![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
53 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
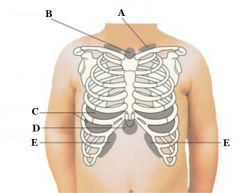
What retractions are found at A?
|
Supraclavicular
|
|
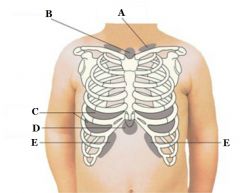
What retractions are found at B?
|
Suprasternal
|
|

What retractions are found at C?
|
Intercostal
|
|
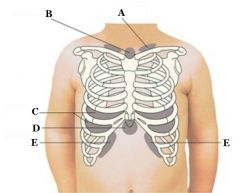
What retractions are found at D?
|
Substernal
|
|
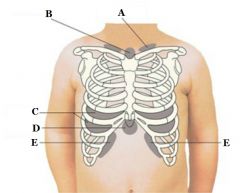
What retractions are found at E?
|
Subcostal
|
|
|
What is the most frequent cause of acute renal failure?
|
Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome
|
|
|
What are the S&S of hemolytic uremic syndrome?
|
bloody diarrhea, vomiting, decreased urination, hematuria, pallor, edema
|
|
|
The prodomal hemolytic uremic syndrome is typically accompanied by what?
|
Toxin producing E. coli
|
|
|
What are the S&S of appendicitis?
|
RLQ pain, n/v, anorexia, rigidity over RLQ, low grade fever
|
|
|
If a patient with appendicitis says that they have pain and then suddenly do not, what do you expect?
|
Perforation
|
|
|
How do you breast feed a child with a cleft lip?
|
Just like you would any other child, they breast forms to the child's mouth
|
|
|
Cryptochordism
|
Detached scrotum
|
|
|
How do you test for cryptochordism?
|
Put the boy in a warm bath and have him get out, they will shrink
|
|
|
What is enuresis?
|
repeated involuntary voiding by a child who has reached an age at which the bladder control is expected
|
|
|
By what age should a child have bladder control?
|
5-6 years
|
|
|
Bed wetting is normal until what age?
|
8 years
|
|
|
If a child has enuresis what should you check for?
|
diabetes mellitus, renal insufficiency, fistulas, sacral dimples, or tufts of hair
|
|
|
What is the treatment for enuresis?
|
fluid restriction, bed wetting alarms, bladder exercises, timed voiding, reward system, medications
|
|
|
What medications treat enuresis?
|
Ditropan and Trofanil
|
|
|
How is Trofanil given?
|
Capsule 1 hour before bed
|
|
|
What is esophageal atresia?
|
Esophagus terminates before it reaches the stomach and of a fistula is present that forms an unnatural connection with the trachea
|
|
|
What are the S&S of esophageal atresia?
|
Can't pass suction catheter at birth, excessive oral secretions, vomiting, abd distention
3 C'S: COUGHING, CHOKING, CYANOSIS |
|
|
What is the ESSR method with cleft lip or palate?
|
Enlargement, Stimulate, Swallow, Rest
|
|
|
What are the S&S of GERD?
|
vomiting, spitting up, failure to thrive
|
|
|
What are the treatments of GERD?
|
Diet, positioning, sleep supine unless risk of aspiration, reglan
|
|
|
Acute glomerulonephritis is a side effect of what?
|
Streptococcal infection
|
|
|
What are S&S of acute glomerulonephritis?
|
Periorbital edema, hypertension
|
|
|
What is Hirschsprung's disease?
|
Congenital aganglionic megacolon: inadequate motility causes mechanical obstruction of the intestine
|
|
|
How do you treat Hirschsprung's disease?
|
monitor fluid and electrolytes, bowel training, measure ad, may have colostomy
|
|
|
What is intussusception?
|
One portion of the intestine prolapses and then telescopes into another
|
|
|
What are the S&S of intussusception?
|
acute episodes of pain, stools red and resemble currant jelly
|
|
|
What are the nursing interventions for intussusception?
|
check for S&S of infection, manage pain, maintain NG tube patency, clear liquids
|
|
|
What is a hydrocele?
|
Fluid filled mass in the scrotum
|
|
|
What is the treatment of a hydrocele?
|
Surgery around 3 months in most newborn boys
|
|
|
What is the primary cause of nephritoc syndrome?
|
Minimal change nephropaty
|
|
|
What is pyloric stenosis?
|
Hypertrophic obstruction of the circular muscle of the pyloric canal
|
|
|
What are the S&S of pyloric stenosis?
|
Projectile vomiting
|
|
|
What can you see on the abdomen in pyloric stenosis?
|
peristaltic waves
|
|
|
What are S&S of organ rejection?
|
fever, swelling, tenderness, decreased urine output, elevated BP
|
|
|
How do you test specific gravity in an infant?
|
Put a cotton ball on their urethra and squeeze it out
|
|
|
What are the early S&S of dehydration?
|
5% body weight loss, alert restless thirsty, normal pulse, normal skin turgor, moist mucous membranes, normal urine, normal respiration, treat with oral fluids
|
|
|
What are the S&S of moderate dehydration?
|
6-8% body weight loss, irritable, alert, thirsty, restless, postural hypotension, rapid pulse, poor skin turgor, dry mucous Montague, concentrated urine, respirations normal or rapid
|
|
|
What are the S&S of severe dehydration?
|
10+% body weight loss, lethargic/comatose, apprehensive, often conscious, rapid weak pulse, poor skin turgor, parched mucous membranes, decreased urine output,
|
|
|
High concenterated formulas have excessive _________ which can lead to dehydration.
|
Sodium
|
|
|
Rimactane in TB turns the urine ______.
|
Orange
|
|
|
What is cystic fibrosis?
|
Genetic multisystem exocrine mucus producing gland dysfunction
|
|
|
What type of stools does a cystic fibrosis kid have?
|
large bulkey loose frothy foul smelling stools
|
|
|
How do you treat cystic fibrosis?
|
Nebulizer, suction, huffing, aeroslized DNase, increase exercise, vitals, pulse ox, check resp status, high protein high calorie diet
|
|
|
What are S&S of resp distress?
|
Tachypnea, paradoxical breathing, adentitious breathing, nasal flairing, check pulses, check color, cough?, behavior changes
|
|
|
What is the goal of bowel management?
|
Keep client clean for 24 hours
|
|
|
What do you do for bowel management?
|
Contrast enema X-ray followed by laxatives or enemas
|
|
|
What is encorpresis?
|
Involuntary defection in a child older than 4 with normal colon and rectal anatomy
|
|
|
What must be done before any disimpatction?
|
Contrast enema
|

