![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
22 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Lung development occurs in _____ stages during week _____ of development |
Five stages Week 4 Begins with formation of lung bud from distal end of respiratory |
|
|
|
Mnemonic Every pulmonologist can see alveoli |
Every - embryonic (weeks 4-7) Pulmonologist - Pseudoglandular (5-17) Can - canalicular (16-25) See - saccular (24 - brith) Alveoli - alveolar (week 36 - 8yrs) |
|
|
|
Error at embryonic stage of lung development can lead to |
Tracheoesophageal fistula |
|
|
|
Error at which stage of lung development makes respiration impossible, incompatible with life? |
Pseudoglandular |
|
|
|
Pneumocytes start developing at ____weeks & respiration is capable at week ____. |
20 weeks 25 weeks |
|
|
|
Blockage of posterior nasal opening is called _____ & When does this worsen and improve? |
Choanal atresia worsens during feeding and improves with crying |
|
|
|
How is choanal atresia diagnosed & confirmed? |
Diagnosed by failure to pass nasopharyngeal tube and confirmed with CT scan. |
|
|
|
Choanal atresia is Often part of multiple malformation syndromes, such as CHARGE syndrome |
C - coloboma of eye H - heart defects A - atresia of choanae R - restricted growth & development G - genitourinary defects E - ear defects |
|
|
|
Pulmonary hypoplasia is associated with |
Congenital diaphragmatic hernia (usually left) Bilateral renal agenesis (potter sequence) |
|
|
|
Nonciliated; low columnar/cuboidal with secretory granules. Located in bronchioles are called? |
Club cells |
|
|
|
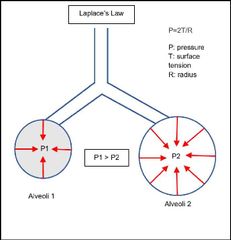
Application of Law of ______ in alveoli–alveoli have increased tendency to collapse on expiration as radius decreases |
Laplace |
|
|
|
Surfactant is composed of multiple lecithins mainly _____ |
DPPC ( dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine ) |
Synthesis begins ~20 weeks of gestation and achieves mature levels ~35 weeks of gestation. |
|
|
_______ are important for fetal surfactant synthesis and lung development |
Glucocorticoids |
|
|
|
How do lung fields appear on Xray in Neonatal respiratory distress syndrome |
Ground glass appearance (Surfactant deficiency) |
|
|
|
What are the risk factors for neonatal respiratory distress syndrome? |
prematurity diabetes during pregnancy C - section delivery |
diabetes during pregnancy (due to fetal insulin), C-section delivery ( release of fetal glucocorticoids; less stressful than vaginal delivery). |
|
|
How can we treat Neonatal respiratory distress syndrome? |
maternal glucocorticoids before birth exogenous surfactant for infant. |
|
|
|
What are the screening tests for fetal lung maturity? |
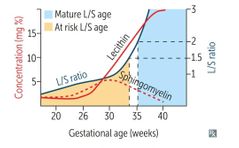
lecithin-sphingomyelin (L/S) ratio in amniotic fluid (≥ 2 is healthy; < 1.5 predictive of NRDS), foam stability index, surfactant-albumin ratio. |
|
|
|
Therapeutic supplemental O2 In NRDS can result in RIB) |
Retinopathy of prematurity, Intraventricular hemorrhage, Bronchopulmonary dysplasia |
|
|
|
Function of club cells |
Degrade toxins via cytochrome P-450; secrete component of surfactant; progenitor cells for club and ciliated cells. |
|
|
|
Alveolar cell types diagram |
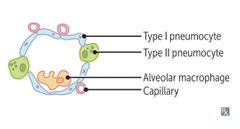
Functions of tyor |
|
|
|
Functions of type II pneumocytes |
1. Serve as stem cell precursors for 2 cell types 2. Secrete surfactant from lamellar bodies |
|
|
|
anatomical communications between alveoli that allow for passing of air, fluid, phagocytes, and bacteria (in pneumonia) are called? |
Pores of kohn |
|

