![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
78 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Clinical manifestations of asthma
|
Elevated IgE levels
Allergic rhinitis Eczema Positive family history of allergy Attacks associated with seasonal, environmental or occupational exposure |
|
|
What are the results of Asthma?
|
Increased microvascular permeability
Mucosal edema Inflammatory exudates Bronchoconstriction Leakage |
|
|
What causes inflammation of the airways?
|
Acute bronchospasm (bronchoconstriction)
Mucosal edema Mucous plug formation Airway wall remodeling |
|
|
What are the chances of people with asthma developing permanent structural changes?
|
1 in every 10
|
|
|
Symptoms of severe Asthma attacks are:
|
Use of accessory muscles of respiration
Intercostal retractions Distant breath sounds with inspiratory wheezing Orthopnea Agitation Tachypnea Tachycardia |
|
|
What Are the Treatments of asthma?
|
O2 therapy
Small-volume nebulizers B2 agonists Corticosteroids Leukotriene modifiers Mast cell inhibitors |
|
|
What are the sign and symptoms of Pneumonia?
|
Crackles (rales) and bronchial breath sounds over affected lung tissue
Chills Fever Cough, purulent sputum Viral Fever, cough, hoarseness, coryza accompanied by wheezing/rales |
|
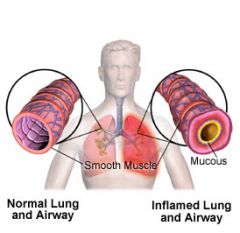
What is Acute Bronchits?
|
Single occurrence or exacerbation of chronic preceded by URI
|
|
|
What are the effects of bronchitis?
|
Increased bronchial wall thickness
Resistance increases work of breathing Increased O2 demands Produce ventilation-perfusion mismatch with hypoxemia and hypercarbia Increases pulmonary artery resistance Pulmonary hypertension Inflammation in bronchial walls with vasoconstriction of pulmonary blood vessels and pulmonary arteries Affects airways not alveoli Blue Bloaters |
|
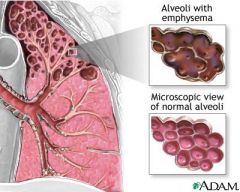
What is Emphysema?
|
Hyperinflation of alveoli and the destruction of alveolar walls as a result of inflammation
|
|
|
What is the treatment for COPD?
|
Bronchodilators – parental, oral, and inhalation - a/w resistance
Antibiotics - Rx infection Flu vaccines, pneumococcal vaccine O2 Rx low flow |
|
|
What is ARDS?
|
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome
|
|
|
What are the diagnostics criteria for ARDS
|
Patient has an identifiable predisposing condition
The chest x-ray reveals diffuse, bilateral infiltrates – advances to white out as ARDS progresses The patient doesn’t have CHF The patient’s pO2/FiO2 ratio will be less than 200 (>300 is normal |
|
|
what are the stages of Edema Formation In ARDS
|
A, Normal alveolus and pulmonary capillary
B, Interstitial edema occurs with increased flow of fluid into the interstitial space C, Alveolar edema occurs when the fluid crosses the blood-gas barrier |
|
|
What are the medical Managemet for ARDS?
|
Support respiration and ventilation
Mechanical ventilation with PEEP Maintain hemodynamic stability Monitor fluids and degree of pulmonary edema Treat underlying condition Monitor for complications |
|
|
What are the treatment of ARDS?
|
Proning
Kinetic Therapy Continuous Lateral Rotation Therapy |
|
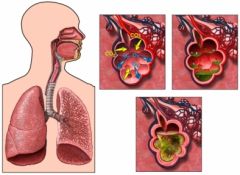
What is pnuemonia?
|
Acute inflammation of lung caused by microorganism
|
|
|
The different types of pneumonia are:
|
Community-acquired pneumonia
Hospital-acquired pneumonia |
|
|
What causes Oppotunistic Pneumonia?
|
Pneumocystis carinii
CMV Fungi Patients with severe protein-calorie malnutrition, immune deficiencies, chemotherapy/radiation recipients, and transplant recipients are at risk |
|
|
What are the signs and symptoms of Pneumonia?
|
Crackles (rales) and bronchial breath sounds over affected lung tissue
Chills Fever Cough, purulent sputum Viral Fever, cough, hoarseness, coryza accompanied by wheezing/rales |
|
|
What are the treatments of pneeumonia?
|
Antibiotic/antiviral therapy
Oxygen for hypoxemia Analgesics for chest pain Antipyretics Influenza vaccine Pneumococcal vaccine Fluid intake at least 3 L per day Caloric intake at least 1500 per day |
|
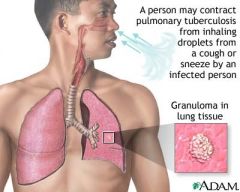
What cause Tuberculosis?
|
Transmitted by airborne droplets
Neutrophils and alveolar macrophages migrate to the lung site These cells engulf the bacteria and seal off the bacilli colonies Infected tissues with tubercle die and form caseation necrosis |
|
|
Those who are at risk for TB are
|
Residents and employees of long-term care facilities and shelters
Prison inmates Homeless Alcoholics IV drug users Family members of infected persons People born in a country where TB is common HIV or other disease that suppresses the immune system Medications that suppress the immune system |
|
|
what are the signs and symptoms of TB?
|
Early: coughing, night sweats, coughing (dry at first), fever, chills, fatigue, weakness, dyspnea on exertion
Brown tinged sputum (hemoptysis, later), anorexia, wt. loss, pleuritic chest pain (sharp) esp. with coughing |
|
|
What are the medication for TB?
|
Rifampin (RIF)= cause urine, tears, and sweat to be orange
Use of ETOH or INH increases risk of hepatotoxicity Isoniazid (INH) = cause peripheral neuropathy vitamin B6 given to prevent Other meds: pyrazinamide (PZA), ethambutol (EMB), streptomycin |
|
|
Restrictive Pulmonary diseases are:
|
The result of decreased expansion of the lungs due to alterations in the lung parenchyma, pluera, chest wall, or neuromuscular function.
|
|
|
Restrictive Pulmonary diseased can be classified as:
|
Pulmonary or Extrapulmonary and represent acute or chronic patterns of lung dysfunction.
|
|
|
Characteristics of the diseases:
|
Decrease in total lung capacity, vital capacity, functional residual capacity, and residual volume.
|
|
|
Interstitial Lung Diseases:
|
A group of disorders that are characterized by acute, subacute, or chronic infiltration of alveolar walls by cells, fluid, and connective tissue.
|
|
|
Diffuse Interstitial Lung Disease or
also known as Diffuse interstitial pulmonary fibrosis |
Restrictive lung disease characterized by thickening of the alveolar interstitium.
|
|
|
Pathogenesis of diffuse interstitial lung disease:
|
Not well understood but possibly related to an immune reaction that usually begins with injury to alveolar epithelial/capillary endothelial cells.
|
|
|
Pathophysiologic changes for diffuse interstitial lung disease:
|
Interstitial and alveolar wall thickening and increased collagen bundles in interstitium.
|
|
|
Immune response in diffuse interstitial lung disease is characterized by:
|
inflammation, fibrosis, and destruction
|
|
|
Clinical Manifestations of diffuse interstitial lung disease:
|
Most common- progressive dyspnea with nonproductive cough.
Others- rapid shallow breathing, clubbing of nail beds, bibasilar end-expiratory crackles, marked dyspnea with exercise |
|
|
Treatment for diffuse interstitial lung disease:
|
Avoid tobacco smoke, administrations of anti-inflammatory and immunosuppresive agents
|
|
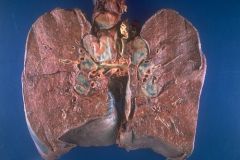
Sarcoidosis
|
Acute or chronic systemic disease of unknown cause although immunologic basis appears likely.
|
|
|
Acute and chronic process of Sarcoidosis
|
Acute occurs more likely in women in the second or third decade of life.
Chronic is seen more in third/fourth decades of life w/highest incidence in North America. |
|
|
Pathogenesis of Sarcoidosis
|
Development of multiple, uniform, noncaseating epitheloid granulomas that affect multiple organ systems, most commonly lymph nodes and lung tissue.
|
|
|
Clinical Manifestations of Sarcoidosis
|
Malaise, fatigue, weight loss, fever, dyspnea, dry nonproductive cough.
Also, erythema nodosum, macules, papules, hyperpigmentation, subcutaneous nodules, hepatosplenomegaly, and lymphadenopathy |
|
|
Diagnosis of Sarcoidosis
|
Leukopenia, anemia, increase eosinophil count, elevated sedimentation rate, and increased calcium levels
Also, 70% patients exhibit anergy (decreased sensitivity to specific antigens) |
|
|
Treatment for Sarcoidosis
|
Administration of corticosteroids and management of symptoms.
For patients with progressive disease that doesn’t respond to corticosteroids the use of immunosuppresive agents maybe used. |
|
|
Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis
( Extrinsic allergic alveolitis ) |
Both a restrictive and occupational disease.
Predominance in nonsmokers (80-90%) |
|
|
Pathogenesis of Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis
|
The causative agent combines with serum antibody in the alveolar walls, leading to type III hypersensitivity reaction.
Genetic predisposition may be involved in exaggerated response to offending agent. |
|
|
Clinical Manifestations of Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis Acute:
|
Acute- symptoms begins within 4-6 houts after exposure and resolve in 18-24 hours.
Symptoms: chills,sweating,shivering, myalgias, nausea, lethargy, headache, and malaise. May or may not have a fever. |
|
|
Clinical Manifestations of Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis Chronic:
|
Progressive diffuse pulmonary fibrosis develops in upper lobes.
Acute febrile episodes and progressive pulmonary fibrosis with cough, dyspnea, fatigue, and pulmonale. |
|
|
Diagnosis of Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis
|
Chest radiographs, skin testing, and laboratory findings could see an increased white blood cell count and decreased Pao2.
|
|
|
Treatment of Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis:
|
Identify offending agent and prevent further exposure. May require change in environment or occupation.
|
|
|
Occupational Lung Diseases
|
Result from inhalation of toxic gases or foreign particles.
|
|
|
Pneumoconiosis
|
Parenchymal lung disease caused by inhalation of inorganic dust particles.
|
|
|
Atmospheric pollutants:
|
Sulfur oxides, nitrogen oxides, and tobacco smoke
|
|
|
Clinical Manifestations of Occupational Lung disease
|
Pneumoconioses generally produce no symptoms in early stages but as it progesses: productive cough and dyspnea.
|
|
|
Treatment of Occupational Lung disease:
|
Preventative measures are key to limiting onset and severity.
Prevent further parenchymal damage and relieve signs/symptoms |
|
|
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome
(ARDS) |
Damage to alveolar-capillary membrane.
|
|
|
Mortality rate of ARDS
|
30-63%
|
|
|
Major disorders associated with ARDS
|
Shock, Trauma, Embolism, Head Injury, Aspiration, Drug Overdose, Inhaled toxins, Radiation, Hematologic disorders, metabolic disorders, Burns, Cancer, anaphylaxis, eclampsia, radiation pneumonitis, high-altitude exposure
|
|
|
Four characteristics of ARDS:
|
Injury to alveoli from wide variety of disorders
Changes in alveolar diameter Injury to pulmonary circulation Disruption in 02 transport/utilization |
|
|
Common findings of ARDS:
|
Sever hypoxemia
Decrease in lung compliance Decrease in FRC Diffuse, fluffly alveolar infiltrates on chest radiograph non-cardiogenic pulmonary edema |
|
|
ARDS leads to three major pathophysiologic processes:
|
Noncardiogenic pulmonary edema, with “leaky” pulmonary capillaries
Atelectasis w/ lack of surfactant Fibrosis associated with inflammatory deposition of proteins. |
|
|
ARDS Symptoms
|
Respiratory rate increased and symptoms of tissue hypoxia may be present.
Crackles, wheezing, dyspnea, pulmonary edema. |
|
|
ARDS Treatment
|
Therapy to enhance tissue oxygenation until inflammatory process resolves. Mechanical ventilation with PEEP and supplemental oxygen is mainstay treatment.
|
|
|
What is flail chest?
|
Flail chest results from multiple rib fractures as a result of trauma to the chest wall.
|
|
|
What is severe acute respiratory syndrome?
|
Caused by a coronavirus. Caused by person to person contact, mostly through droplets. Can spread through contaminated surfaces.
|
|
|
Clinical Manifestations of SARS
|
Fever, myalgias, headache, nonproductive cough, and dyspnea
|
|
|
What is Pulmonary Tuberculosis?
|
Caused by mycobacterium tuberculosis, an acid fast aerobic bacillus. Most common sites are the lung and the lymph nodes.
|
|
|
What is pulmonary tuberculosis subdivided into?
|
Primary and reactivating
|
|
|
What is the difference between primary and reactivating tuberculosis?
|
Primary is the initial infection while the reactivating occurs many years after initial infection
|
|
|
What are the clinical manifestations of tuberculosis?
|
History of contact with an infected person, low grade fever, cough, night sweats, fatigue, weight loss, malaise and anorexia. Chronic cough is the most common symptom.
|
|
|
How do you get a diagnosis of tuberculosis?
|
Sputum culture and characteristic nodules on chest radiographs
|
|
|
What is a restrictive lung disease?
|
Restrictive pulmonary disorders are those that restrict lung expansion.
|
|
|
Charcterized by the accumulation of air pleural space
|
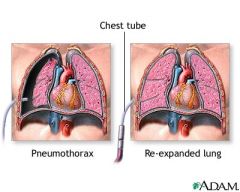
Pneumothorax
|
|
|
Pleural Effusion
|
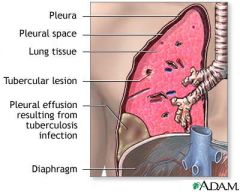
A pathologic collection of fluid or pus in the pleural cavity as a result of another disease process.
|
|
|
A viral dsisease in which the poliiovirus attacks the motor nerve cells of the spinal chord and brianstem
|
Poliomyelitis
|
|
|
A degenarative disease of the nervous system that involces both upper and lower motor neurons
|
Amytrophic Lateral Sclerosis
|
|
|
Muscular Dystrophies
|
A hereditary disease( X-linked recessive), passed from mother to sons.
|
|
|
A disorder that is pressumed to have a immunologic basis
|
Guillain-Barre Syndrome
|
|
|
A bony deformity of the chest wall occurs as a result of of kyphosis.
|
Kyphoscoliosis
|
|
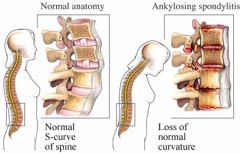
Ankylosing Spondylitis
|
A progressive inflammotory disease leading to immobilty of the vertebral joints and fixation if the ribs.
|
|
|
Flail Chest
|
Chest wall instability due to fracture at two distant sites on the same rib.
|

