![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
16 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
NSCLC characterized by adenocarcinoma should be tested further for specific molecular alterations in ?
|
In the United States, NSCLC accounts for approximately 85% of all lung cancer cases.[3] It is frequently possible to diagnose and histologically characterize NSCLC as either adenocarcinoma or squamous cell carcinoma on the basis of morphology alone.[1] In cases where the histology of NSCLC is indeterminate (also called NSCLC, not otherwise specified [NOS]), immunohistochemical (IHC) staining can be helpful. NSCLC characterized by adenocarcinoma should be tested further for specific molecular alterations in EGFR and ALK genes.[2] Other ancillary studies such as flow cytometry may be necessary if a lymphoproliferative disorder is suspected
|
|
|
what is the approach to lung biopsy specimen?
|
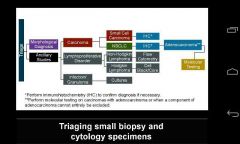
|
|
|
what should carcinoid tumors be called? what is the survival of metastatic well diff dz?
|
Neuroendocrine tumor
survival is similar to metastatic colon CA, about two yrs |
|
|
what are the different types of NET?
|
high grade NET have been also called neuroendocrine carcinoma.
pancreatic (insulomas, VIPomas, gastronomas), GI, very heterogenous entity: aggressive vs indolent, welldiff vs poor, etc |
|
|
what are the symptoms of VIPoma and glucagonoma?
|
VIPoma: diarrhea with hypoK
glucagonoma: diabetes, erythema necrolyticans migrans |
|
|
what are markers for NET?
|
Neuroendocrine tumors, despite differingembryological origin, have common phenotypiccharacteristics.[citation needed]
NETs show tissue immunoreactivity for markers of neuroendocrine differentiation (pan-neuroendocrine tissue markers) and may secrete various peptides and hormones. There is a lengthy list of potential markers in neuroendocrine tumors; several reviews provide assistance in understanding these markers.[40][41] Widely used neuroendocrine tissue markers are various chromogranins,synaptophysin and PGP9.5. Neuron-specific enolase (NSE) is less specific.[1][12] |
|
|
what does NET look like grossly?
|
NETs are often small, yellow or tan masses, often located in the submucosa or more deeply intramurally, and they can be very firm due to an accompanying intense desmoplastic reaction. The overlying mucosa may be either intact orulcerated. Some GEP-NETs invade deeply to involve the mesentery.
|
|
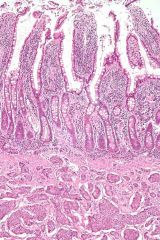
what is this?
|
Small intestinal neuroendocrine tumor at bottom third of image, showing the typical intramural(within the wall) location, and overlying intact epithelium. H&E stain.
|
|

describe (lesion in small intestine)
|
Histologically, NETs are an example of "small blue cell tumors," showing uniform cells which have a round to oval stippled nucleus and scant, pink granular cytoplasm. The cells may align variously in islands, glands or sheets. High power examination shows bland cytopathology. Electron microscopy can identify secretory granules. There is usually minimalpleomorphism but less commonly there can beanaplasia, mitotic activity, and necrosis.
|
|
|
what stains are used for FNA smears of NSCLC? what features ddx squamous vs adenoCa?
|
adenoca: diffquik
squamous cell CA: papanicolou For adenocarcinomas we look for gland formation, mucin production, or signet rings using a Romanowsky stain such as Diff-Quik, and for squamous cell carcinoma we look for keratinization on a Pap stain |
|
|
how is a FNA processed? (Rapid Onsite Specime Evaluation) ROSE
|
One slide is air-dried for Diff-Quik stain and immediate assessment.
The second slide is placed in alcohol for Pap staining in the laboratory later. The remaining material is allowed to clot and placed in formalin for cell block preparation. |
|
|
how does KI67 affect Rx of NET?
|
KI67 greater than 20% needs chemo.
lesw rhan 2% can watch and wait. less than 10% warrants somatostatin analogs and interferon Alpha. MUST report ki67 on path report |
|
|
When morphologic analyses alone do not provide a determination of tumor histology in NSCLC, IHC staining is performed. what stains?
|

When morphologic analyses alone do not provide a determination of tumor histology, IHC staining is performed. Nevertheless, it is very important to limit the use of IHC stains and IHC testing to the extent necessary to accurately determine tumor histology, thereby preserving the specimen for subsequent molecular analyses. A proposed minimalist approach to the use of IHC staining involving TTF-1 and p63 staining is presented here. This algorithm starts by stratifying samples according to thyroid transcription factor (TTF-1) staining, which is a sensitive and specific marker of lung adenocarcinoma.[17] The grid on the upper left portion of the slide summarizes the histological characterization on the basis of the presence or absence and intensity of staining of both IHC stains.
|
|
|
what percentage of lung adenoCa test posotive for Alk? is if affected by ethinicity?
|
2-4percent.
no. affected by smoking only. |
|
|
what are the grading criteria of IHC stain positivity? (1+vs 2+ etc)
|

|
|
|
What featrures indicate a rectal resection as Complete? What margin should be inked? What is the frossing process called?
|
Intact, bulky mesorectum, no defects deeper than 5mm, no coning of specimen. Ink below the serosal surface (peritoneal reflection).
Do the complete Quirke Method. In the fresh state: After assessing quality of TME (Total mesorectal excision?), radial margin is inked. Ink the radial margin (below peritoneal reflection) green anteriorly and black posteriorly. Measure the anus, posterior peritoneal reflection is at __ from the anterior resection margin, etc. Cut out lymph nodes WITH the radial margin (so you can measure the distance) DONOT cut through the tumor in the fresh state. Must fix for a few days (72hrs min) In your report, need to include more than just CAP: Extramural depth of invasion, venous invation (intramural- within muscularis proprio ; vs extramural). Must mention distance to all three margins, not just the closest. Consider elastin stain to show venous invasion (expected to be seen in 30% of specimen) |

