![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
98 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Pathogenesis of Bartholin cyst.
|
preceding infection (gonorrhea) -> obstruction of Bartholin duct.
|
|
|
What is this disease?
- painful chronic inflammation of submucosal gland posterior to introitus with overlying ulcers |
vestibular adenitis
|
|
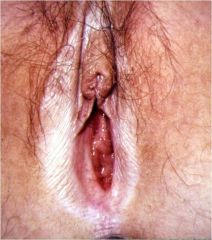
What is this called?
|
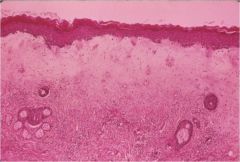
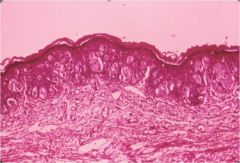
Vulvar dystrophy (lichen sclerosis type)
- white patchment like skin - hyperkeratosis, thinned epidermis with atrophy of adenexa - hyalinized and edematous dermis |
|
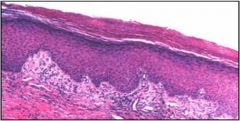
This lesion occurs on the vulvar, itchy, thick epithelium.
|
Vulvar dystrophy (lichen simplex chronicus)
- thickened epithelium - hyperkeratosis - dermal inflammation |
|
|
Is vulvar dystrophy pre-malignant?
|
not if no coexisting dysplasia
|
|
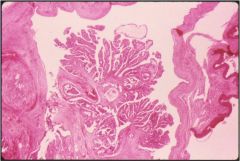
What is this?
- painful module on labia majora |
Papillary hiradenoma
- benign tumor of apocrine sweat gland |
|
|
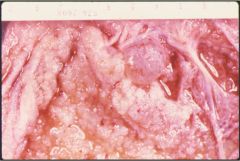
What is this disease? What would you see histologically?
- raised or flat warty surface on labia, often coalesce - STD |
condyloma acuminatum
- koilocytes: virally infected cells - assoicated with low risk HPV |
|
|
This is a lesion fond on the vulva.
- acanthosis - associated with high risk HPV(16,18) |
VIN I
- mild dysplasia - nucleomegaly, koilocytosis - atrophic on non-dysplastic epithelium |
|
|
What are some malignant tumors of the vulva?
|
- vulvar squamous cell carcinoma
- extramammary paget disease |
|
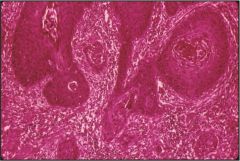
What is this vulvular disease?
Gross - exophytic or ulcerated growth |
vulvar squamous cell carcinoma
- invasive nests of dysplastic squamous cells - risk factors: HPV16, smoke, immunodeficiency |
|
|
What is this persion's prognosis of vulvar squamous cell carcinoma?
- 35 yrs old - pre-existing dysplasia (VIN) |
good prognosis
|
|
|
What is this persion's prognosis of vulvar squamous cell carcinoma?
- 65 yrs old - with dystrophies and dysplasia - p53 overexpression |
poor prognosis
|
|
|
Prognosis of vulvar squamous carcinoma is poor if ____.
|
- tumor size: >2cm diameter, > 1mm depth
- lymphatic invasion |
|
|
Where does vulvar squamous cell carcinoma first metastasize to?
|
inguinal nodes
|
|
What is this vulvular disease?
- pruitic, red, sharply demarcated lesion |
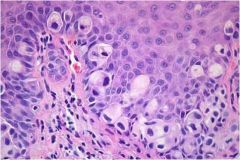
extramammary paget disease
- intraepithelial nests of atypical glandular cells with abundant cytoplasm (mucin containing) |
|
|
Compare mammary and extra-mammary paget disease.
|
extramammary paget
- mucin containing intraepithelial glandular cells - good prognosis if completely in situ mammary paget disease - mucin stain negative - associated with underlying carcinoma - poor prognosis |
|
|
What are some malignancies associated with vagina?
|
- squamous cell carcinoma (95%)
- vaginal adenocarinoma - rhabdomyosarcoma (sarcoma botryoides) |
|
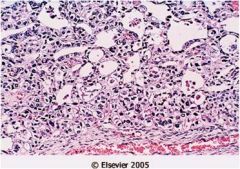
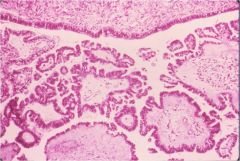
What is this vaginal disease? what is the precursor lesion?
- mom used DES during pregnancy |
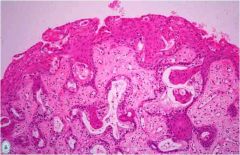
This is vaginal adenocarcinoma clear cell type (vacuolated tumor cells forming glands and clusters). Cervix also at risk.
Precursor lesion: vaginal adenosis (see picture): columnar epithelium replaces squamous cells) |
|
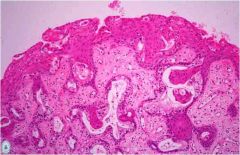
What is this vagional lesion? what might it progress into if not treated?
|
Vaginal adenosis
- columnar epithelium replaces squamous cells - may progress to vaginal adenocarnoma |
|
|
What is the most common vaginal malignancy?
|
squamous cell carcinoma(95%)
|
|
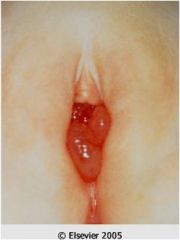
What does this 5 yr old girl has?
|
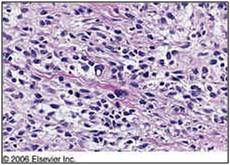
rhabdomyosarcoma (sarcoma botryoides)
- locally invasive - treat surgically with chemo |
|
|
Where does this metastasize to?
- vaginal carcinoma of lower 1/3 |
inguinal nodes
|
|
|
Where does this metastasize to?
- vaginal carcinoma of upper2/3 |
pelvic nodes
|
|
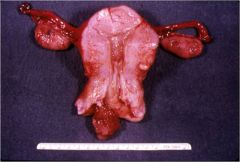
What is this cervial lesion?
- spotting, bleeding gross - soft, filled with cystic mucus glands |
benign endocervical polyps
- dense fibrous stroma surfaced by endocervical epithelium |
|
|
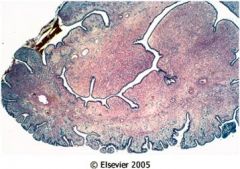
What is the histological progression of CIN?
|
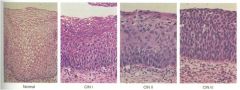
|
|
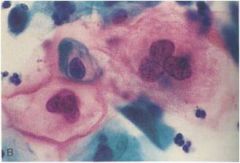
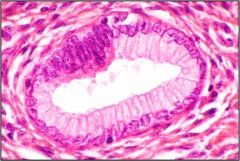
Which stage of CIN is this based on this pap smear?
|
CIN I
- 3x of size of nucleus |
|
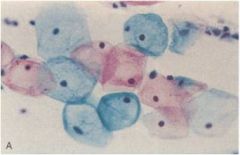
Which stage of CIN is this based on this pap smear?
|
Trick question! this is completely normal.
|
|
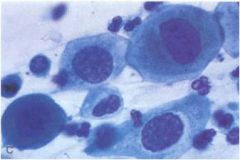
Which stage of CIN is this based on this pap smear?
|
CIN II
- big nucleus - basophilic cytoplasm |
|
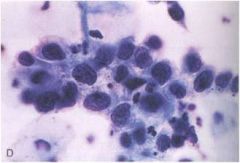
Which stage of CIN is this based on this pap smear?
|
CIN III
- small hyperchromic - high N/C ration |
|
|
What is the mean age of women who develop CIN?
|
30
|
|
|
What are some malignancies associated with the cervix?
|
- squamous carcinoma (75-90%)
- adenocarcinoma (10-25%) |
|
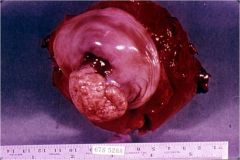
50 yr old lady developed a mass on the cervix.
|
squamous carcinoma of cervix
- exophytic/ulcers/infiltrative |
|
|
Squamous carcinoma of cervix: mirco or grossly invasive?
- width< 7mm - depth < 3mm |
microinvasive (minimal)
|
|
|
Squamous carcinoma of cervix: mirco or grossly invasive?
- width < 7mm - depth 3-5 mm |
microinvasive (microscopic)
|
|
|
Squamous carcinoma of cervix: mirco or grossly invasive?
- width < 7mm - depth > 5mm |
microinvasive (macroscopic)
|
|
|
Squamous carcinoma of cervix: mirco or grossly invasive?
- width > 4cm |
grossly invasive
|
|
|
Staging of squamous carcinoma of cervix:
- invasion < 5mm - within cervix |
stage IA
- 90% 5 yr survival |
|
|
Staging of squamous carcinoma of cervix:
- invasion > 5mm - within cervix |
stage IB
- 86% 5 yr survival |
|
|
Staging of squamous carcinoma of cervix:
- extend beyond cervix - spares lower 1/3 of vaginal and pelvic wall |
stage II
- 70% 5 yr survival |
|
|
Staging of squamous carcinoma of cervix:
- externd beyond pelvic wall or - extend beyond lower 1/3 of vagina |
stage III
- 35% 5 yr survival |
|
|
Staging of squamous carcinoma of cervix:
- extend beyond true pelvis or - involve bladder or rectum |
stage IV
- <25% 5 yr survival |
|
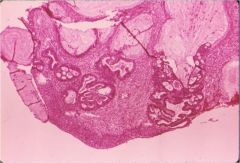
This lesion is on the cervix, HPV associated more than DES.
|
Adenocarcinoma in situ
|
|
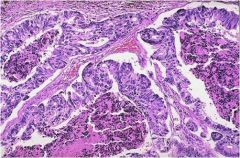
This lesion is on the cervix, HPV associated more than DES.
|
adenocarcinoma (invasive)
|
|
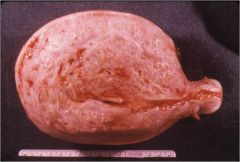
What is this disease of the uterus?
- menorrhagia - dysmenorrhea - pelic pain |
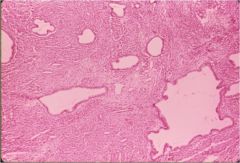
adenomyosis
- invagination of stratum basalis in myometrium -> glands and stroma thicken myometrial tissue -> uterine enlargement - cystic endometrial glands within abundant endometrial stroma |
|
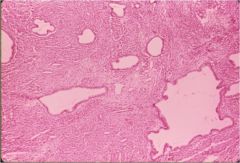
What is this disease of the cervix?
Gross - thickened myometrium with hemorrhagic spots |
adenomyosis
- invagination of stratum basalis in myometrium -> glands and stroma thicken myometrial tissue -> uterine enlargement - cystic endometrial glands within abundant endometrial stroma |
|
|
Pathogenesis of adenomyosis.
|
adenomyosis
- invagination of stratum basalis in myometrium -> glands and stroma thicken myometrial tissue -> uterine enlargement |
|
|
Pathogenesis of endometriosis.
|
endometrial glands and stroma outside the uterus
- reverse menses (most common) - coelomic metaplasia (vascular or lymphatic spread) |
|
|
What is this disease?
- dysmenorrhea - painful stooling - intestine obstruction and bleeding during menses - risk for ectopic pregnancy |
endometriosis
|
|
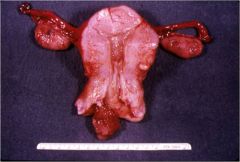
What is this disease of the uterus?
- dysfunctional bleeding |
endometrial polyp
- proliferation of endometrial glands and stroma, may contain endometrial hyperplasia or carcinoma - dilated glands and abundant endometrial stroma |
|
|
Pathogenesis of EIN.
|
- prolonged high level of estrogen stimulation with diminshed progesterone: anovulation/high-dose estrogen therapy
- inactivation of PTEN |
|
|
What are some types of EIN?
|
- simple hyperplasia without atypia: increased number of dilated glands, no glandular crowding
- complex hyperplasia without atypia: increased number of dilated glands with braching, glandular crowding - hyperplasia with atypia: glandular crowding, dysplastic epithelium, risk for endometrial cancer - hyperplasia with squamous metaplasia |
|
|
Whch gene is involved in pathogenesis of EIN and endometrial carcinoma?
|
PTEN inactivation
|
|
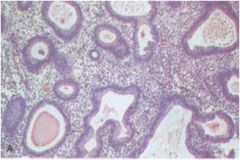
Which type of EIN is this?
- dysfunctional uterine bleeding |
simple hyperplasia without atypia
- increased number of cystically dilated glands - no glandular crowding |
|
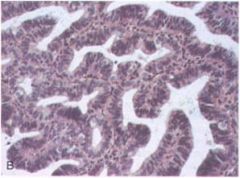
Which type of EIN is this?
- dysfunctional uterine bleeding |
complex hyperplasia without atypia
- increased number of dilated glands with branching - glandular crowding |
|
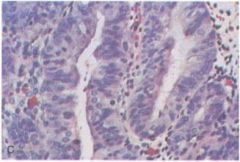
Which type of EIN is this?
- dysfunctional uterine bleeding |
hyperplasia with atypia (high grade)
- glandular crowding - dysplastic epithelium - risk for endometrial cancer |
|
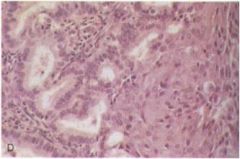
Which type of EIN is this?
- dysfunctional uterine bleeding |
hyperplasia with squamous metaplasia
|
|
|
What is the most common gynecologic tumor?
|
endometrial carcinoma
- adenocarcinoma (85%) |
|
|
What are the two types of endometrial carcinoma? What are some differences?
|
1) endometreoid type
- estrogen driven, well differentiated - PTEN inactivation - hyperplasia is the precursor - better prognosis - micro: no stroma 2) papillary serous type - P53 mutation - hyperplasia is not a precursor - less favorable prognosis |
|
|
What is the cutoff thickness of endometrial carcinoma for grading of invasion?
|
1/2 thickness of myometrium as cutoff for invasion
|
|
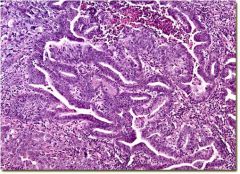
What is this disease of the uterus?
- obese women with no previous pregnancies, late menopause |
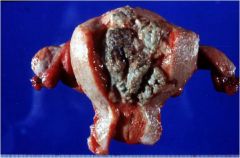
endometrial adenocarcinoma (endometreoid type)
- no stroma, well differentiated cells - PTEN inactication |
|
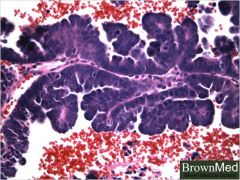
What is this disease of the uterus?
- obese old white lady on estrogen replacement therapy |
endometrial adenocarcinoma (papillary serous type)
- P53 mutation - high grade |
|
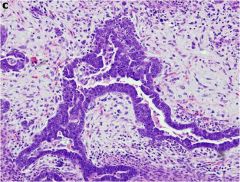
What is this disease of the uterus?
- post menopausal women - gross: bulky necrotic mass protruding through cervical os - dysfunctional bleeding |
malignant mixed mullarian tumor
- endometrial carcinoma + malignant mesenchymal tumor |
|
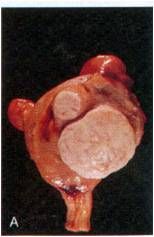
What is this disease of the uterus?
- most common neoplasm in women |
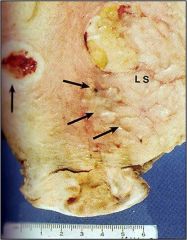
Leiomymoma ("fibroids")
- estrogen driven - dysfunctional uterine bleeding - do not transform into leiomyosarcoma - micro: well differentiated spindle cells of smooth muscle origin |
|
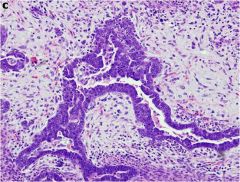
What is this disease of the uterus?
- post menopausal women - gross: bulky necrotic mass protruding through cervical os - dysfunctional bleeding |
malignant mixed mullarian tumor
- endometrial carcinoma + malignant mesenchymal tumor |
|
|
Do leiomyoma transform into leiomyosarcomas?
|
No
|
|
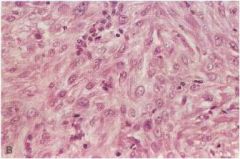
What is this disease of the uterus?
|
leiomyosarcoma
- invasive margin - rare - prone to recur |
|
|
What is the most common cause of PID in the U.S?
|
chlamydia
|
|
|
What is the criteria for primary fallopian tube tumors?
|
- bulk of the tumor must be in the tube
- must demomstrate origin from tubal mucosa |
|
|
What is the most common tumor associated with fallopian tube?
|
papillary serous adenocarcinoma
|
|
|
Is it common to see primary malignancies in the fallopian tube?
|
rare
|
|
|
What gene is associated with fallopian tumors?
|
BRCA mutations
|
|
|
Name 2 cystic diseases of the ovary.
|
- follicular and luteal cysts
- PCOD |
|
|
What are the top 3 most common cancer in female genital tract?
|
1. endometrial
2. cervical 3. ovarian |
|
|
Benign or malignant?
- 80% of all ovarian tumors - younger women (20-45) - can be bilateral |
benign
|
|
|
Benign or malignant?
- 20% of all ovarian tumors - older women (40-65) - can be bilateral |
malignant
|
|
|
What is the most comon tumor in ovaries?
|
- surface epithelial tumors (65-70%)
- germ cell tumors (10-20%) |
|
|
What is the most common tumors in the ovary?
|
- surface epithelial tumors (65-70%)
- germ cell tumors (10-20%) |
|
|
What type of ovarian surface epithelial cell tumor is this?
- cysts lined by ciliated cells (similar to follopian tube) |
serous type
|
|
|
What type of ovarian surface epithelial cell tumor is this?
- cysts lined by mucus secreting cells (similiar to endocervix) |
mucinous type
|
|
|
What type of ovarian surface epithelial cell tumor is this?
- not much stroma (similar to endometrial cancer) |
endometroid type
|
|
|
What is the prognosis of this surface epithelial cell tumor?
- not capsulated |
poor prognosis
|
|
|
Is this surface epithelial cell tumor benign or malignant?
- grossly solid, necrotic - papillaty lining of the cysts - thickened cyst lining |
malignant
|
|
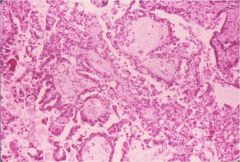
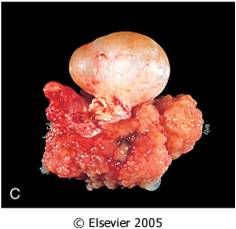
What type of surface epithelial cell tumor is this?
|
serous cystadenocarcinoma
|
|
What of surface epithelial cell tumor is this?
|
serous borderline tumor
|
|
|
What are the most common germ cell tumor in the ovary?
|
benign cystic teratomas (dermoid cysts)
|
|
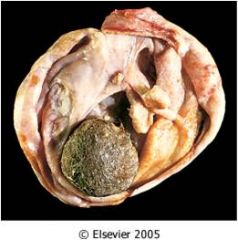
What is this called? How does it look under microscope?
|
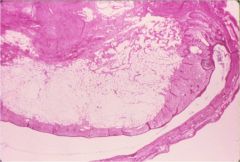
mature cystic teratoma (dermoid cysts)
- squamous epithelium and skin appendages (ectoderm), adipose tissue (mesoderm) |
|
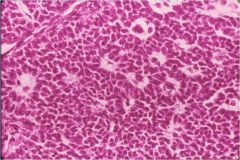
What is this tumor of the ovary?
|
granulosa cell tumor (more common sex cord stromal tumor)
- follicular like structures (Exner bodies) - risk for carcinomas - make estrogen |
|
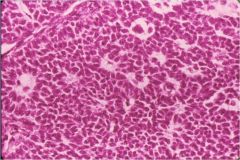
What is the disease?
- postmenopausal women present with new onset vaginal bleeding |
Granulosa cell tumor
- secrete estrogen |
|
|
What are some risk factors for ectopic pregnancy?
|
- PID
- tubal adnesions secondary to endometriosis - appendicitis - prior surgeries |
|
|
Identical or fraternal twins?
- monochorionic monoamnionic |
identical
- separatest no later than 21 days after |
|
|
Identical or fraternal twins?
- monochorionic diamnionic |
identical
|
|
|
Identical or fraternal twins?
- dichorionic diamnionic - fused |
identical or fraternal
|
|
|
What age group has the highest risk for hyatidiform mole?
|
age 40-50
|
|
|
What is this called?
- cystic swelling of chorionic villi with trophoblastic proliferation |
hydatidiform mole
|
|
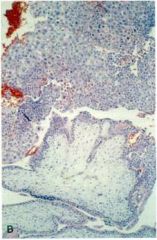
Parial or complete hydatidiform mole?
|
complete
- all villi are edematous - diffuse trophoblast proliferation - dilated swollen villi without blood vessels - high hCG in tissue - atypia |
|
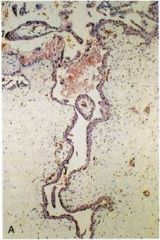
Complete or partial mole?
|
Partial
- some villi are edematous - focal trophoblast proliferation - no atypia - low hCG in tissue and serum |
|
|
What is this disease?
- invasion of unterine wall by molar villi - hogh hCG level - respond to chemo |
invasive mole
|
|
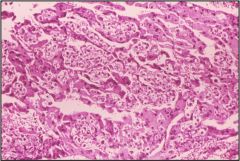
What is this disease?
- proliferating syncytiotrophoblast and cytotropoblasts |
choriocarcinoma
- no villi formed - most are intrauterine |

