![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
6 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What are the improvements for this experiment? |
Ensure wire is free from kinks and held as straight as possible to measure the length Measure the mean diameter at several points along the wire with a micrometre to reduce uncertainty When increasing length of the wire increase the potential difference across the wire to maintain a constant current Switch off power supply between readings to keep resistance constant |
4 points |
|
|
What are some of the safety aspects for experiment? |
Disconnect crocodile clips between readings to minimise heating preventing burns If the wire is tight wear safety goggles in case of snapping |
|
|
|
What is the control variable for this experiment? |
The test wire being used
The current through the length of wire |
2 points |
|
|
Describe Circuit Diagram |
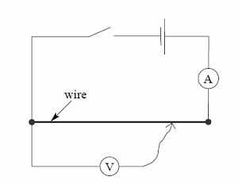
Variable cell or battery Ammeter in series with power supply Voltmeter in parallel with wire Switch in series to power supply |
4 points |
|
|
Describe the graph for this experiment |

Resistance against length
Values are proportional to line of best fit is a straight line through the origin Gradient of line can be used to calculate resistivity of wire
Gradient of line can be used to calculate resistivity of wire Gradient of line can be used to calculate resistivity of wire |
3 points |
|
|
Describe the calculation that can be made for this experiment |
Calculating mean cross sectional area of wire πD^2/4 Gradient x cross sectional area = resistivity of wire |
2 points |

