![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
43 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Alveolar Air Equation |
( Fio2 x 7 ) - ( PaCO2 + 10) = PAO2 |
Fio2 : 40%= 280 50%= 350 55%=385 60%=420 |
|
|
Chest x ray reveals : *Lowered flattened diagram *Increased radioluncency in lung fields *presence of bullets and blebs *decrease in peripheral vascular markings * a narrow mediastinum |
Severe Emphysema |
Obstructive Disorder CBABE |
|
|
Rate is 12 mins and Expiratory Time is 3.25 sec . What is inspiratory time ? |
I = (60\F)- E = (60\ 12)-3.25= 1.75 |
|
|
|
Pressure Volume Detects |
Detects Compliance ( slope of curve) Resistance ( width of curve ) Suspect Over inflation ( beaking appearance ) |
|
|
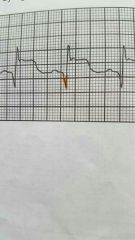
What is this ECG tracing |
Myocardial infraction |
|
|
|
Define Hypo ventilating |
CO2 retainers , Respiratory Acidosis Increase MV, VT, RR Increase Rate = decrease E-time Increase Peak Inspiratory Flow (Increase Flow = decrease I time and Increase E time ) Remove tubing to decrease mechanical dead space PaCO2 increased needing to be lower patient is not ventilating >45 increase the following : Volume Control :VT Pressure Control : PIP HF Jet : driving Pressure HF Oscillator : Amplitude BIPAP : IPAP |
|
|
|
Define Hyperventilating ( blowing off to much) |
Respiratory Alkalosis PaCO2 low needing to be raised patient is ventilating <35Lower the following : Decrease MV, Vt,PIP, RR Decrease Peak Inspiratory Flow Add tubing to increase mechanical dead space |
|
|
|
Difference between FVC and FEV1 |
FVC measures volumes and used to assess the patients ability to cough and deep breath FEV1 measures flow and used to assess to inhaled bronchodilator |
|
|
|
Auto Peep defined as positive airways pressure at the end of exhalation caused by an expiratory time that is too short. How can you fix it ? |
Decrease Inspiratory Time Increase Flow Increase expiratory time Decrease Vt, RR, MV |
|
|
|
Volume, Pressure and Flow are accuracy verified by |
Volume = Spirometry 3l syringe Pressure =Water/ Mercury manometer Flow = Rotameter (Respirometer) |
|
|
|
Pharmacology : Prophylactic Asthma Management in 2 years of age only approved ? |
Montelukast (Singular ) Cromolyn Sodium (Intel ) Mast Cell Stabilizer |
|
|
|
Pharmacology: What are the top three reversing agents for Benzodiazepine ? Opioid ? Nondepolarizing neuromuscular agents ? |
Benzodiazepine : Flumazenil (Romazicon) Opioid or Analgesics : Naloxone (Nardin ) Neuromuscular blocking agents reversal anticholinesterase inhibitors: Neostigmine ( Prostigmin) Pyridostigmine ( Mestinon) Edrophonium (Tensilon) |
|
|
|
Metabolic Alkalosis Low K+ Interverted T wave ischemia. ..patient on diuretics use a K+ sparing agent ?
|
Amiloride " Midamor" or Ronolactone |
|
|
|
Metabolic Acidosis High K+ what do you do to lower it ? |
High doses aerosolized albuterol or K+ wasting Lasix |
|
|
|
Inspiratory Hold and Expiratory Hold measure what ? |
Plateau pressure is measured by Inspiratory Hold Auto Peep is measured by Expiratory Hold |
|
|
|
Side effects of Inhaled Nitric Oxide and how to detect it ? |
Methemoglobinemia and Hemioximetry |
|
|
|
When should an RRT replace a Tracheostomy Tube ? |
Suction catheter unable to pass and Patients Oxygen desaturated |
|
|
|
Major Component of Surfactant is |
Phospholipids |
|
|
|
Mean Airway Pressure will change when ? |
Inspiratory Time allows increase in VT , RR and PIP ... PEEP is most influence of Mean Airway Pressure that primarily effects oxygenation . |
|
|
|
Ethylene Oxide is used on equipment like ? |
Bird Mark VII Flow Meter Non-disposable resuscitation bags |
|
|
|
Best method Effectiveness of Equipment Sterilization ? |
Biological Indicator |
|
|
|
Alkaline Glutaraldehyde "Cidex" is used on what equipment? |
Reusable plastic Mouthpieces Tubing Nebulizer Humidifiers Fiber optic Bronchoscope |
|
|
|
Patient breathing at a rate of 25 with a minute volume of 10 L/min. What is the patients tidal volume? |
Vt=10÷25=0.4 L or 400L |
|
|
|
Patient chest- xray shows Hyperlucent between visceral and plural spaces. Indicates? |
Pneumothorax |
|
|
|
PEP therapy improves expectoration for |
Cystic Fibrosis and Pneumonia Patients |
|
|
|
To transport a patient with a Flow Meter that is NOT effected by gravity, an RRT would use ? |
Bourbon Gauge Flow Meter |
|
|
|
PEFR measures the |
Obstructive Airway |
|
|
|
The best way to check the accuracy of a water seal spirometry is to use a |
Wright Respirometer |
|
|
|
A physiological goal of CPAP in a atelectasis is to increase |
Functional residual capacity |
|
|
|
Chest Tubes Suction Control Bottle What is Normal, Leak and excessive bubbling and what to do ? |
*Normal bubbling is gentle bubbling *Leak or Obstruction is No Bubbling/ not enough water ... increase suction pressure and check water level *Excessive Bubbling and decrease suction pressure at wall source |
|
|
|
Air to Oxygen Entrainment ratios : Fio2 of 28% , 32% 36 % 40% ? Magic Box for Air to Oxygen ratio ( if forget ) |

|
|
|
|
P/F ratio less than 200 indicates shunting and the need for ... |
PEEP and CPAP |
|
|
|
A patient with chest xray shows left lower lobe pneumonia is ordered for CPT with postural drainage . What would best be patient position? |
Trendelenburg Prone |
|
|
|
High Frequency Oscillation Ventilation... What are the indications and how do you control PaCO2 and PaO2 and what is the range frequency ? |
Indications : PIP greater than 50cm Air Leak Syndrome: 1. Bronchopleural Fistula 2. Pulmonary Interstitial Emphysema 3. Pneumothorax Primary PaCO2 Amplitude then Frequency in hertz PaO2 Mean Airway Pressure 3-45 cmH20 3-15 Hertz range but 180 to 900in |
|
|
|
Confirm metabolic involvement by assessing the Base Excess (BE), with values of ...? |
Values Greater than +2 indicating metabolic Alkalosis and Values Less than -2 indicating metabolic Acidosis |
|
|
|
The Severity of Hypothermia are ...? |
Mild : PaO2 60 -70 torr Moderate : PaO2 40-59 torr Severe : PaO2 < 40 torr |
|
|
|
Bland Aerosol Therapy is indicated to treat upper Airway edema , laryngotracheobronchitis and subglottic and postextubation edema . What else can it be used for ? |
*Help overcome a humidity deficit in patients *Patients at risk for retained secretions *Used for sputum induction procedures |
|
|
|
The depolarizing agent such as Succinylcholine (Anectine) have a short duration of action. Used for ? |
Short term paralysis during intubation |
|
|
|
The nondepolarizing agents produce prolonged paralysis and are used for controlled mechanical ventilation that are? |
Pancuronium Pavulon Vecuronium Norcuron Cisatracurium (Nimbex)
|
|
|
|
Patient demonstrate gastric distress , suctioning of gastric content from the trachea and loss of tidal volume. Symptoms indicate ? |
Tracheoesophageal |
|
|
|
Increase PEEP may cause decreased venous return , which will decrease both ? |
Cardiac Output and Urinary Output |
|
|
|
If a patient on 10 cm PEEP and 75 % O2 has a PaO2 of 175 torr , the concern and solution is ? |
The high FIO2 is most concern ( O2 toxcity) FIO2 should be lowered |
|
|
|
If a patient is on 18 cm PEEP and 45% oxygen has a PaO2 of 150 torr , the concern would and solution ? |
The high PEEP level is of the most concern ( barotrauma ) and should be lowered. |
|

