![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
42 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Normal tidal volume? |
6-8ml/kg
~500ml for a 70kg person |
|
|
|
Function of the nose and upper airway? |
1) olfaction
2) filtering particulates to prevent them entering the alveoli
3) warm and humidify air as it enters the body |
|
|
|
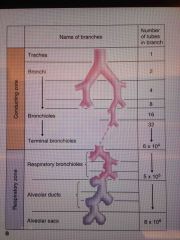
What are the different parts of the airways? |
1) UPPER AIRWAY Nose, nasal cavity, nasopharynx, oropharynx, mouth, laryngopharynx, larynx,
2) CONDUCTING AIRWAYS (conducting zone) Trachea, first 16 branches of bronchi, bronchioles, terminal bronchioles
3) ALVEOLAR AIRWAYS (respiratory zone) Last 7 generations of the 23 Respiratory bronchioles, alveolar ducts, alveoli |
|
|
|
Describe the change in cross sectional area through the airway generation and thus the effect on velocity of flow. |
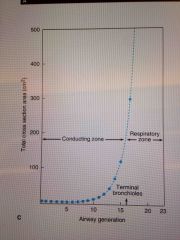
Very large increase in area, with a significant increase within the respiratory zone.
2.5cm2 --> 11800cm2
VEEY SLOW FLOW At the ALVEOLI END!! |
|
|
|
Describe the epithelium within the respiratory tract. |
Pseudo stratified in the trachea and bronchi --> cuboid in bronchioles --> squamous epi in alveoli |
|
|
|
Substance that are secreted by airway epi? |
IgA Collecting Defensins Proteases ROS Reactive nitrogen species Chemokines and cytokines
Ie antimocrobial |
|
|
|
Function of cilia |
Beat at 10-15hz Move small particles out of the airway s
2-5um
Impaired in smoking, other pollutants and genetic disorders |
|
|
|
Autonomic function on lungs ? |
Beta 2 - bronchodilation and increased secretions
Alpha 1 - inhibit secretion |
|
|
|
Discuss cystic fibrosis - cause, prevalence, inheritance, clinical |
3% of population Autosomal recessive
CFTR gene on chromosome 7 - different type of mutations _ delta 508 most common
Chloride channel is abnormal or missing from epithelial cells
CLINICAL - pulmonary infections, pseudomonas, pancreatic, gi, sweat test |
|
|
|
What is the respiratory zone? |
Last 7 divisions of the airways where gas exchange occurs. Includes respiratory bronchioles, alveolar ducts, alveoli |
|
|
|
Describe the 2 types of alveolar epithelium. |
Type 1 - 95% of surface area, 40% of pneumocytes, large flat,
Type 2 - granular, thicker, containing numerical inclusion bodies, 5% of SA, 60% of cells, produce SURFACTANT - capable of cellular division and can give rise to further type 1 cells |
|
|
|
Surfactant is made up of ? |
Phospholipids mainly which act to reduced surface tension and help keep the alveoli open |
|
|
|
What value/% of change in volumes does the diaphragm produce during quiet respiration? |
70% |
|
|
|
What value/% of change in volumes does the diaphragm produce during quiet respiration? |
70% |
|
|
|
Main muscles of inspiration? |
Diaphragm - phrenic nerve C3-5
External intercostals - arranged down and inward - lift the rib cage forward and up
Accessory - SCM, scalene |
|
|
|
Muscles of expiration? |
Normally quiet event with no work
Active expiration a internal intercostals and abdominal muscles |
|
|
|
Normal amount of pleural fluid? |
15-20 ml |
|
|
|
Describe the branching of the pulmonary arteries. |
They branch with the bronchi - down to the respiratory bronchioles |
|
|
|
Describe the usual BP in the following areas.
Systemic Capillary Venous RA RV PA LA LV |
Systemic - 120/80 Capillary - 30 Venous - 10 RA - 2 RV - 25/0 PA - 25/9 LA - 8 LV - 120/0 |
|
|
|
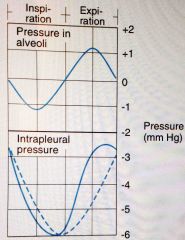
Draw a graph demonstrating the change in alveolar pressure and intrapleural pressure over time. |
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
What is the normal range of alveolar pressure and intrapleural pressure ? |
Alveolar --> -1 inspiration --> +1 expiration
Intrapleural --> -6 to -3 |
|
|
|
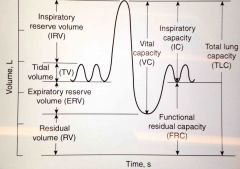
What are lung volumes vs capacities? |
Volumes are single measurements that all add together to give you the total lung capacity (TLC)
Volumes include - inspiratory reserve volume (IRV), tidal volume (TV), expiratory reserve volume (ERV) and the residual volume (RV)
Capacities are combinations of volumes |
|
|
|
Draw the relationship between the lung volumes and capacities |
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
What are the lung capacities? |
Capacities are subdivisions which contain 2 or more volumes.
FRC - functional residual capacity ( ERV + RV) VC - vital capacity ( IRV + TV + ERV) IC - inspiratory capacity (TV + IRV)
TLC - total lung capacity - all volumes |
|
|
|
What are normal valves for the lung volumes ? |
IRV - 2L
TV - 500-750ml
ERV - 1L
RV - 1.3L
Total ~ 5L |
|
|
|
What is a normal minute ventilation? |
12 breaths/min x 500ml TV = 6L /min
MV = RR x TV |
|
|
|
What is compliance? |
Tendency for a tissue to resume its original position after an applied force has been removed.
Compliance = change in volume/ change in pressure |
|
|
|
Give examples of respiratory pathology and their effect on compliance. |
Emphysema - increased compliance - increased lung volumes.
ILD - reduced compliance / stiff lungs, smaller volumes, hard to inflate - loss of elasticity |
|
|
|
What is hysteresis? |
The difference in pressure volume curves when inflating lungs with saline vs air with the difference representing surface tension and its effect on requiring increased pressure to produce the same volume change |
|
|
|
What is the function of surfactant? |
Splint alveoli open during expiration as the closing pressure increases due to reducing radius but no change in tension
It also acts to prevent/ inhibit pulmonary oedema |
|
|
|
How do you calculate work from a pressure volume curve? |
Work = ABCA (excluding the stored elastic work) |
|
|
|
What are the components of work of breathing? |
65% Elastic work 7% Moving inelastic tissues 28% Moving air through respiratory passages |
|
|
|
How do you calculate work from a pressure volume curve? |
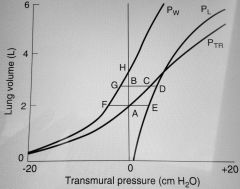
Work = ABCA (excluding the stored elastic work)
AFGBA = stored elastic work in the thorax AESCA = elastic work required by the lungs These 2 equal each other and are not counted when working out WOB |
|
|
|
What is the normal energy expenditure for breathing ? |
3% of total body energy expenditure
Can increase significantly during exercise or diseased states |
|
|
|
What is the difference in intrapleural pressure from the base to the apex?
Clinical significance? |
Apex -10 Base - 2.5
The more negative intrapleural pressure at the apex keeps the alveoli more expanded and therefore less volume change can occur at this point with inspiration as the pressure changes
Ie INCREASED VENTILATION AT THE BASE |
|
|
|
What is the difference in intrapleural pressure from the base to the apex?
Clinical significance? |
Apex -10 mmHg Base - 2.5
The more negative intrapleural pressure at the apex keeps the alveoli more expanded and therefore less volume change can occur at this point with inspiration as the pressure changes
Ie INCREASED VENTILATION AT THE BASE |
|
|
|
What is the difference in intrapleural pressure from the base to the apex?
Clinical significance? |
Apex -10 mmH20 Base - 2.5
The more negative intrapleural pressure at the apex keeps the alveoli more expanded and therefore less volume change can occur at this point with inspiration as the pressure changes (flatter part of the P/V curve)
Ie INCREASED VENTILATION AT THE BASE |
|
|
|
What are the types of dead space? |
Anatomic dead space - ~ 150ml Alveolar dead space - ventilated alveoli without perfusion (shunt) - no gas exchange
Physiologic - total dead space |
|
|
|
How do you calculate the anatomic dead space from a single breath N2 curve? |
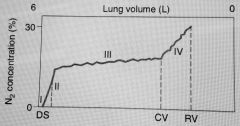
Midpoint for phase II
Patient takes 1 breath of 100% O2 and then breaths out- at first 100% 02 (dead space) then mix of dead space and alveolar, then alveolar |
|
|
|
How do you calculate total dead space? |
Bohr's equation
Vd = Vt - ( PeCO2 x Vt) / PaCO2 |
|
|
|
What are the main constituents of air? |
21% oxygen 0.05% carbon dioxide 78% nitrogen 0.92% other - helium, argon etc |
|
|
|
How do you calculate the partial pressure of oxygen at sea level? |
Barometric pressure = 760
Oxygen is 21%
Therefore the partial pressure of oxygen is 0.21 x 760 = 160mmHg
The pressure that reached the airways is less due to temperatues and water vapor |
|

