relapse within 5 years after treating the cancer ?
|
57%
|
|
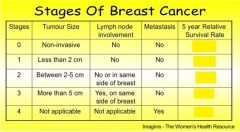
what is the survival rate for Stage 4 patients if the cancer does not relapse within 5 years after treating the cancer ?
|
20%
|
|
|
how many stages of breast cancer are there ?
|
5 stages : Stage 0, 1, 2, 3, 4
|
|
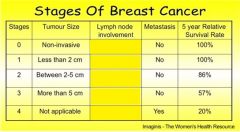
which stage(s) do not involve the lymph nodes
|
Stage 0 and Stage 1 and Stage 2
|
|
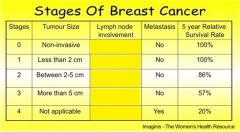
which stage(s) involves the lymph nodes
|
Stage 2 and Stage 3
|
|
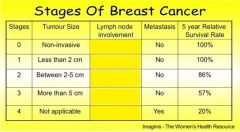
which stage(s) can have lymph node involvement and also have no lymph node involvement
|
Stage 2
|
|
|
which stage(s) have lymph node involvement on the same side of the breast
|
Stage 2 and Stage 3
|
|
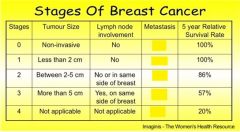
which stage(s) have no metastasis
|
Stage 0, 1, 2, 3
|
|
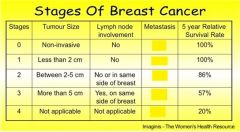
which stage(s) have metastasis
|
Stage 4
|
|
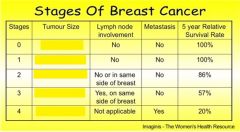
which stage(s) is a non-invasive tumour
|
Stage 0
|
|
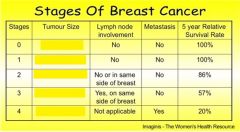
Stage 1 has a tumour size of
|
less than 2 cm
|
|
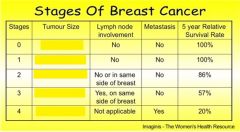
Stage 2 has a tumour size of
|
between 2-5 cm
|
|
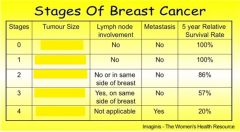
Stage 3 has a tumour size of
|
more than 5 cm
|
|
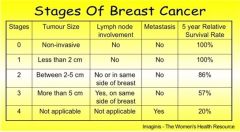
why is the tumour size and lymph node involvement not applicable in Stage 4
|
at this stage, the cancer cells have already metastasize to other parts of the body
|
|
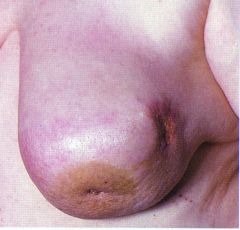
the breast look oedematous and looks like an orange. what is this condition called
|
peau d'orange
|
|
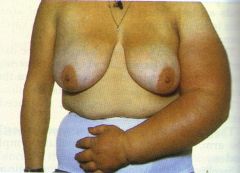
state the condition of the patient
|
Secondary lymphoedema of the left arm caused by metastases in the lymph glands
|

