![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
139 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What are the organs of the respiratory system? |
Nose, Pharynx, Larynx, Trachea, Bronchi, Lungs (alveoli) |
|
|
|
What is the function of the Respiratory System? |
Gas exchanges between blood and external environment |
|
|
|
What makes up the upper respiratory tract? |
Nose to Larynx |
|
|
|
What makes up the lower respiratory tract? |
Trachea to alveoli |
|
|
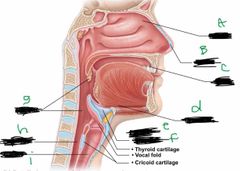
What is label A? |
Conchae |
|
|
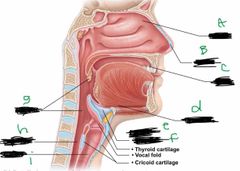
What is label B? |
Nostril |
|
|
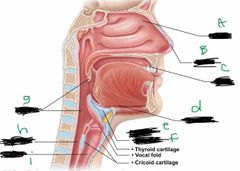
What is label C? |
Mouth |
|
|
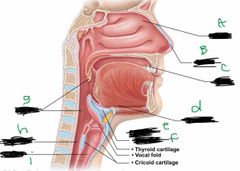
What is label d? |
Hyoid bone |
|
|
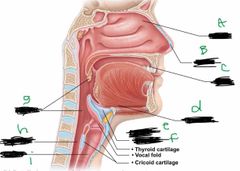
What is label E? |
Larynx |
|
|
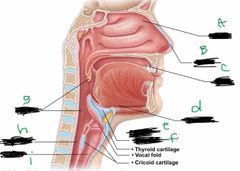
What is label F? |
Epiglottis |
|
|
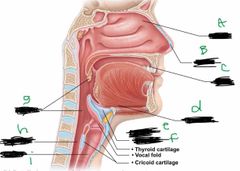
What is label G? |
Pharynx |
|
|
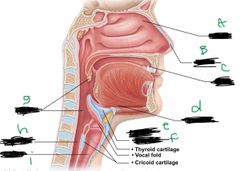
What is label H? |
Esophagus |
|
|
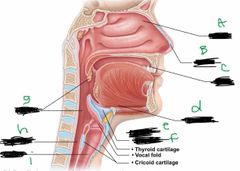
What is label I? |
Trachea |
|
|
|
Where are the olfactory receptors located? |
In the mucosa of the nose |
|
|
|
What does the respiratory mucosa do? |
Moistens air, Traps foreign particles, Enzymes in the mucous destroy bacteria chemically |
|
|
|
What are Conchae? |
projections from lateral wall of nose |
|
|
|
What do Conchae do? |
Increase surface air to help catch foreign particles coming in the nose |
|
|
|
What is the function of the paranasal sinuses? |
Lightens the skull, Acts as resonance chambers for speech, Produces mucus |
|
|
|
The pharynx is also known as...? |
Throat |
|
|
|
What is the Pharynx? |
A muscular passageway from the nasal cavity to the larynx |
|
|
|
What are the three regions of the pharynx? |
Nasopharynx, Oropharynx, Laryngopharynx |
|
|
|
What serves as the common passageway for air and food? |
Oropharynx and laryngopharynx |
|
|
|
What is the function of the epiglottis? |
Routes food into the esophagus and air to the trachea, Protects the opening of the larynx |
|
|
|
What is the larynx commonly called? |
Voice box |
|
|
|
What does the Larynx do? |
Routes air and food into proper channels, Helps with speech |
|
|
|
What is the larynx made of? |
Eight rigid hyaline cartilages |
Adam’s apple |
|
|
What is the epiglottis? |
A flap of elastic cartilage |
|
|
|
How does the epiglottis open and close? |
During swallowing the epiglottis rises and forms a lid over the opening of the larynx |
|
|
|
What is the trachea also known as? |
Windpipe |
|
|
|
What is special about the walls of the trachea? |
The C shaped rings of hyaline cartilage that keeps the trachea open |
|
|
|
What is the trachea lined with? |
Ciliated mucosa |
|
|
|
What do the cilia in the trachea do? |
They beat in the opposite direction of incoming air to expel mucus loaded with dust and debris |
|
|
|
Where does each bronchus enter the lung? |
At the hilum |
|
|
|
What’s the difference between the right and left bronchi? |
The right bronchus is wider, shorter, and straighter than the left bronchus |
|
|
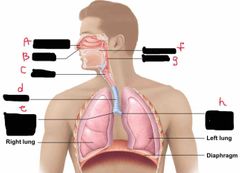
What is label A? |
Nasal cavity |
|
|
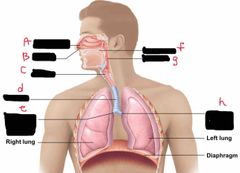
What is label B? |
Nostril |
|
|
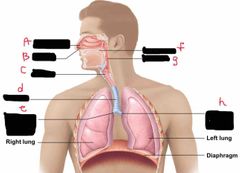
What is label C? |
Larynx |
|
|
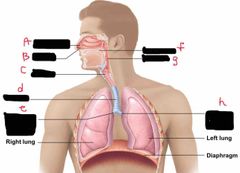
What is label d? |
Trachea |
|
|
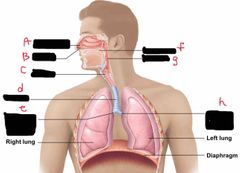
What is label e? |
Right main bronchus |
|
|
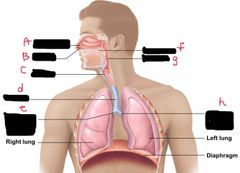
What is label F? |
Oral Cavity |
|
|
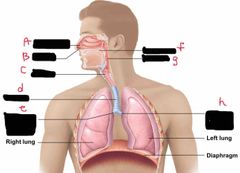
What is label g? |
Pharynx |
|
|
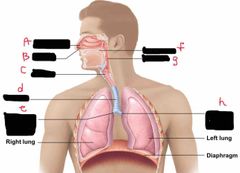
What is label h? |
Left main bronchus |
|
|
|
Where is the apex of the lung? |
By the clavicle |
|
|
|
Where is the base of the lungs? |
On the diaphragm |
|
|
|
What is each lung divided into? |
Lobes |
|
|
|
How many lobes does the left lung have? |
Two lobes |
|
|
|
How many lobes does the right lung have? |
Three lobes |
|
|
|
What covers the outer surface of the lungs? |
Pulmonary pluera |
|
|
|
What lines the walls of the thoracic cavity? |
Parietal pleura |
|
|
|
What does the respiratory zone include? |
Respiratory bronchioles, Alveolar ducts, Alveolar sacs |
|
|
|
Where does gas exchange occur? |
In the alveoli |
|
|
|
The alveoli is how many cells thick? |
One |
|
|
|
What covers the surface of the alveoli? |
Pulmonary capillaries |
|
|
|
The respiratory membrane is what kind of barrier? |
Air- blood barrier |
|
|
|
How does gas cross the respiratory membrane? |
Diffusion |
|
|
|
What is surfactant? |
A lipid molecule |
|
|
|
What does surfactant do? |
Coats gas exposed alveolar surfaces to prevent them from sticking together |
|
|
|
What do alveolar macrophages do? |
Eat bacteria, carbon particles, and other debris |
|
|
|
What is the function of the respiratory system? |
To supply the blood with oxygen and dispose of carbon dioxide |
|
|
|
What is ventilation? |
The movement of air into and out of the lungs |
|
|
|
What is inspiratory reserve volume (IRV)? |
Amount of air taken in forcibly over the tidal volume |
|
|
|
On average, how many milliliters of air is moved in and out of the lungs during IRV? |
3100ml |
|
|
|
What is expiratory reserve volume? |
The amount of air forcible exhaled after a tidal expiration |
|
|
|
On average, how many milliliters of air is moved in and out of the lungs during ERV? |
1200ml |
|
|
|
What is residual volume? |
The air remaining in the lungs after respiration |
|
|
|
What are the two parts of ventilation? |
Inspiration and expiration |
|
|
|
What is respiration? |
Gas exchange between blood and tissue |
|
|
|
What does the respiratory gas transport do? |
It transports oxygen and carbon dioxide through the bloodstream |
|
|
|
On average, how many milliliters of air is moved in and out of the lungs during TV? |
500ml |
|
|
|
What happens to the body in response to inspiration (inhalation)? |
Intrapulmonary volume increases, Gas pressure decreases, Air flows into the lungs |
|
|
|
What does the body do to perform expiration (exhalation)? |
It contracts the internal intercostal muscles to depress the rib cage |
|
|
|
What happens to the body in response to expiration (exhalation)? |
Intrapulmonary volume decreases, Gas pressure increases, Gases flow out to equalize the pressure |
|
|
|
What is tidal volume (TV)? |
Normal quiet breathing |
|
|
|
How many milliliters of air is moved in and out of the lungs during TV? |
500ml |
|
|
|
On average, how many milliliters of air is remaining in the lungs after respiration? |
1200ml |
|
|
|
What is vital capacity? |
The total amount of exchangeable air |
|
|
|
How do you calculate the vital capacity? |
TV+IRV+ERV |
|
|
|
What’s the average vital capacity for men? |
4800ml |
|
|
|
What’s the average vital capacity for women? |
3100ml |
|
|
|
What is dead space volume? |
Volume of air that remains in the conducting zone and never reaches the alveoli |
|
|
|
What’s the average dead space volume? |
150ml |
|
|
|
What are respiratory capacities measured with? |
Spirometer |
|
|
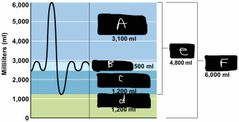
What is label A? |
IRV |
|
|
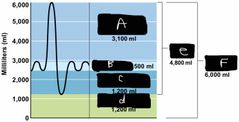
What is label B? |
TV |
|
|
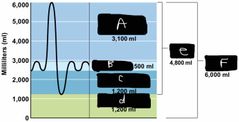
What is label C? |
ERV |
|
|
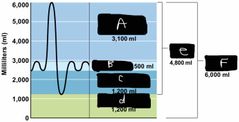
What is label d? |
Residual volume |
|
|
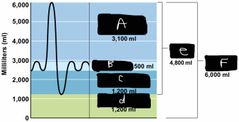
What is label e? |
Vital capacity |
|
|
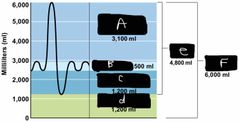
What is label F? |
The total lung capacity |
|
|
|
What does oxygen bind to in the blood? |
Hemoglobin |
|
|
|
What does hemoglobin with an attached oxygen form? |
oxyhemoglobin (HbO2) |
|
|
|
How is carbon dioxide transported in the blood? |
In the form of a bicarbonate ion (HCO3-) |
|
|
|
What change does carbon dioxide go through to diffuse out of the blood into the alveoli? |
The bicarbonate ion must bind with H+ forming carbonic acid. The carbonic acid then splits into carbon dioxide and water. The carbon dioxide can now diffuse into alveoli. |
|
|
|
Where are the neural centers that control rate and depth of respiration? |
Medulla and pons |
|
|
|
What does the medulla do to control respiration? |
It sets a basic rhythm of breathing and contains a pacemaker |
|
|
|
What does the pons do? |
Smooths out respiratory rate |
|
|
|
What is the normal respiratory rate? |
12 to 15 per minute |
|
|
|
What is COPD? |
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease |
|
|
|
What are some symptoms of COPD? |
Labored breathing, coughing, infections, and hypoxia eventually respiratory failure |
|
|
|
What are the characteristics of chronic bronchitis? |
Mucosa of lower respiratory tract gets severely inflamed which impairs gas exchange and causes patients to become cyanotic |
|
|
|
What are the characteristics of emphysema? |
Destroyed alveoli or enlarged alveoli, chronic inflammation, fibrosis, loss of elasticity, barrel chest, cyanosis |
|
|
|
What is lung cancer most commonly caused by? |
Smoking |
|
|
|
After birth, how long does it take for the lungs to fully inflate? |
Two weeks |
|
|
|
The change from nonfunctional to functional lungs after birth depends on.......? |
Surfactant |
|
|
|
Does respiratory rate change throughout life? |
Yes |
|
|
|
What is asthma? |
Chronically inflamed hypersensitive bronchioles |
|
|
|
How does aging effect the respiratory system? |
Elasticity decreases, vital capacity decreases, blood O2, |
|
|
|
What is hypernea? |
Increased respiratory rate- due to extra oxygen needs |
|
|
|
What are the physical factors that influence respiration rate and depth? |
Increased body temperature, Exercise, Talking, Coughing |
|
|
|
What emotional factors can influence the rate and depth of respiration? |
Fear, anger, and excitement |
|
|
|
What chemical factors influence the rate and depth of respiration? |
Carbon dioxide |
|
|
|
What does carbon dioxide do to the pH of the blood? |
deceases pH, makes it more acidic |
|
|
|
Changes in CO2 act directly on the _______ _________. |
Medulla oblongata |
|
|
|
How are changes in oxygen concentration detected? |
Chemoreceptors |
|
|
|
What does hyperventilating do to CO2 levels? |
Blows off or loses CO2 |
|
|
|
What does hypo-ventilating do to the CO2 levels? |
Retains CO2 levels |
|
|
|
What is the normal respiratory rate? |
12 to 15 per minute |
|
|
|
What is COPD? |
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease |
|
|
|
What are some symptoms of COPD? |
Labored breathing, coughing, infections, and hypoxia eventually respiratory failure |
|
|
|
What are the characteristics of chronic bronchitis? |
Mucosa of lower respiratory tract gets severely inflamed which impairs gas exchange and causes patients to become cyanotic |
|
|
|
What are the characteristics of emphysema? |
Destroyed alveoli or enlarged alveoli, chronic inflammation, fibrosis, loss of elasticity, barrel chest, cyanosis |
|
|
|
What is lung cancer most commonly caused by? |
Smoking |
|
|
|
After birth, how long does it take for the lungs to fully inflate? |
Two weeks |
|
|
|
The change from nonfunctional to functional lungs after birth depends on.......? |
Surfactant |
|
|
|
Does respiratory rate change throughout life? |
Yes |
|
|
|
What is asthma? |
Chronically inflamed hypersensitive bronchioles |
|
|
|
How does aging effect the respiratory system? |
Elasticity decreases, vital capacity decreases, blood O2, |
|
|
|
What is hypernea? |
Increased respiratory rate- due to extra oxygen needs |
|
|
|
The flap of tissue that prevents food from entering the trachea is A. soft palate B. hard palate C. vocal chord D. epiglottis |
D |
|
|
|
In which function is the larynx not involved in? A) Swallowing B) Sound production C) Digestion D) The larynx is not involved in any of these processes |
C |
|
|
|
Which of the following is the correct order for the movement of air to the lungs? A. Nose, larynx, pharynx, trachea, bronchi B. Nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi C. Nose, pharynx, larynx, bronchi, trachea D. Nose, bronchi, larynx, bronchi, trachea |
B |
|
|
|
What are the physical factors that influence respiration rate and depth? |
Increased body temperature, Exercise, Talking, Coughing |
|
|
|
What emotional factors can influence the rate and depth of respiration? |
Fear, anger, and excitement |
|
|
|
What chemical factors influence the rate and depth of respiration? |
Carbon dioxide |
|
|
|
What does carbon dioxide do to the pH of the blood? |
deceases pH, makes it more acidic |
|
|
|
Changes in CO2 act directly on the _______ _________. |
Medulla oblongata |
|
|
|
How are changes in oxygen concentration detected? |
Chemoreceptors |
|
|
|
What does hyperventilating do to CO2 levels? |
Blows off or loses CO2 |
|
|
|
What does hypo-ventilating do to the CO2 levels? |
Retains CO2 levels |
|
|
|
Gas exchange in the lungs occurs in the A. alveoli B. bronchioles C. bronchi D. none of the above |
A |
|

