![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
49 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
STD / STI |
Syphilis Chlamydia Gonorrhea HSV (Herpes Simplex Virus) HPV (Human Papillomavirus) |
Sexually Transmitted Diseases Sexually Transmitted Infections |
|
|
Syphilis |
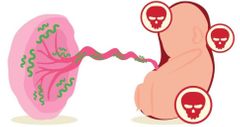
Bacterial infection commonly spread by sexual contact & during pregnancy can cross the placenta which can harm or kill the baby. |

|
|
|
syphilis symptoms |
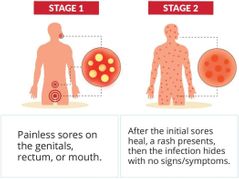
|
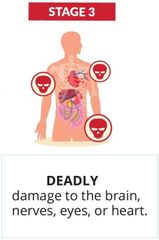
|
|
|
syphilis screening during pregnancy |

|

▪︎if allergic to penicillin, 1st assess 2nd penicillin desensitization by giving it in a slow gradual manner which allows the patient to slowly tolerate it without a massive reaction Do the screen because this infection can cross placenta & harm the baby Side note: Doxycycline & Tetracycline which can be harmful during pregnancy |
|
|
Chlamydia |

Chlamydia is the most common STD affecting people of all ages, but it most common in young women & those with multiple sex partners. it commonly goes untreated due to the lack of symptoms & leads to infertility issues other signs: dysuria, spotting after sex, abnormal vaginal discharge |

|
|
|
Gonorrhea |

a Sexually Transmitted bacterial infection if untreated can also cause infertility, it's asymptomatic & often goes untreated for this reason therefore annual screening is highly recommended for all Sexually active females |

|
|
|
HSV |
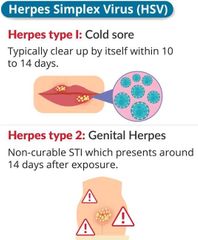
|

|
|
|
HSV Signs ... |

|

- signs have periods of remission & outbreak (active) - PRIORITY to report to HCP during pregnancy since this virus is very deadly to fetus causing permanent neurological damage & if peresnt at the onset of labor then an immediate c-section is PRIORITY to avoid infection to infant with that vaginal birth - start acyclovir immediately specially for clients who are close to their delivery - after the outbreak resolves with no active Lesions, condoms are recommended - Mild soap & warm water to provide relief to itching - it's OK to use a fan or a dryer on cool setting to dry Lesions |
|
|
acyclovir |

|
|
|
|
HPV |
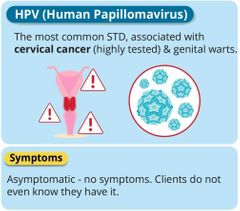
|

|
|
|
vaginal birth |
Rubella (German measles): maternity infection during first 8 weeks of gestation = fetal infection Syphilis cross placenta Gonorrhea, Chlamydia, HPV vaginal birth = infection of infant genital herpes simplex vaginal birth may be acceptable cesarean if visible leasion HIV exposure to secretions during birth & via breast milk |
کاهش ریسک انتقال HIV به جنین با تزریق پریناتال Zidovudine vaginal birth is possible if viral load is less than 1000 copies/ml درغیراینصورت cesarean pregnancy itself suppresses immune system pregnancy + HIV = life threatening infections Zidovudine antepartum: orally after 12 weeks of gestation intrapartum: IV during labor 1 hour before vaginal birth 3 hours before cesarean postpartum: syrup to newborn 2 hours after birth every 12 hours for 6 weeks HIV diagnosis 1st : ELISA if reactive → repeat ELISA with same blood sample → if reactive → western blot or IFA → if positive → HIV confirmed if ELISA is positive/reactive → but western blot/IFA is negative → HIV is NOT considered negative → repeat in 3-6 months HIV interventions : 1. Prenatal: avoid Amniocentesis & fetal scalp sampling 2. Intrapartum: avoid internal scalp electrodes for monitoring & avoid episiotomy & avoid oxytocin (because contractions induced by oxytocin can be strong, causing vaginal tears or necessitating an episiotomy) & minimize neonate exposure to maternal blood or body fluids & promptly remove neonate from blood & Suction fluids promptly & Place heavy absorbent pads under the mother's hips to absorb amniotic fluid & maternal blood 3. Postpartum: put mother in protective isolation ایزوله معکوس & restrict breast feeding & newborn can room with mother or may place in NICU for first 24 hours |
|
|
AIDS |
Acquired ImmunoDeficiency Syndrome a viral disease caused by HIV, which destroys T-cells & has a long incubation period (10 years or longer) •Three-drug combination HAART (highly active antiretroviral therapy) is recommended to reduce MTCT (mother-to-child transmission). • Zidovudine for prevention of MTCT a. Antepartum: Orally beginning after 12 weeks of gestation, to reduce the viral load to undetectable. b. Intrapartum: Intravenously during labor 1 hour before vaginal birth 3 hours before cesarean if the HIV RNA is greater than or equal to 400 copies/mL or unknown. this may not be required if the HIV RNA is less than 400 copies/mL but is given at the discretion of the provider. A vaginal birth is acceptable if the viral load is less than 1000 copies/mL; otherwise, a cesarean section is recommended c. Postpartum: syrup for newborn 2 hours after birth & every 12 hours for 6 weeks the newborn may be placed in NICU to begin initial therapy. ▪︎Transmission1. Sexual exposure to genital secretions of an infected person 2. Parenteral exposure to infected blood & tissue 3. Perinatal exposure of an infant to infected maternal secretions via birth or breast-feeding |
▪︎High-risk groups: - heterosexual / homosexual contact with high risk individuals - IV drug abusers- receiving blood products - Health care workers - Babies born to infected mothers ▪︎Assessment : - influenza-like symptoms - Lymphadenopathy for at least 3 months - Leukopenia - night sweats (also in TB, Hodgkins, sarcoidosis) - opportunistic cancer (kaposi's sarcoma, cervical cancer, B-cell non-Hodgkin's sarcoma) - infections: bacterial fungal: candidiasis viral: cytomegalovirus, herpes simplex protozoal: PJP ▪︎Interventions: - protective isolation precautions (A mother with HIV is managed as high risk because she is vulnerable to infections.) - Standard & necessary precautions - meticulous skin care - nutritional support as prescribed |
|
|
Kaposi's sarcoma |
a slow growing tumor that appears as purplish-red lesions of internal organs & skin in individuals with compromised immune system |
|
|
|
AIDS diagnostics & tests to evaluate progression |

|

|
|
|
Newborn of a Mother With Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) |

|

|
|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
|
|
Hepatitis |

|
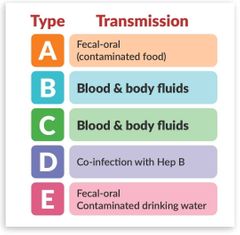
|
|
|
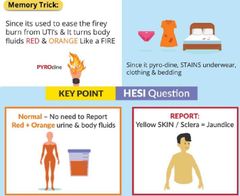
hepatitis signs |
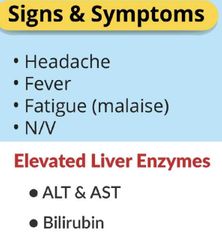
|
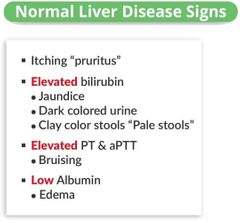
|
|
|
hepatitis stages |
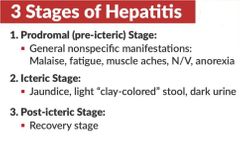
|
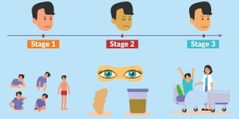
|
|
|
hepatitis treatments & education |

|

|
|

|

|

|
|
|
PID |
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease Inflammation in the pelvic area that typically develops from untreated STD like gonorrhea or chlamydia. If untreated due to lack of symptoms it can cause massive inflammation! |

|
|
|
PID complications & Risk factors |

|
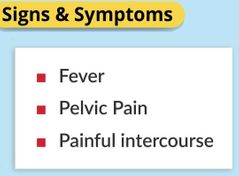
Treatment: A mix of antibiotics to kill the bacteria Surgery - remove any scar tissue or adhesions within the reproductive areas |
|
|
UTI |

|

|
|
|
UTI diagnostics |

|

|
|
|
Pyelonephritis |
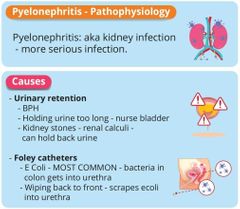
|

|
|
|
Pyelonephritis Signs & Symptoms |

|
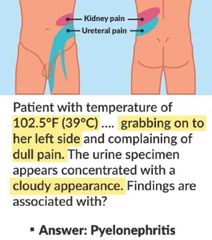
|
|
|
Pyelonephritis complications & treatment |
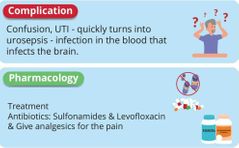
|
UTI can cause Acute Delirium (limited short-term confusion) |
|
|
Sulfonamides |

Trimethoprim sulfamethoxazole (Brand: Bactrim) MOA: Stops bacteria folic acid synthesis |
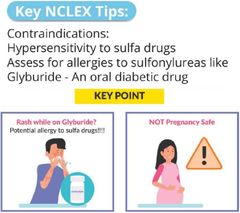
|
|
|
Fluoroquinolones |

|
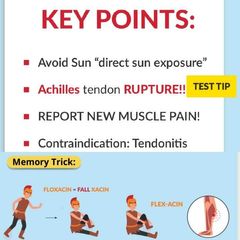
|
|

Phenazopyridine |
|

|
|
|
Pyelonephritis Nursing interventions |

|
|
|
|
Trichomoniasis Bacterial vaginosis Vaginal candidiasis |

|

|
|
|
Rubella |

|

|
|
|
Antepartum diagnostic testing Rubella titer |

|

|
|
|
TORCH complex acronym |

|

|
|

|

|

|
|
|
Tuberculosis |

|

|
|
|
Tuberculin Skin Test |

|
|
|
|
Hepatitis B |

|
|
|
|
Care of a child with HIV infection/AIDS |

|

|
|
|
Care of a child with HIV infection/AIDS |

|

|
|
|
Care of a child with HIV infection/AIDS |

|

|
|
|
common assessment findings in children with HIV infection |

|
|
|
|
Hepatitis in infant & child |

|

|
|
|
Hepatitis in infant & child |

|

|
|
|
Hepatitis in infant & child |

|

|
|
|
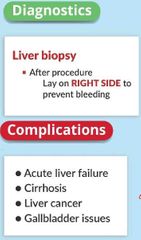
hepatitis diagnostics, complications, causes |
|

|

