![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
8 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
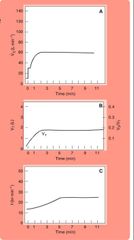
Short term light to mod |
Sharp increase in VE, slightly less sharp increase for VT and the lowest increase for f. All platue at steady state. The contribution of f to Increase Ve is minimal and gradual.
|
|
|
Short term light 3 graphs |
|
|
|
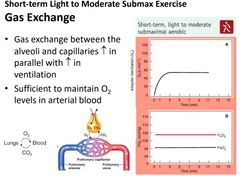
Gss exchange short term light |
Gas exchange between alveoli and capillaries increase in parallel with an increase in ventilation.
Sufficient to maintain 02 levels in arterial blood |
|
|
Gas exchange 2 graphs |
|
|
|
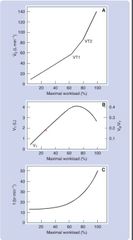
Incremental to max |
Linear increase in VE at light to mod intensities until it gets to VT1 and VT2. VT1 indicates the upper boundary of moderate. VT2 seperates heavy from very heavy non sustainable exercise.
Increase in Ve at low-mod intensities due to VT. At heavy intensities depht of breathing may decrease.
When Vt reaches peak, further increase in VE can only occur due to an increase of f. |
|
|
Incremental graphs |
|
|
|
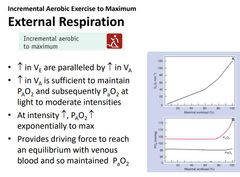
Gas exchange incremental to max |
Increase in ve paralled by increase in VA. An increase in VA is sufficient to maintain PAO2 and subsequently PaO2 at light to mod exercise intensities.
When intensity increases PA02 increases to max.
Provides a driving force to get to an equilibrium with venous blood so Pa02 is maintained. |
|
|
Gas exchange graphs incremental to max |
|

