![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
149 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
reproductive aging begin in ________________.
# follicles at 20 wks gestation? # follicles at birth? # follicles at menarche? follicular loss accelerates when the total number of follicles is _________. Menopause occurs when follicles are sufficiently depleted (# follicles < ________). |
embryonic life
20wks gestation = 6-7 M Birth = 1.5-2M Menarche = 300-400K follicular loss accelerates when total is about 25K Menopause at <1000 follicles |
|
|
Inhibin is produced by the ___________
|
granulosa cells of the follicle
|
|
|
________ declines with involution of the Corpus Luteum and ________ rises
|
Estradiol declines
FSH rises |
|
|
________ stimulates follicular development and consequently the production of which hormones?
|
FSH
estragiol and inhibin B |
|
|
major hormonal changes present in menopausal wome in comparison to younger women?
|
Day 3 FSH and estradiol are higher in menopausal women -- Why: fewer follicles in aged women, so less production of inhibin B and thus less inhibition of FSH from AP -- FSH will rise earlier, follicular development is advanced and thus production of estradiol is seen earlier. Also, overall FSH levels are higher in older women and rise in FSH seen earlier so we see a subsequent shorter follicular phase (or shorter time to ovulation) - shorter cycle
|
|
|
at what age does fertility begin to decline?
|
age 32. More rapid decline starting at 37-38yo
|
|
|
Define Perimenopause and its duration
|
follows period of declining fertility
period that preceeds menopause characterized by cycle irregularity (shortening then lengthening) and increasing sx durate = 2-8yrs with an average of 5 yrs |
|
|
how do you dx perimenopause?
|
clinical dx based on menstrual cycle pattern
early rise in FSH (3d level) + sx = helps you solidify dx rule out hypothyroid, depression, and hyperthyroid |
|
|
sx of perimenopause
|
vasomotor instability = 85% (hot flashes)
others: sleep disturbances mood disturbance somatic sx (fatigue, palpitations, HA, increased migraine (rise in E levels just before period can cuase this), breast pain, enlargemnt) oligomenorrhe to anovulation (heavier or irreg cycles) |
|
|
CA associ with perimenopause
|
endometrial CA
|
|
|
In managing perimenopause, what do you want to manage and what tx are best?
|
Endometrial CA prevention (OCP, Mirena, EPT)
Birth Control (OCP, Mirena) Menstrual Cycle Control (OCP) Sx Relief (OCP > EPT) Note: OCP = oral or ring EPT = estrogen plus progesterone |
|
|
define menopause and how do you dx?
|
12 months of amenorrhea - marks the end of reproductive life - egg depletion and estrogen no longer produced due to natural aging or surgery
clinical dx |
|
|
average age at menopause
|
51yo
|
|
|
factors that impact age at menopause
|
maternal age at menopuase
tobacco use (earlier) SES/Education ETOH use BMI |
|
|
Factors with no impact on menopause age
|
OCP use
parity race height |
|
|
key physical changes that occur with menopause
|
vasomotor instability
metabolic changes CAD accelerated bone loss skin changes urogenital atrophy cognition and libido loss = controverisal |
|
|
How long do hot flashes usually last?
|
#1 complaint to the physician
few seconds to several minutes usually most severe at night or during times of stress last from 1-2 yrs usually but can last up to 5yrs (35%) more common in overwt women |
|
|
How are hot flashes managed?
|
estrogen treatment (primrin) - short term use if fine; long term use CI with women having an intact uterus (use EPT instead); long term use is fine in women without a uterus
SSRI for women who can't take estrogen Alternatives: high dose progestins tibolone SSRI (paroxetine, fluoxetine) SNRI (velafaxine) Gabapentin |
|
|
CAM approaches to tx of hot flashes
|
Black Cohosh
Soy/phytoestrogens (bind estrogen receptors so may have same side effects as estrogens) |
|
|
mechanism of increased adipositiy of women in menopausal life
|
hormonal changes leading to higher adrogen levels and lowered E levels cause increased abdominal and intra-abdominal adiposity
|
|
|
What is the menopausal metabolic syndrome?
|
1. Lipid triad (high TGs, high LDL, low HDL)
2. Abnormalities in insulin (insulin resistance, decreased secretion and elimination that leads to hyperinsulinemia -- hormone tx can reduce onset of DM and improve insulin resistance) 3. other factors=increased BP, visceral fat, uric acid, decreased SHBG, increased PAI-1 (increases risk of thrombosis), increased endothelial dysfunction |
|
|
In order to provide cardioprotective effects, when should HRT be initiated?
|
In general HRT should not be continued or started to prevent heart disease
|
|
|
the greatest change in bone marrow density in the postmenopausal period occurs in the ________ yrs after menoapuse. fracture risk increases with __________
|
4-5 yrs after menopause but increases with age
fracture risk increases with age |
|
|
consequences of osteoperosis in menopausal women
|
SPINAL COMPRESSION FRACTURES (back pain, loss of height and mobility,postural deformities)
Colles' (forearm) fractures hip fractures tooth loss |
|
|
When does one measure MBD in postmenopausal women?
|
present with one or more of the following
65 or older caucasian family hx hx of fracture or falls bad eyesight demential early menopause (<45) smoker low body wt etoh immobility poor niturition meds certain medical condition |
|
|
prevention of osteoperosis in menopause
|
1500mg of Ca daily (one dairy servicng has 300mg) - divided doses w/ meals
400IU/daily of Vitamin D with 20mins/day of sunshine wt bearing exercise smoking cessation moderate ETOH intake (not recommended = HRT, raloxifene, bisphosphonates unless woman is osteopenic or can't tolerate hormones or has high risk factors) |
|
|
first line agents for the tx of osteoperosis for the prevention of fractures
|
bisphosphonates (limit osteoclast destruction of bone by b/coming incorportated in bone -- SE = osteonecrosis of jaw)
raloxifene (doesn't relieve hot flashes - give to older women w/o hot flashes; for younger women, give estrogen) SE = heart dz |
|
|
Urogenital sx assoc with menopause and tx
|
dysuria
urgency frequency recurrent UTI dysparunia pruritus stenosis tx = vag E (no prog needed) or HRT |
|
|
best relief for vaginal atrophy due to menopause
|
estrogen - vaginally
|
|
|
benefits of HRT
|
decreased hot flashes
prevents/tx osteoperosis and hip and vertebral fractures prevents/tx urogenital atrophy |
|
|
risks of HRT
|
increased risk for venous thrombosis and embolism (more if systemic - consider transdermal administration)
inc risk for breast CA with prolonged (>3-5yr use) -- EPT, not estrogen alone increased risk for endometrial cancer (w/estrogen alone -- not EPT) and only if uterus is present EPT - older women - possible increase in cardiac events -- contraversial probable increase in is chemic stroke in older women started on HRT BENEFITS OF HRT ARE DEPENDENT ON NUMBER OF MENOAPUSE RELEATED SX |
|
|
INDICATIONS FOR HRT
|
ESTROGEN DEFICIENCY SX:
vasomotor (night sweats, hot flashes) disturbed sleep patterns (fatigue, concentratoin, memory) GU atrophy (bladder irritability, vaginal dryness, dyspareunia) min dose for shortest time req and consider non-hormonal alt |
|
|
evaluate all post menopausal over 65 for ________
|
osteoperosis
|
|
|
Causes of perimenopause
|
surgical removal of uterus, ovaries, or premature ovarian failure (sex chromosome abnormalities usually involving x chromosome, fragile X premutation, autoimmune, chemo/RT)
screen all perimenopausal women for fragile X |
|
|
evaluation of premature ovarian failure with perimenopausal women
tx? |
karyotype (<30yo)
asess fragile X premutation by number of CGG repeates autoimmune (hypothyroid, adrenal insuff) HRT!!! counseling -- oocyte donatin if they want to still have kids unless they have turner's which carries a high mortality in PG and is one cause of POF |
|
|
sx of menopause tend to mirror those of ________
|
HIV
mean age of HIV infected women is 47-48 -- safety of HRT in HIV not studied currently |
|
|
most common Gyn CA
|
endometrial cancer Type I
- estrogen related - less aggressive - younger and heavier - low grade histology - perimenopausal have better prognosis - 80% with PTEN mutation and only some with p53 mutation, - ER/PR+ - defects in DNA mismatch repair - associated with KRAS2 |
|
|
most common endogenous risk factor associated with endometrial cancer type I subtype
|
obesity (>30lbs = increased 3x; >50lbs = increased 10x)
unopposed estrogen - 9.5xrisk (others = nulliparity, htn, tumors, high fat diet, other CA, amenorrhea, DM, PCOS, Liver dz, caucasian, no exercise) |
|
|
exogenous risk factors for endometrial cancer
|
pelvic irradiation
hormone therapy tamoxifen (antiestrogen effects in breast but estrogen effects in uterus) sequential OCP combination OCP = protective (against undue proliferation) |
|
|
Most common single agents causing PID
PID caused by bacteria assoc with IUDs? other couases secondary to tissue damage + infection? |
N gonorrhea
Chlamydia Mycoplasma Actinomyces -- assoc with IUDs (infections are typically polymicrobial, but single agent causes = first two listed) (can also be caused by E coli, staph, strep, clostridium, bacteroides -- 2nd infection following tissue damage) |
|
|
symptoms of PID
|
pelvic pain
dysmenorrhea menstrual abnormalities Acute abdomen |
|
|
complications
|
infertility from tubal scarring
ectopic pregnancy peritonitis intestinal obstruction from adhesions bacteremia |
|
|
numerous neutrophils within the tube lumen
|
acute salpingitis
|
|
|
chronic salpingitis is commonly associated with what complication? how does it present? what are predisoposing factors? dx? complications? tx?
|
ectopic pregnancy
(pelvic pain w/ or w/o menstural irregularity) risk factors = anything altering the normal structure/function of the tube = PID, prior pelvic surgery, endometriosis dx = HCG level + U/S Complications = rupture and hemorrhage tx? MTX - terminates the PG and given when the conceptus is smaller than 4 cm |
|
|
most common tumors found in the fallopian tubes
|
mets (adenocarcinomas similar to those seen in the ovaries), implants from ovarian or endometrial tumors >>> primary tumors
|
|
|
what type of mutation presents a risk for tubal carcinoma?
where is it most likely found? |
BRCA1 mutation
fimbriated region |
|
|
most common fallopian tube tumor
most common fallopian tube primary malignancy |
adenomatoid tumor (small, circumcribed, mesothelial origin)
adneocarcinoma (50-60yo, bilateral 25%, poor prognosis b/c of late stage detection, tx like ovarian CA) |
|
|
most common cause of enlarged ovaries
|
cysts
|
|
|
cysts arising from invaginated surface epithelium
|
serous cysts or simple cysts
|
|
|
follicular and corpus luteal cysts are considered _________ and arise from ___________
causes |
functional cysts
arise from ovarian follicles follicular cysts = related to abnormalities in pituitary gonadotropin release corpus luteum cyst results from delayed resolution of corpus luteum's central cavity |
|
|
characterized by inappropriate gonadotropin secretoin, hyperandrogenemia, increased peripheral conversion of androgens to estrogens, chronic anovulation, polycystic ovaries
|
PCO (polycystic ovaries)
|
|
|
common presentation:
secondary amenorrhea or oligo infertility hirsutism hx of premenarcheal obesity in 3rd decade |
PCO
|
|
|
prolonged or excessive uterine bleeding occurring irregularly and more frequently than normal
causes? |
menometorrhagia
caused by hormonal imbalance endometriosis uterine fibroids cancer (can lead to anemia) |
|
|
pathogenesis of PCO
|
increased ovarian production of androgens due to abnormal regulation of 17ahydroxylase (expressed in ovary and adrenal gland) --- this causes :
1. premature follicular atresia (resulting in anovulation and decreased progesterone and subseq increased secretion of LH) 2. hyperandrogenemia (resulting in hirsuitsim, acen, adnrogen dependent allopecia) 3. multiple follicular cysts 4. persistent anovulatory state this results in conversion of excess androgens to estrogens in peripheral adipose -- long term effects of unopposed E are endometrial hyperplasia and adenocarcinoma insulin resistence also noted |
|
|
carcinoma that tends to present at high stage is cause of 1/2 deaths related to tumor of the female genital tract
risk factors? |
ovarian carcinoma
risk factors = older age, nulliparity, family hx of ovarian or breast CA (think common epith neoplasms here b/c these account for over 90% of ovarian cancers) |
|
|
3 cell origins from which ovarian cancers arise
|
serosal epithelium
germ cell gonadal stromal |
|
|
most important prognostic factor in OVCA
|
stage/extent of dz at presentation
(other = histologic type -- serous/clear cell = poor prognosis; grade; amount of residual tumor following surgical debulking) |
|
|
benign surface epith tumor of the ovary that has a think, translucent wall, lined by a single layer of cilaiated tubal type epithelium, smooth walls
|
cystadenoma
|
|
|
lining of benign serous cystadenom is ________
|
non-stratified serous epithelium
|
|
|
ovarian epithlial tumor characterized by papillary excrescenses from the cyst wall
|
tumors of low mlaignant potential OR atypical proliferating tumors
|
|
|
malignant epithelial tumor that cystic and solid or just solid -- most common malignancy of the ovary
|
cystadenocarcinoma
|
|
|
multiple psammoma bodies may be seen in association with what type of ovarian tumor?
|
cystadenocarcinoma or serous carcinoma
these are lamellated purple caclifications |
|
|
__________ is an epith tumor of the ovary with a complex, confluent glandular architecture formed by mucinous type epith
|
mucinous adenocarcinoma
mucin = gray within cell cytoplasm those that lack benign or borderline components are often mets from GI sites such as appendix or colon |
|
|
adenocarcinoma from epith origin of ovary that is composed of malignant glands arranged in acribrioform pattern composed of mucin producing columnar cells
|
endometroid adenocarcinoma
(occurs mostly after menopause, most of these tumors are malignant and 1/2 are bilateral) |
|
|
epith adenocarcinoma of ovary that often occurs in assoc with endometriosis -- displays sheets of malignant cells with clear cytoplasm
|
clear cell adenocarcinoma
rare tumors of the ovaries that are almost always malignant |
|
|
neopolasms derived from granulosa cells, theca, sertoli, leydig or fibroblast cells -- may produce E or Androgens
|
sex cord stromal tumors of the ovary
|
|
|
Typically benign, 75% of sex cord stromal tumors, peak presentaion during perimenopause -- solid, white tumors = 1/2 well differentiated spindle cells + collagen
|
fibroma (sex cord stromal tumor of the ovary)
|
|
|
think post meno women ; always benign, produce estrogens and adrogens so in premen women, irregularity of emnstrual cycle and breast enlargement is common
|
thecoma (sex cord stromal tumor of the ovary)
|
|
|
may be associated withMeigs syndrome = triad of ovarian fibroma, ascites, hydrothorax
|
fibroma of the ovary
|
|
|
associated with precocious puberty -- tumor that secretes estrogen and sig cause of benign endometrial hyperplasia and assoc with endometrial carcinoma
|
granulosa cell tumor (sex cord stromal tumor of the ovary)
- estrogen secretion = cause of complications |
|
|
solid tumor of the ovary with focal hemorrhages and lipid laden luteninzed granulosa cells -- characteristic follicular patern of tumor cells around central spaces on microscopy
|
granulosa cell tumor -- Call Exner bodies!!
|
|
|
comprise 60% of ovarian neoplasms in children and adolescents -- 1/3 are malignant
|
germ cell tumors (from primitive germ cells of embryonic gonad)
|
|
|
ovarian tumor common in women <20
ovarian tumor common in women >20 ovarian tumor common in women of all ages |
germ cell tumor
surface epith tumor sex cord-stromal tumors |
|
|
most common ovarian germ cell tumor in adults
|
usually occur in women <20, but in adults, benign mature cystic teratomas (aka dermoid cysts) are most common
germ cell tumors are usually malignant in kids and benign in adults |
|
|
most common ovarian cancer in children
|
germ cell tumors
|
|
|
malignant germ cell tumor that is analagous to the testicular seminoma
|
dysgerminoma
|
|
|
aggressive germ cell tumor of the ovary that secretes HCG
|
choriocarcinoma
|
|
|
germ cell tumor of the ovary that produces AFP and analogous to endodermal sinus tumor fhte testis
|
yolk sac tumor (endodermal sinus tumor)
this is malignant |
|
|
germ cell tumor of the ovar thtat is derived from 2 or 3 embyronic layers - can be mature (benign) or immature (malignant)
|
teratoma
|
|
|
Genetic tumor cells are diploid genetically (46XX)
Peak incidence in third decade Due to endoreduplicatoin of haploid germ cells |
mature cystic teratoma or dermoid cyst = 20% of ovarin tumors and 90% of germ cell tumors
(cyst lined by skin, including hair follicles, bone, tooth cartilaget, focal calcifications etc may be present) |
|
|
ovarian tumor composed of embyronal tisuse and three germ layers -- usually solid, lobulated, with multiple small cysts and solid areas containing immature bone and cartilage
|
immature teratoma
|
|
|
Usually unilateral germ cell tumor
Presents in women under the age of 30 2nd most common malignant germ cell tumor Extensive necrosis and hemorrhage Honey comb structure micro Secretes AFP |
yolk sac tumor or endodermal sinus tumor
|
|
|
germ cell tumor associated with schiller duval body
|
yolk sac tumor or endodermal sinus tumor
|
|
|
germ cell tumor that manifests in young girls as precocious sexual development, menstrual irregularities, or rapid breast enlargment
|
chriocarcinoma
highly aggressive responds to chemo secretes HCG (so + PG test) bilateral theca lutein cysts may be found |
|
|
characteristics of mets to the ovaries
|
multinodularity (usually remove both ovaries even if only one found to be positive)
bilateral mcc primary sites = breast (lobular carcinoma) > lg intestine > endometrium > stomach of GI origin = krukenburg tumor -- stomach, colon, pancreas, appendix |
|
|
most common site of met to ovary being the stomach, ovarian cells replaced bilaterally by mucin secreting signet ring cells
|
krukenburg tumors
stomach = 75% of origin colon = next mcc |
|
|
give the type of ovarian tumors the following are markers for:
CA125 CEA AFP HCG Inhibin |
CA125 - serous/endometrioid
CEA = mucinous yolk sac tumor = AFP HCG = choriocarcinoma inhibin = granulosa cell tumor |
|
|
clear cytoplasmic vacuoles are seen in the ______ phase of hte endometrium wherease mitotic figures are more characteristic of the ________ phase
|
secretory
proliferative |
|
|
abnormal uterine bleeding secondary to ovulatory dysfunction is ______
must exclude with dz first before dx? |
DUB = dysfunctional uterine bleeding
polyps carcinoma exogenous hormones complications of pregnancy postmenopausal blleeding |
|
|
main causes of DUB
|
anovulatory cycles (most common cause)
luteal phase abnormalities |
|
|
cuases of the following:
acute endometritis chronic endometritis pyometra |
Acute: think staph aureus or trept -- spontaneous abortion; currettage; post-partum -- presence of PMNs in the endometrium usually from ascending infection of cervix after breach of cervical barrier
Chronic: PID, IUD (actinomyces), retained products of conception, TB PYO = pus in endometrial cavity -- secondary to cervical stenosis |
|
|
endometritis presentation
|
bleeding, pelvic pain, or both
|
|
|
endometrial glands and stroma in ectopic locations
mcc site of involvement? sx? complication? |
endometriosis
ovaries > uterine ligaments > rectovaginal seputm > pelvic peritoneum menstrual related pain ' NOT cancer (unless longstanding -- then endometroid adenoCA or clear cell adenoCA)-- think infertility |
|
|
chocolate cysts -- think
|
endometriosis -- menstrual type bleeding in ectopic endometrium resulting in blood filled cysts
|
|
|
presence of endometrial glands and stroma within the myometrium presenting with abnormal bleeding and pain
|
adenomyosis
due to downgrowth of endometrial basalis into myometrium 20% of uterus have this upon removal |
|
|
uterus is thick, not nodular, presents with multiple tiny hemorrhagic cysts
sx of abnormal bleeding and pain |
adenomyosis
|
|
|
benign focal hyperplasia of the basalis with sx of abnormal bleeding
|
endometrial polyp
|
|
|
endometrial hyperplasia is caused by __________
what are the subtypes? |
unopposed estrogen
simple hyperplasia w/o atypia (prop increase in glands and stroma) complex hyperplasia without atypia increase glands > increase in stroma atypical hyperplasia simple or complex w/ cytologic atypia |
|
|
risk of progression of endometrial hyperplasia to carcinoma by subtype
|
simple hyperplasa = 1% over 10-15yr
complex hyperplasia = 3% over 10-15yr atypical hyperplasia = 25-35% over 4-5 yrs |
|
|
mcc invasive CA of the female genital tract and 4th most common CA in women
|
endometrial adenocarcinoma
|
|
|
endometrial CA associated with unopposed estrogent, premen, perimen, hyperplasia, low grade, minimal invasion, stable behavior
subtype? mutation? |
type 1
endometrioid PTEN |
|
|
endometrial CA associated with no unopposed estrgen, postmen, no hyperplsia, high grade, deep invaskion and progressive behavior
subtype? mutation? |
type II
serous, clear cell p53 |
|
|
receptor status of endometrial adenocarcinoma that is more favorable
|
ER/PR +
|
|
|
most common uterine tumor and most common of all tumors in women
|
leiomyoma (bening smooth muscle tumor)
increased incidence in AA women |
|
|
leiomyomas lie within the ___________ and have sx of ________________
usually senstivie to ________ |
myometrium
subendometrial or subperitoneal locations sx = mennorhagia Estrogen |
|
|
cause of leiomyosarcoma
appearance? |
usually never due to malignant transformtion of leiomyoma to malignancy
arises de novo lack whorled appearance and not as sharply circumscribed (as with leiomyoma) |
|
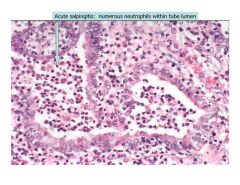
|
acute salpingitis
|
|
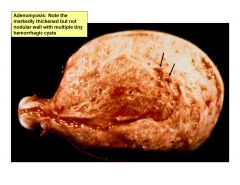
|
adenomyosis
|
|
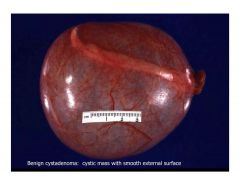
|
benign cystadenoma
|
|
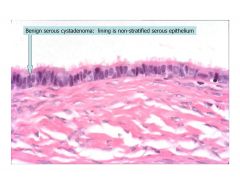
|
benign cystadenoma
|
|
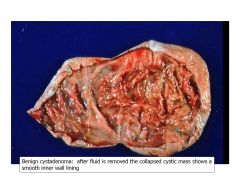
|
benign cystadenoma
|
|
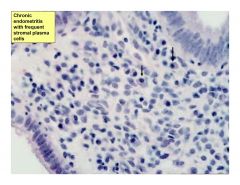
|
chronic endometritis
|
|
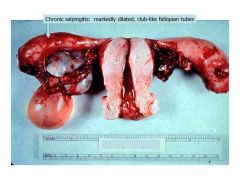
|
chronic salpingitis
|
|
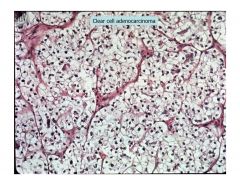
|
clear cell adenocarcinoma
|
|
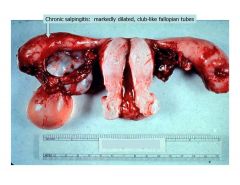
|
chronic salpingitis
|
|
|
type of inheritance?
vertical transmission = each generatoin males and females affected in equal frequency unaffected individual do not transmit the phenotype |
autosomal dominant
(affected parent has 50% chance of transmitting phenotype ) |
|
|
for most single gene d/o with AD inheritance, only the _____ phenotype is known
|
heterozygous
usually, homozygous phenotype is not viable (SAB) exception = Hungtingtons's Disease - vast majority are heterozygous |
|
|
AD defects are usually with ________
|
proteins
rarely involve enzyme defects |
|
|
delayed manifestation of dz
incomplete penetrance sporadic cases variable expressivity germline/somatic mosicism all are characteristics of what pattern of inheritance? |
AD
sporadic appearing -- could be due to a new mutation (ex: achondroplasia - 80%; NF1 = 50%) also, think about variable expressivity due to incomplete penetrance (tuberous sclerosis) |
|
|
AD d/o assoc with new mutations are often associated with __________
|
advanced paternal age
|
|
|
What do these diseases have in common?
achondroplasia Huntingtons Dz osteogenesis imperfecta tuberous sclerosis von Willebrand's Dz NF1 NF2 |
all AD dz
most common AD dz is von Willebrand's dz |
|
|
males and females affected equally
only one generation affected or skipping generation parents are typically unaffected carriers |
AR inheritance pattern
associated with consanguinity |
|
|
most common type of mendelian gene d/o
|
AR
|
|
|
AR sx usually have onset during _______ phase of life
|
early
|
|
|
sickle cell and CF have what in common
|
both AR resulting in protein defect
(most AR d/o involve enzyme deficiencies) |
|
|
inborn errors of metabolism most commonly have what type of inheritance pattern
|
AR (think enzyme deficiency)
|
|
|
affected males transmit the mutant gene to all daughters = characteristic of ________ inheritence?
and daughters are usually asym? |
X linked
asym? = X linked recessive |
|
|
no male to male transmission
males are affected, but generally not females female has 1/4 chance of conceiving an affected son asymptomatic females transmit d/o to 50% of offspring |
x-linked recessive
|
|
|
in what event will an X linked recessive d/o manifest sx in a female?
|
1. maternally derived X w/o mutant gene invactivated, leaving the mutant X from paternal side active = skewed X inactivation
2. only one structurally normal X in female -- contains mutant gene |
|
|
risk of offspring affected by dz if sex is unknown is calculated by ?
|
risk of having inherited gene x 1/2 (accounts for 50/50 chance of being male or female)
|
|
|
dz that is X linked recessive where 1/2 of cases represent new mutations and 2/3 of the time the mother is a carrier
|
duschenne's muscular dystrophy
applies to case where only one male is affected in pedigree -- can either be a new mutation or from carrier - here the carrier is most likely to be mom b/c DMD males usually do not survive to reproduce |
|
|
most common type of proteins affected in XR d/o
|
enzymes
|
|
|
what inheritance pattern do these have?
Lesch-Nyhan Fragile X agammaglobulinemia (bruton's) CGD testicular feminization |
XR
|
|
|
MCC mendelian d/o that causes mental retardation
|
Fragile X (XR inheritance)
|
|
|
affected males have all affected daughters and no affected sons
variable expressoin in females |
X-linked Dominant
|
|
|
chance of affected female in an XD d/o transmitting it to children is _______
|
50% - regardless of sex
|
|
|
acrocentric chromosomes
|
13,14, 15, 21,22
short arms of these chromosomes contain redundant genetic material -- loss of the short arm does not confer an abnormal phenotype |
|
|
what are problems of early growth development that are indicated for obtaining a karyotype/microarray?
|
FTT
developmental delay dysmorphic facies multiple malformations short starture ambig genitalia mental retardation |
|
|
indications for karyotype/microarray
|
problems of early gorwth and develpment
stillbirth/neonatal death (7-10% +) fertility problems (3-6%+) family hx w/ 1st degree relative neoplasia PG of AMA births defects by US anbormal maternal serum screen |
|
|
abnormal chromosome number with not structural abnormality is assicated with (normal or abnormal phenotype) usually?
|
abnormal phenotype
facts that can produce a milder or undetectable phenotype include mosaicism (nondisjunction in mitosis) and sex chromosome aneuploidy |
|
|
karyotypes with an abnormal number with no structural abnormalities = _______
|
unbalanced
don't karyotype the relatives -- due to nonkisjunctoin - parents offered prenatal dx in future PG |
|
|
abnormal karyotype containing a structural abnormality may be _________ and associated with a noraml phenotype
|
balanced
structural abnormalities can be inherited or de novo |
|
|
is a translocation balanced or unbalanced?
|
can be either
|
|
|
most common robertsonian translocations?
|
13q14q and 14q21q
2 acrocentric chromosomes fuse at long arms with loss of short arms |
|
|
"der" means?
|
structural abnormality involving 2 or more chromosomes
|
|
|
karyotypes with a balanced robertsonian translocatoin have ____ chromosomes
|
45
loss of short arms don't matter -- long arms fuse -- one less chromosome |
|
|
___________ occur between usually 2 non-homologous chromosomes with receprocal exchange of parts. the total number of chromosomes in this type of tranlocation when balanced = ?
|
balanaced reciprocal translocations
46 -- remains unchanged still have risk of ;passing unbalanced chromosomes to offspring |
|
|
in translocations, normal phenotypes result when ...
|
no detectable significant material is lost or gained
|
|
|
der del and add signify what types of karyotypes
|
abnormal chromosome - unbalanced
can also have extra or missing chromosome copy (aneuploidy) = +21 or -21 |

