![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
62 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What 4 structures make up the upper respiratory system? |
1) Nose 2) Nasal Cavity 3) Paranasal sinuses 4) Pharynx |
|
|
What 4 structures make up the lower respiratory system? |
1) Larynx 2) Trachea 3) Bronchi 4) Lungs |
|
|
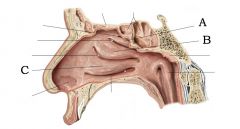
A) Superior Concha B) Middle Concha C) Inferior Concha |
|
|
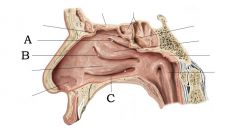
A) Superior Meatus B) Middle Meatus C) Inferior Meatus |
|
|
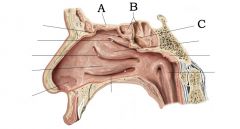
A) Cribriform plate B) Sphenoid sinus C) Superior concha |
|
|
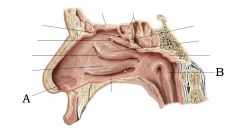
A) Nasal Vestibule B) Salpingopharyngeal fold |
|
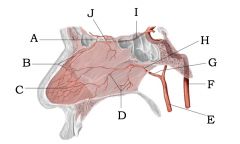
|
A) Anterior ethmoidal artery B) Anterior septal branches C) Kiesselbach's area D) Posterior septal branches E) External carotid artery F) Internal carotid artery G) Maxillary artery H) Sphenopalantine artery I) Ophthalmic artery J) Posterior ethmoidal artery |
|
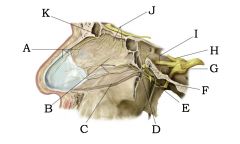
|
A) Internal nasal branches of V1 B) Medial superior posterior nasal branches of V2 C) Nasopalantine nerve D) Sphenopalatine foramen E) Pterygopalatine ganglion F) CN V3 G) Trigeminal ganglion of CN V H) V1 I) V2 J) Olfactory bulb and fibers K) Anterior ethmoidal nerve off V1
|
|
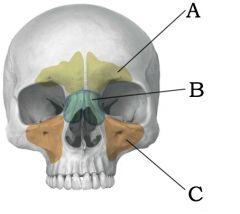
|
A) Frontal sinus B) Ethmoid sinus C) Maxillary sinus |
|
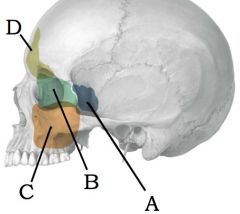
|
A) Sphenoid sinus B) Ethmoid sinus C) Maxillary sinus D) Frontal sinus |
|
|
What duct drains the frontal sinus?
To where does drainage go? |
Frontonasal duct to hiatus semilunaris of middle meatus
|
|
|
What do the anterior cells of the ethmoid sinus drain into?
middle?
posterior? |
Anterior - hiatus semilunaris in middle meatus
Middle - bulla ethmoidalis in the middle meatus
Posterior - superior meatus |
|
|
What does the maxillary sinus drain into? |
hiatus semilunaris in the middle meatus |
|
|
What does the sphenoid drain into? |
Sphenoethmoid recess |
|
|
In what direction does the frontal sinus grow?
Between what ages? |
Superior and lateral
1 - 20 |
|
|
In what direction do the maxillary sinuses grow?
Between what ages? |
Inferior and lateral
1 - 60 |
|
|
What landmark separates nasopharynx and oropharynx? |
Uvula |
|
|
What landmark separates oropharynx from laryngopharynx? |
Epiglottis |
|
|
What nerve innervates sensation of the larynx above the vocal fold? |
internal laryngeal nerve |
|
|
What nerve innervates sensation of the larynx below the vocal fold? |
recurrent laryngeal nerve |
|
|
What symptom would occur if an aortic aneurysm pushed against the recurrent laryngeal nerve? |
Hoarseness of voice |
|
|
What nerve innervates the motor control for the larynx? |
Recurrent laryngeal nerve |
|
|
What part of the larynx does not receive motor innervation form the recurrent laryngeal nerve?
From where does its motor innervation come? |
cricothyroid
external laryngeal nerve |
|
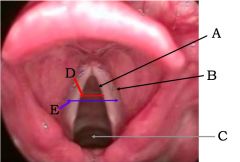
|
A) True vocal fold B) False vocal fold C) Trachea D) Rima glottidus E) Glottis |
|
|
What are the three layers of intercostal muscles and in what direction do their fibers run? |
External intercostals run inferior medially
Middle intercostals run superior medially
Innermost intercostals run superior laterally |
|
|
Where do each intercostal vein, artery, and nerve run? |
On the inferior posterior aspect of each rib |
|
|
What is the space between the lung, diaphragm, and pleural cavity called? |
Costodiaphragmatic space |
|
|
What nerve roots supply the motor innervation for the diaphragm? |
C3, C4, C5 |
|
|
What are the external and internal layers of pleura called? |
External - parietal pleura Internal - visceral pleura |
|
|
Where are the visceral and parietal pleurae continuous? |
root of the lung |
|
|
What fills the space between the two pleura?
What is its purpose? |
Serous fluid to hold two pleura together while reducing friction between them. |
|
|
Name the 4 borders parietal pleura. |
1) Cervical 2) Costal 3) Diaphragmatic 4) Mediastinal |
|
|
What is parietal pleura in contact with externally? |
Endothoracic fascia |
|
|
What nerves innervate the parietal pleura? (2) |
intercostal and phrenic nerves |
|
|
What is the nature of pain from the parietal pleura? |
localized |
|
|
What is the nature of pain from the visceral pleura? |
generalized |
|
|
What is the thickening of endothoracic fascia on the cervical parietal pleura called? |
Suprapleural membrane |
|
|
What is the lowest point of the pleural cavity if a patient is upright? |
Costodiaphragmatic recess |
|
|
What recess is behind the mediastinum? |
Costomedial recess |
|
|
Describe the lobes of the left and right lung. |
Right lung: 3 lobes: superior, middle, inferior
Left lung: 2 lobes: superior, inferior |
|
|
Describe the fissures of the left and right lung. |
Right lung: horizontal over the oblique fissure
Left lung: just an oblique fissure |
|
|
What is the indention of the heart on the left lung called? |
Cardiac notch |
|
|
How many anatomically and functionally separate bronchopulmonary segments are there in each lung? |
10 per side |
|
|
What level bronchus enters each bronchopulmonary segment? |
tertiary bronchus |
|
|
How do the pulmonary arteries and veins differ besides oxygen concentration? |
Pulmonary arteries run between bronchopulmonary segments (intersegmental)
Pulmonary veins run through bronchopulmonary segments (intrasegmental) |
|
|
At what spinal level does the trachea begin? |
C6 |
|
|
At what spinal level does the trachea divide into left and right primary bronchi? |
T4 |
|
|
Which primary bronchus is wider and more vertical? |
right primary bronchus |
|
|
What 4 nerve types make up the pulmonary plexus? |
- postganglionic sympathetic fibers - preganglionic parasympathetic fibers - postganglionic parasympathetic fibers - Visceral afferents |
|
|
From what nerve does sympathetic innervation to the primary plexus come?
parasympathetic innervation? |
symp - cardiac nerves
parasymp - Vagus nerve |
|
|
What does sympathetic stimulation of the lungs cause? (3) |
- Bronchodilation - Inhibition to alveolar glands - Vasoconstriction to pulmonary vessels |
|
|
What does parasympathetic stimulation of the lungs cause? (3) |
- Bronchoconstriction - Increase in alveolar gland secretion - Vasodilation of pulmonary vessels |
|
|
What are the purposes of reflex afferent fibers in the lungs? (4) |
- cough - stretch - blood pressure - blood gas levels |
|
|
What are nociceptive afferent fibers meant to detect in the lung? (3) |
- chemical irritants - ischemia - excessive stretch |
|
|
From what two arteries do the systemic bronchial arteries branch? |
thoracic aorta or upper posterior intercostal muscles |
|
|
To what two vein systems do the bronchial veins drain? |
azygos or superior intercostal veins |
|
|
What are the 5 groups of tracheobronchial lymph nodes? |
- tracheal - superior tracheobronchial - inferior tracheobronchial - bronchopulmonary - pulmonary lymph nodes |
|
|
Where do efferent lymph vessels from the lungs drain? |
- brochomediastinal trunks |
|
|
What portion of the lungs is not protected by the rib cage? |
Apex |
|
|
Along what rib is the horizontal fissure? |
4th rib |
|
|
Between what two points does the right oblique along lie? |
T2/T3 to 6th rib lateral curvature |
|
|
Along what ribs is the cardiac notch? |
4th - 6th |

