![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
37 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
In breast embryology, when does development begin?
|
6 weeks
|
|
|
In puberty, what induces the growth of mamillary ducts? And what effect does this have?
|
Estrogen and progesterone cause ducts to elongate and aquire a thickened epithelium
|
|
|
What happens to the periductal stroma in puberty?
|
During puberty, periductal stroma is hormonally sensitive --> causing differentiation
|
|
|
What forms the terminal ducts
|
Lobules derive from solid masses of cells form the terminal ducts
|
|
|
Until what age does the process of breast development in women occur?
|
Into the 20s
|
|
|
In normal breast tissue, which is responsive to oxytocin? Ductal epithelium, myoepithelial cells, intralobular and interlobular stroma, or vessels-nerves-and fat?
|
Myoepithelial cells are responsive to oxytocin
|
|
|
At which part of menstrual cycle are the porliferative eithelial changes and stromal edema greatest? (First half or second half)… what is the effect on size, nodularity and sensitivity?
|
In the second half of the menstrual cycle are the porliferative eithelial changes and stromal edema greatest… maximum size, nodularity and sensitivity occuring.
|
|
|
In which part of the cycle should breast be examined?
|
Breast examination should take place during the first half - proliferative/follicular phase.
|
|
|
What happens to breast ducts, lobules, and stroma during menopause?
|
During menopause: breast duct atrophy, stroma shrinks, and lobules atrophy then eventually regress
|
|
|
During Menopause, what is lobular atrophy, in breast, dependent upon?
|
During menopause, lobular atrophy in breast varies with estrogen levels
|
|
|
What is the dense stroma (seen in young women) replaced by in menopausal women? How does this effect mamography?
|
In menopause, breast stroma is replaced by fat… this causes increased sensitivity of the mamogram in older women.
|
|
|
Match the lesion (papiloma, hyperplasia-most carcinomas, fibroadenoma, traumatic fat necrosis) with the anatomic location ( Adipose, lactiferous duct, terminal duct, linterlobular stroma of TDLU).
|
Papiloma=lactiferous duct… traumatic fat necrosis=adipose… terminal duct & lobule=hyperplasia-most carcinoma… fibroadenoma=interlobular stroma of TDLU
|
|
|
Which condition (Fibroadenoma, Large duct papilloma, Acute mastitis, Duct ecasia) is characteristic of the following features?
(1)Brancing papillae with fibrovascular cores covered by layer of epithelial and myoepithelial cells, dilated duct. (2) distint from small duct papillomas solitary, involve lactiferous duct, nipple d/c, no increse in cancer (3) age range 30-50 y/o. |
Large duct papilloma:
(1)Brancing papillae with fibrovascular cores covered by layer of epithelial and myoepithelial cells, dilated duct. (2) distint from small duct papillomas solitary, involve lactiferous duct, nipple d/c, no increse in cancer (3) age range 30-50 y/o. |
|
|
Name 4 developmental breast disorders.
|
Acessory/ectopic breast tissue, congenital nipple inversion, premature dev, macromastia (can be bilateral or uni)
|
|
|
Name 5 benign breast inflammatory condition.
|
Benign inflammatory conditions: fat necrosis, duct ecasia, acute mastitis, recurrent subaerolar abcess, granulomatous mastitis.
|
|
|
what are the features of a recurrent subaerolar abcess?
|
Recurrent subaerolar abcess:edemitis
|
|
|
Match thes feature to the benign inflammatory conditions: localized, related to trauma, mimics cancer clinically, stage dependent features [*surrounded by foamy macrophages, giant cells, fibroblasts, fibrosis; +/- Ca++] (fat necrosis, duct ecasia, acute mastitis, recurrent subaerolar abcess, granulomatous mastitis)
|
Fat necrosis: (1) Localized necrosis of fat tissues, (2) related to trauma, (3) mimics cancer clinically, (4) stage dependent features [*surrounded by foamy macrophages, giant cells, fibroblasts, fibrosis; +/- Ca++]
|
|
|
What are the features of acute mastitis?
|
Acute mastitis: staph infection
|
|
|
Match thes feature to the benign inflammatory conditions: dilated ducts with inspissated secretions, multparous women in 40s and 50s, clinically mimics cancer. (fat necrosis, duct ecasia, acute mastitis, recurrent subaerolar abcess, granulomatous mastitis)
|
Duct ecasia: dilated ducts with inspissated secretions, multparous women in 40s and 50s, clinically mimics cancer.
|
|
|
what are the features of granulomatous mastitis?
|
Granulomatous mastitis: ??? Not discussed
|
|
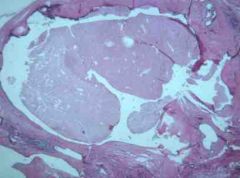
Identify this image and state what clincial findings are associated with it.
|
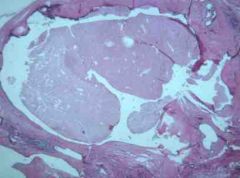
Duct Ectasia: Dilated ducts with inspissated secretions: Periductual inflammation often with thick nipple d/c --> firosis --> mass --> +/- skin retraction
|
|
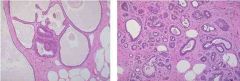
Identify the class of cells for both images (hint: same class)
Identify the specific subtypes. Name all 4 of the subtypes within this class. How do these fibrocystic changes manifest? Are they mass forming? Do these changes lead to an increased risk of cancer? |
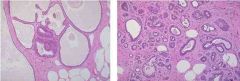
1. Non proliferating fibrocystic changes
2. Cysts on left... adenosis on right 3. Cysts, fibrosis, mild epithelial hyperplasia w/o atypia, , and adenosis (increased number of acini in a lobule) are non-proliferative causes of fibrocystic changes… 2. Manifestations: Their changes are mixed, mulitfocal, bilateral, and MASS FORMING... 3. NOT MASS FORMING 4. Do these changes lead to an increased risk of cancer? NO |
|
|
What is adenosis (in the breast)?
|
Adenosis = increased number of acini in a lobule
|
|
|
what are the 3 Prolferative (w/o atypia) causes of fibrocystic changes? Do these changes lead to an increased risk of cancer?
|
Sclerosing adenosis, small duct papilomas, and epithelial hyperplasia are all proliferative causes of fibrocystic changes… These proliferative condition lead to an increased risk of developing invasive breast cancer
|
|
|
Which of the proliferative fibrocystic changes conditions (Sclerosing adenosis, small duct papilomas, and epithelial hyperplasia) has the following characteristics? (1) Increased number of epithelial cells within pre-existign spaces, (2) affects ducts/tubules, (3) usually no mass forming, (4) may be assoicated with cellular and/or stuctural atypia--> increased cancer risk.
|
Epithelial hyperplasia (1) Increased number of epithelial cells within pre-existign spaces, (2) affects ducts/tubules, (3) usually no mass forming, (4) may be assoicated with cellular and/or stuctural atypia--> increased cancer risk.
|
|
|
Which of the proliferative fibrocystic changes conditions (Sclerosing adenosis, small duct papilomas, and epithelial hyperplasia) has the following characteristics? (1) Increased number of distorted and compressed acini to at least 2x normal number, (2) may be present with other fibrocystic or forma mass by itself
|
Sclerosing adenosis: (1) Increased number of distorted and compressed acini to at least 2x normal number, (2) may be present with other fibrocystic or forma mass by itself
|
|
|
Which of the proliferative fibrocystic changes conditions (Sclerosing adenosis, small duct papilomas, and epithelial hyperplasia) has the following characteristics? (1) Distinct from large duct papilomas - (a) multiple (b) involve small ducts d/c… (2) fibrovascular cores extend into duct lumens coverd by epithelium
|
Small duct papilomas: (1) Distinct from large duct papilomas - (a) multiple (b) involve small ducts d/c… (2) fibrovascular cores extend into duct lumens coverd by epithelium
|
|
|
Which has a greater increased risk for invasive breast cancer, Nonproliferative, proliferative w/atypia, or proliferative w/o atypia?
|
Nonproliferative=none… Proliferative w/o atypia=1.5-2 x the risk… proliferative w/atypia=4-5x incrased risk
|
|
|
Where do you see proliferative w/atypia?
|
atypical ductal or atypical lobular hyperplasia
|
|
|
Which condition (Fibroadenoma or Large duct papilloma) is characteristic of the following features? (1) most common benign tumor, (2) arise from interlobular stroma of the TDLU involved, (3) well circumscribed, oval, rubbery, mobile mass, (4) seen in young women, peak @ 20-30 y/o, (5) slight increase in cancer risk (1.3-1.9x).
|
Fibroadenoma: (1) most common benign tumor, (2) arise from interlobular stroma of the TDLU involved, (3) well circumscribed, oval, rubbery, mobile mass, (4) seen in young women, peak @ 20-30 y/o, (5) slight increase in cancer risk (1.3-1.9x)
|
|
|
Which of the following is not true for gynecomastia? Localized or diffuse, tender, symmetrical area of firmneess and enlargement, uni or b/l, associated w/ hypoestrinism, medications and carcinomas.
|
gynecomastia is associated with: Localized or diffuse, tender, ASYMMETRICAL NOT symmetrical areas of firmneess and enlargement, uni or b/l, associated w/ HYPERESTRINISM NOT hypoestrinism, medications and carcinomas.
|
|
(1) Identify the following image:
a) epithelial hyperplasia b) fat necrosis c) fibroadenoma d) large duct papilloma e) sclerosing adenosis f) small duct papilloma 2) describe it pathologic findings |
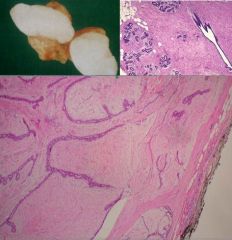
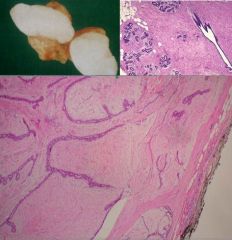
(1) Identify the following image:
c) fibroadenoma 2) describe it pathologic findings: (a) arise from interlobular stroma of the TDLU involved, (b) well circumscribed, oval, rubbery, mobile mass, |
|
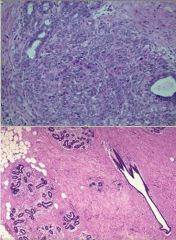
(1) Identify the following image:
a) epithelial hyperplasia b) fat necrosis c) fibroadenoma d) large duct papilloma e) sclerosing adenosis f) small duct papilloma 2) describe it pathologic findings *NOTE bottom image is normal for comparison |
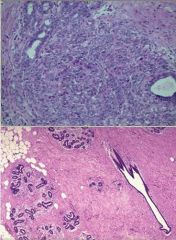
(1) Identify the following image:
e) sclerosing adenosis 2) describe it pathologic findings: Increased number of distorted and compressed acini to at least 2x normal number |
|
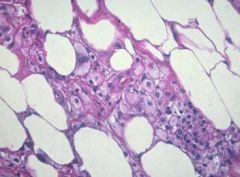
(1) Identify the following image:
a) epithelial hyperplasia b) fat necrosis c) fibroadenoma d) large duct papilloma e) sclerosing adenosis f) small duct papilloma 2) describe it pathologic findings |
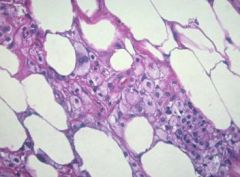
(1) Identify the following image:
b) fat necrosis 2) describe it pathologic findings (a) Localized necrosis of fat tissues (b) related to trauma, (c) mimics cancer clinically, (d) stage dependent features [*surrounded by foamy macrophages, giant cells, fibroblasts, fibrosis; +/- Ca++] |
|
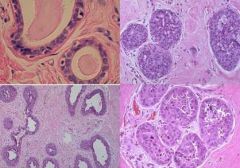
(1) Identify the following image:
a) proliferative epithelial hyperplasia b) fat necrosis c) fibroadenoma d) large duct papilloma e) sclerosing adenosis f) small duct papilloma 2) describe it pathologic findings |
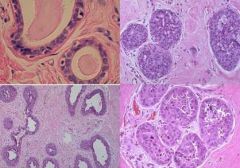
(1) Identify the following image:
a) proliferative epithelial hyperplasia 2) describe it pathologic findings (a) increased epithelial cells (b) Thickened epithelium (bottom left image) c) affects ducts or lobules d) Usually not mass forming e) Can be w/atypia - nuclear abnormalities (bottom right image) f) florid (two right images) |
|
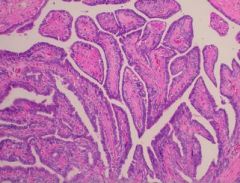
(1) Identify the following image:
a) epithelial hyperplasia b) fat necrosis c) fibroadenoma d) large duct papilloma e) sclerosing adenosis f) small duct papilloma 2) describe it pathologic findings |
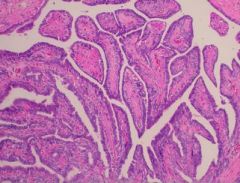
(1) Identify the following image:
d) large duct papilloma 2) describe it pathologic findings: (a)Brancing papillae with fibrovascular cores covered by layer of epithelial and myoepithelial cells, dilated duct. (b) distint from small duct papillomas solitary, involve lactiferous duct, nipple d/c, no increse in cancer c) age group: 30-50 *note: nipple d/c w/ blood is sign of cancer |
|
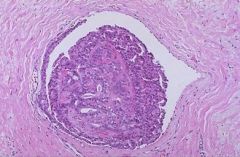
(1) Identify the following image:
a) epithelial hyperplasia b) fat necrosis c) fibroadenoma d) large duct papilloma e) sclerosing adenosis f) small duct papilloma 2) describe it pathologic findings |
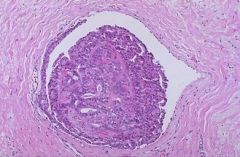
(1) Identify the following image:
f) small duct papilloma 2) describe it pathologic findings (a) Distinct from large duct papilomas i) multiple ii) involve small ducts d/c… (b) fibrovascular cores extend into duct lumens coverd by epithelium |

