![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
41 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Describe the life cycle of D viviparus |
Pre patent period: ingestion of L3, L4 migrate through bloodstream to lungs, L5 move to upper RT Patent period: Adults lay eggs in alveoli and eggs are coughed up, swallowed eggs are hatched and L2 excreted |
|
|
Where does pathology occur in the d viviparus life cycle |
Alveolitis in the prepatent period, bronchiolitis and bronchitis Parasitic bronchitis and pneumonia due to foreign body resopnse |
|
|
What can lead to further damage in postpatent phase |
Alveolar epithelialisation Superimposed bacterial infection |
|
|
What spp does d arnfeldii infect |
Horses and donkeys |
|
|
What is the life cycle of muelleris capillaris |
Adult worms lay effs and L1 hatch in bronchi and trachea Coughed up and swallowed and shed L3 development within snails PPP between infection and shed is 1 month |
|
|
What does metastrongylus cause |
Bronchi/bronchiole parasite of pigs |
|
|
What is aelurostrongylus |
Cat lungworm |
|
|
What forms hyatid cysts |
Echinococcus granulosus |
|
|
What is type one hypersensetivity |
When antigen is presented to CD4 TH2 cells that are specific to an antigen this stimulates B cells to produce IGE This binds to the antigen and then to FC receptros causing degranulation of mast cells |
|
|
What is type 3 hypersensetivity |
Immune complexes deposited in vasculature Triggers complement Influx of phagocytes and granulocytes producing inflammatory mediators |
|
|
What is PIE |
Type 1 hypersensetivity Pulmonary infiltration with eosinophillia Eosinophils predominate airways |
|
|
What is Extrinsic allergic alveolitis? |
Type 3 hypersensitivity reaction caused by mouldy hay - fungal spores Micropolyspora faeni and thermacinomyces vulgaris Primarily housed animals in winter |
|
|
What do you see macroscopically with Extrinsic allergic alveolitis? |
Normal but may have numerous very small grey nodules |
|
|
What would you see microscopically with extrinsic allergic alveolitis |
Lymphocytic/plasmocytic bronchitis/bronchiolitis Thickening of alveolar septae also present Chronicl esions - type 2 hyperplasia May lead to cor pulmonale in sever cases |
|
|
What is COPD |
Chronic obstructive pulmonary diease Chronic coughing and poor performance Respiratory distress - increased expiratory effort Characteristic heave line |
|
|
What is aspiration pneumonia |
Response of lungs to aspirated foregn material Severe necrotising pneumonia and gangrenous necrosis |
|
|
What is lipid pneumonia? |
Endogenous or exogenous - accumulation of lipids in pulmonary macrophages if endogenous or inhalation of oils/lipids producing a macrophage dominant reaction |
|
|
What is uraemic pneumonia |
Ureamia causes increased permeability of the blood air barrier In addition to the oedema there may also be degeneration and calcifiction of the smooth muscle and CT |
|
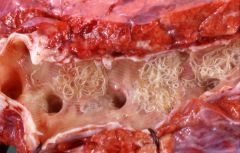
|
What causes this Patent phase of D. Viviparus |
|
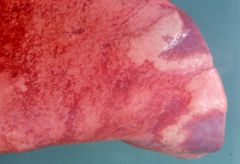
|
D viviparus Patent phase - foreign body response - dark red collapsed areas |
|
|
Prepatent phase of d. viviparus |
Larvae appear in the alveoli and cause alveolitis Bronchiolitis and bronchitis occur Plug airways resulting i collapse distal to the lsion Interstitial emphysema and oedema in severe burdens |
|
|
Patent pahse of d viviparus |
Parasitic bronchitis - inflammatory response Epithelial hyperplasia Pneumonia - aspiraiton of eggs and larvae into alveoli - dark red collapsed areas |
|
|
Postpatent phase of d viviparus |
recovery phase alveolar epithelialisation superimposed bacterial infeciton |
|
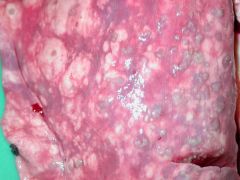
What is this a pathognomonic leison of |
Muelleris capillaris Lead shot lesions in dorsal regions of caudal lobes very little significance |
|
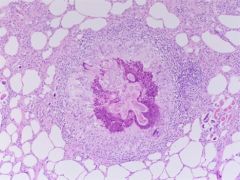
|
Mueleris capillaris |
|
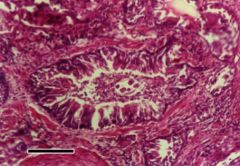
What is this and what spp would you find it in |
Aulurostrongylus abstrusus Lungworm of cats Foreign body reaciton |
|
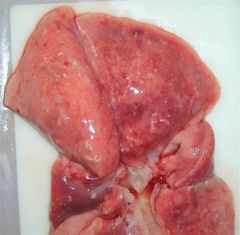
|
Subpleural firm yellow nodules scattered throughout the parenchyma - more frequent at the periphery |
|
|
What would you see with a. abstrusus |
Submucosal gland hypertrophy Smooth muscle hytpetrrophy Foreign body response - macrophages and giant cells |
|
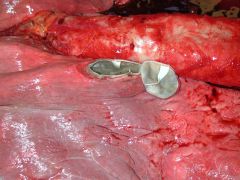
|
Echinococcus granulosus - little significance |
|
|
Where does A vasorum reside and what does it cause |
Pulmonary arteries and ventricles Pulmonary hypertension and oedema |
|
|
What is type 1 hypersensetivity |
IgE bound mast cell binds to the antigen and degranulates causing urticaria athsma |
|
|
What is a disease relating to type 1 hypersensetivity |
Feline allergic bronchitis
|
|
|
What is PIE |
Small group of diseases where there are eosinophils in the airways |
|
|
What is type 3 hypersensetivity |
Immune complex deposition Degranulation and vasculitis |
|
|
What is associated with type 3 hypersensetivity |
Bovine farmers lung - thermactinomyces, micrpolyspora spores
|
|
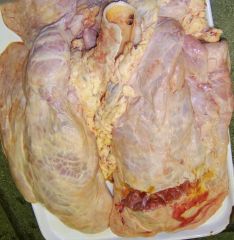
|
Diffuse fibrosing alveolitis Proliferative end phase Fibrosis of many diseases - now falling out of favour |
|

What causes this and what is it |
Heave line caused by COPD Type 3 hypersensetivity to environmental allergens |
|
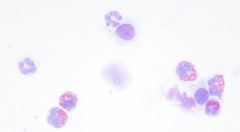
|
BAL showing eosinophils characteristic of COPD |
|
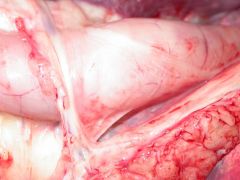
What causes this? |
Persistant right aortic arch |
|
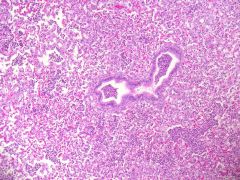
|
Aspiration pneumonia due to inhalation of food sue to PRAA - gangrenous necrotising pneumonia |
|
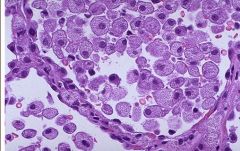
|
Lipid accumulation in pulmonary macrophages - multifocal white nodules (surfactant is the lipid or can be exogenous) Intersititial thickening |

