![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
38 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Which of the following structures that are derived from the Müllerian ducts: lower 1/5 of the vagina, upper 4/5 of the vagina, cervix, endometrium, cul de sac, ovaries, fornix, peritoneum.
|
Which of the following structures that are derived from the Müllerian ducts: upper 4/5 of the vagina, cervix, endometrium, ovaries, peritoneum.
|
|
|
Name the 4 major types of neoplasms seen in müllerian derived structures (upper 4/5 of the vagina, cervix, endometrium, ovaries, peritoneum)
|
Name the 4 major types of neoplasms seen in müllerian derived structures (upper 4/5 of the vagina, cervix, endometrium, ovaries, peritoneum) Serous papillary, endometroid (most are adenocarcinomas), mucinous, clear cell
|
|
|
Where sqamous and mullerian columnar cells meet: is this the squamocolumnar junction, TZ or migration?
|
Where sqamous and mullerian columnar cells meet: is this the squamocolumnar junction
|
|
|
What is happening in the transformation zone?
|
where columnar is being replaced by basal cells that are transforming into sqamous cells
|
|
|
Which direction does migration of the TZ move?
|
cephalic
|
|
|
Where does squamous metaplasia occur?
|
Where does squamous metaplasia occur? In the TZ
|
|
|
Where do the majority of cervical carcinomas occur?
|
Where do the majority of cervical carcinomas occur? The TZ
|
|
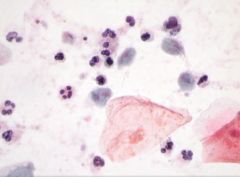
name the following pathology: is it candida, trichomonas, Herpes simplex virus (decribe what you see)
|

name the following pathology: trichomonas [INSERT PICTURE] green with eye balls
|
|
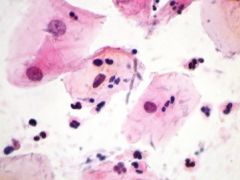
Name the following pathology: is it candida, trichomonas, Herpes simplex virus (decribe what you see)
|
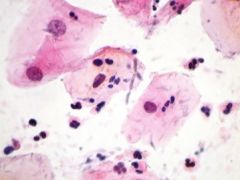
Name the following pathology: is it candida, [INSERT PICTURE] - Hyphae (branches) with spores
|
|
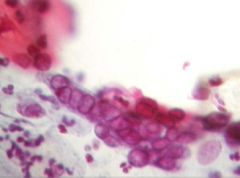
Name the following pathology: is it candida, trichomonas, Herpes simplex virus (decribe what you see)
|
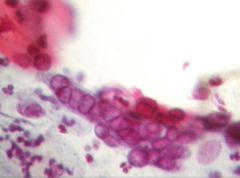
Name the following pathology: simplex virus [INSERT PICTURE] Pink and dense cells
|
|
|
What is the definition of a malignancy (carcinoma/cancer)?
|
What is the definition of a malignancy (carcinoma/cancer, carcinoma in situ)? Malignancy is capable of invasion and metastasis, thus can be lethal
|
|
|
What is the definition of a premalignancy (carcinoma in situ, dysplasia)?
|
What is the definition of a premalignancy (carcinoma in situ, dysplasia)? Not yet capable of invasion or metastasis, but has the risk of progression if untreated.
|
|
|
What is the basis of screening?
|
What is the basis of screening? Find lesions in the premalignant stage and avoid malignancy
|
|
|
T/F all HPV infx lead to Ca.
|
T/F all HPV infx lead to Ca…. FALSE (Due to immune system)
|
|
|
Which CIN (cervical intraepithelial neoplasm) matches this description: moderate dysplasia, 2/3 undifferentiated, HGSIL (high grade squamous intraepithelial lesion)?
|
Which CIN (cervical intraepithelial neoplasm) matches this description: moderate dysplasia, 2/3 (undifferentiated???) HGSIL (high grade squamous intraepithelial lesion)? CIN II
|
|
|
Which CIN (cervical intraepithelial neoplasm) matches this description: mild dysplasia, 1/3 undifferentiated, LGSIL (L grade squamous intraepithelial lesion)?
|
Which CIN (cervical intraepithelial neoplasm) matches this description: mild dysplasia, 1/3 (undifferentiated???) LGSIL (L grade squamous intraepithelial lesion)? CIN I
|
|
|
Which CIN (cervical intraepithelial neoplasm) matches this description: severe dysplasia,3/3 undifferentiated, HGSIL (L grade squamous intraepithelial lesion)?
|
Which CIN (cervical intraepithelial neoplasm) matches this description: severe dysplasia, 3/3 (undifferentiated???) HGSIL (L grade squamous intraepithelial lesion)? CIN III
|
|
|
Are all CINs precancerous?
|
Are all CINs precancerous? Yes
|
|

Name the CIN grade for the image above and describe the features. Which HPV subtypes are seen with this CIN?
|

Name the CIN grade for the image above and describe the features. CIN II: 2/3 undifferentiated with miosis up till the middle cells… Which HPV subtypes are seen with this CIN? 16, 18, 31, 33 (same as type CIN III)
|
|

Name the CIN grade for the image above and describe the features. Which HPV subtypes are seen with this CIN?
|
Name the CIN grade for the image above and describe the features. CIN I/ LGSIL: little if any undifferentiated cells, Koilocyte (large ballooning cells, with enlarged dark irregular nucleus, with a halo)… Which HPV subtypes are seen with this CIN? HPV subtypes: 6, 11, 42, 44
|
|

Name the CIN grade for the image above and describe the features. Which HPV subtypes are seen with this CIN?
|
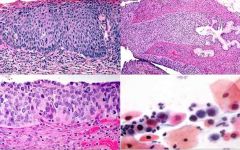
Name the CIN grade for the image above and describe the features: CIN III/HGSIL: full 3/3 thickness of undifferentiated cells, smaller cells w/ larger nucleus, Which HPV subtypes are seen with this CIN? 16, 18, 31, 33 (same as type CIN II)
|
|
|
T/F: low grade cervical lesion can have high risk subtypes, while high grade lesions will always have high risk lesions.
|
T/F: low grade cervical lesion can have high risk subtypes, while high grade lesions will always have high risk lesions. TRUE
|
|
|
Which CIN types (I, II, or III) has a higher risk of persistance and progression?
|
Which CIN types (I, II, or III) has a higher risk of persistance and progression? CIN III
|
|
|
If there is no HPV do cell CINs regress or progress (to invasion)?
|
If there is no HPV do cell CINs regress or progress? Regress yes, progress no.
|
|
|
How often to CIN I and CIN II regress or progress (to invasive)?
|
How often to CIN I and CIN II regress or progress? Regress most of the time (57% and 43% respectively), almost never progress (1% and 5% respectively)
|
|
|
If CIN III only progresses to invasive neoplasms 12% of the time, why do we treat all people with CIN III ?
|
If CIN III only progresses 12% of the time, why do we treat all people with CIN III? We don't know which patient will progress
|
|
|
Where do carcinomas of the cervic present? (hint: where on the cervix)
|
Where do carcinomas of the cervic present? In the TZ
|
|
|
What does staging in cancer represent?
|
What does staging in cancer represent? Metastasis
|
|
|
For cervical cancer, which staging has the worst prognosis?
|
For cervical cancer, which staging has the worst prognosis? When it reaches the cervical wall
|
|
|
What is the survival rate after 5 years for stage III cervical cancer versus stage II?
|
What is the survival rate after 5 years for stage III cervical cancer versus stage II? Stage II: 70%… Stage III: 35%
|
|
|
For which is morbidity from cervical cancer worst, direct extension or metastasis?
|
For which is morbidity from cervical cancer worst, direct extension or metastasis? Direct extension
|
|

Identify the image and describe the finding.
|
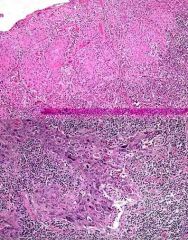
Identify the image and describe the finding. Squamous carcinoma No longer organized
|
|
|
T/F cervical lesions progress quickly
|
T/F cervical lesions progress quickly… FALSE they progress slowly
|
|
|
Match the proceedure tool (cryo, laser, LEEP, conization) with the decriptions: burn, wire-scoops out lesion, freeze, excise area with LEEP or knife
|
Match the proceedure tool (cryo, laser, LEEP, conization) with the decriptions: Laser=burn, LEEP=wire-scoops out lesion, freeze=cryo, excise area with LEEP or knife=conization
|
|

Describe the picture above and which HPV is it most associated with?
|
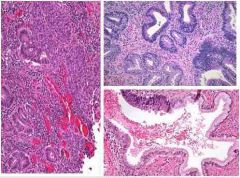
Endometrial adenocarcinoma… HPV 18 (maybe 16)
|
|
|
Describe the gross finding in a cervical polyp.
|
fibromuscular stroma lined by benign epithelium
|
|
|
Polyps can bleed, what is the significance of this?
|
Polyps can bleed, what is the significance of this? Clincally insignificant, but you should know this since bleeding is a sign of cancer
|
|
|
Which HPV subtypes account for 70% of all cervical cancers? What is the name of the vaccine that includes these subtypes? Which other subtypes are included in this vaccine?
|
Which HPV subtypes account for 70% of all cervical cancers? 16 and 18… What is the name of the vaccine that includes these subtypes? Gardisil… Which other subtypes are included in this vaccine? 6, 11, 16, 18
|

