![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
56 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
gonads
|
the body's reproductive glands, known as testes for thee males and ovaries for females
|
|
|
testes
|
The male gonads that are oval and paired, suspended in a pouchlike sac, the scrotum, outside of the pelvic cavity. They produce the male sex cells, and testosterone, the male sex hormone.
|
|
|
ovaries
|
The female gonads, paired almond
sized organs located in the pelvic cavity, and produce two steroid hormone groups the estrogns and pregesterone. The endocrine and exocrine functions do not begin until the onset of puberty. |
|
|
gametes
|
sex cells
|
|
|
spermatozoa
|
Sperm cells.
|
|
|
oocytes
|
female eggs
|
|
|
fertilization
|
creation by the physical union of male and female gametes
|
|
|
amphimixis
|
union of sperm and egg in sexual reproduction
|
|
|
zygote
|
the cell resulting from the union of an ovum and a spermatozoon (including the organism that develops from that cell)
|
|
|
gubernaculum
|
guides the descent of the testes into the lower abdominal cavity and through the inguinal canal
|
|
|
inguinal canal
|
oblique passage through the lower abdominal wall Ex. in males it is the passage through which the testes descend into the scrotum and it contains the spermatic cord; in females it transmits the round ligament of the uterus
|
|
|
cryptorchidism
|
failure of one or both testes to move into the scrotum as the male fetus develops
|
|
|
prostate
|
A small gland encircling the male urethra just inferior to the bladder (only reproductive structure not paired). Its secretion contain nutrients and enzymes
|
|
|
hypertrophy
|
abnormal enlargement of a body part or organ
|
|
|
BPH
|
enlarged prostate
|
|
|
seminal vesicles
|
produce about 60% of seminal fluid, these are located at the posterior wall of the urinary bladder close to the terminus of the ductus deferens. They produce a substance that nourishes the sperm passing through the tract or that promote the fertilizing capabiltiy of sperm in some way
|
|
|
bulbourethral
|
aka cowper's (2) size of a pea secrete thick alkaline mucous 2 functions 1) neutralizes urine residue in urethra 2) lubricates top of penis for insertion
|
|
|
epididymus
|
structure in the male reproductive system in which sperm are fully matured and are stored c shaped sits on top and back of testes, series of highly coiled tubules
|
|
|
vas deferens
|
A thick muscular tube that connects the epididymis of the testes to the urethra. Muscular contractions of the vas deferns during ejaculation ehp propel the sperm outward
|
|
|
ejaculatory duct
|
duct formed by the union of the vas deferens with the duct of seminal vesicle; its fluid is carried into the urethra
|
|
|
ampulla
|
The ampulla is the second portion of the uterine tube. It is an intermediate dilated portion, which curves over the ovary.
|
|
|
scrotum
|
A sac like puch that has 2 functions that holds testes and regulates the temperature
|
|
|
spermatic cord
|
a structure resembling a cord that suspends the testis within the scrotum and contains the vas deferens and other vessels and nerves
|
|
|
tunica vaginalis
|
serous membrane that covers the outside of each testis and lines the scrotal cavity
also reduces friction between the opposing surfaces |
|
|
tunica albuginea
|
a dense connective tissue capsule that covers each testes....litterally "white tunic." extensions of this sheath enter the testes and divide into a number of lobes
|
|
|
septa
|
extension of tunica albuginea plunging into testis and dividing it into lobules
|
|
|
lobules
|
little lobes 200
300 contain semineferous tubules |
|
|
seminiferous tubules
|
where sperm are made 1
4 per lobule, highly coiled |
|
|
spermatogenesis
developmental stages |
1) spermatogonium 2) primary spermatocyte 3) secondary spermatocytes 4) spermatids 5) spermatozoa
|
|
|
spermatogonium
|
diploid, 46c, goes through mitosis and differentiation, becomes primary spermocyte
|
|
|
primary spermatocyte
|
the product of a mitotic division of a spermatogonium under the influence of FSH (follicle
stimulating hormone) after puberty. this cell is destined to undergo meisosis. it under goes a growth phase and then meiosis I takes place (DNA replicates before the division) |
|
|
secondary spermatocyte
|
the result of meiosis I of the primary spermatocyte is this haploid which is smaller in size. two are made out of one primary spermatocyte, they are destined to undergo meiosis II (DNA is not replicated before division)
|
|
|
spermatids
|
haploid, 23c, spermiogenisis, form from secondary spermocytes and form 4 spermatozoons or sperm cells
|
|
|
spermatogonia
|
stem cells, form during embryonic development but remain dormant until puberty. once mature, each division of this cell cause one daughter cel to remain at seminiferous tubule as undifferentiated stem cell, while another cell is pushed down toward the lumen 2n = 46 chromosomes
|
|
|
sustentacular cells
|
AKA sertoli cells; large cells that are attached to the basement membrane at the tubular capsule – newly formed spermatids are embedded in within the cytoplasm of these cells
|
|
|
interstitial cells
|
aka Leydig cells, cells lying external to and between the seminiferous tubules. LH and ICSH (interstitial
cell stimulating hormone) promotes these cells to produce testosterone and acts synergistically with FSh to stimulate sperm production |
|
|
GNRH
|
(from the hypothalamus) stimulates pituitary to release FSH and LH
|
|
|
LH
|
a gonadotropic hormone that is secreted by the anterior pituitary
|
|
|
FSH
|
Stimulates follicle development of ovaries and development of sperm cells
|
|
|
ICSH
|
a gonadotropic hormone that is secreted by the anterior pituitary
|
|
|
ABP
|
androgen
binding protein, binds to testosterone to make it available to developing sperm cells |
|
|
5 hormones needed for spermatogenesis
|
FSH, ABP, LH, Testerone, and GNRH
|
|
|
inhibin
|
A protein hormone secreted by sustenacular cells of the testes that acts to inhibit the release of FSH and LH from the anterior pituitary.
|
|
|
sperm pathway
|
semineferous tubules
straight tubule rete testis efferent ductule head of epididymis body of epididymis body of epididymis tail of vas deferens ampula ejacularory duct prostatic urethra membraneous urethra penial urethra |
|
|
bulbourethral glands
|
tiny, pea
shaped glands inferior to the prostate, they produce a thick clear alkanline mucus that drains into the membranous urethra. acts to wash residual urine out of the urine when ejaculation of semen occurs. |
|
|
acrosome
|
head of the sperm that releases hydrolytic enzymes allowing it to enter the egg
|
|
|
hyaluronidase
|
enzyme that breakdown hyaluronidic acid
|
|
|
dartos muscle
|
in the scrotal wall, causes the skin of the scrotum to bel held close to the testes or to hang loosely, thus regulating the temperature for sperm production and survival (in cold water, they shrink)
|
|
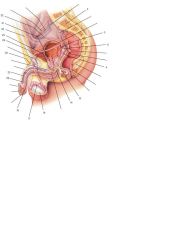
|
2 Sacrum
5 Opening of ureter 6 Ampulla of ductus deferens 9 Seminal vesicle 13 Ejaculatory duct 14 Bulbourethral gland and duct 16 Testis 17 Epididymis 18 External urethral opening 22 Corpus spongiosum 23 Corpus cavernosum 26 Suspensory ligament of penis 28 L. ductus deferens 29 Sphincter urethrae 30 Peritoneum 31 Prostate gland 32 R. ductus deferens |
|
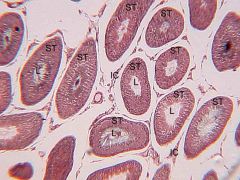
|
Seminiferous Tubules
Low Magnification ST-seminiferous tubules L- lumen IC- interstitial cells |
|
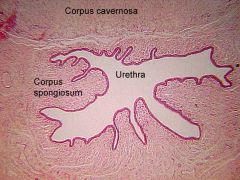
|
?
|
|
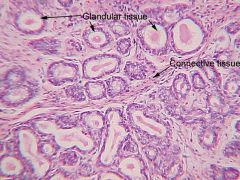
|
?
|
|
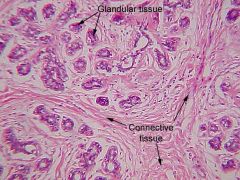
|
?
|
|
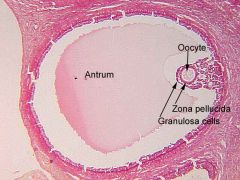
|
?
|
|
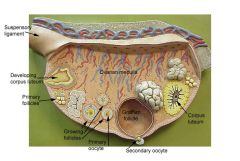
|
?
|
|
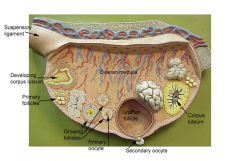
|
?
|

