![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
87 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the fate of the inner cell mass?
|
becomes the embryo
|
|
|
What are the 3 components of the blasotcyst?
|
inner cell mass, blastocyst cavity, trophoblast
|
|
|
After implantation what sort of differentiation occurs to the trophoblast?
|
trophoblastic cells --> (a) i. Cytotrophoblast (inner layer of cuboidal cells)… (b) Syncytiotrophoblast (outer layer of muntinucleanated synctial cells)
|
|
|
What happens to the blastocyst after implantation?
|
the blastocyst is completely embedded:
|
|
|
With respect to the blastocyst, what part of the endometrium is the DECIDUA CAPSULARIS? Is it fetally or maternally derived?
|
Decidua capsularis superficial portion of endometrium overlying the blastocyst… fetally derived
|
|
|
With respect to the blastocyst, what part of the endometrium is the DECIDUA BASALIS? Is it fetally or maternally derived?
|
Deciudua Basalis: the endometrium underlying the blastocyst (maternally derived)
|
|
|
Which is maternally derived, the decidua capsularis or basalis?
|
Basalis is maternally derived
|
|
|
When do you see the chorion and connecting stalk form?
|
2nd week
|
|
|
In the second week the amnionic cavity forms… what is it?
|
amnioinic cavity is the the slit-like space between the inner cell mass and the trophoblast
|
|
|
In the second week what happens to the inner cell mass?
|
it becomes the bilaminar embryonic disk
|
|
|
What forms the primary yolk sak?
|
blastocyst cavity lined with the exocoelomic membrane --> primary yolk sak
|
|
|
Where does the extra embryonic mesoderm grow?
|
Extra-embryonic mesoderm grows under trophoblast
|
|
|
What is the primative chorion made of?
|
Mesoderm + trophoblast → primitive chorion
|
|
|
What is the Chorionic cavity?
|
Chorionic Cavity (fused spaces in the mesoderm)
|
|
|
What eventually develops into the UMBILICAL CORD?
|
[Embryonic disk + amnion + yolk sac + alantois] – attach to chorion – suspended by connecting stalk → Umbilical Cord
|
|
|
What structure grows and surrounds the embryo?
|
the amnion grows and surrounds the embryo
|
|
|
What is the primordial villi composed of?
|
Mesodermal tissue beneath the trophoblast → trophoblastic cell mass → primordial villi (each villus = mesoderm core surrounded by inner cytotophoblast and outer synctiotrohoblast cells.
|
|
|
What is the placenta derived from?
|
Primordial villi branch over bloastocyst → primordial frondosum… (The primordial frondosum over the deciduas capsularis atrophies → chorion laeve [smooth chorion])… 3. The part that does not atrophy and invades deciduas basalis→ placenta… SHORT ANSWER: the PRIMORDIAL VILLI --> PRIMORDIAL FRONDOSUM --> PLACENTA
|
|
|
Before the third week, where does the embryo collects its nutrition?
|
Lacunae (blood lakes) form in synctiotrophoblast (day 9.. maternal blood) → this serves as Nutrition: Until 3rd week
|
|
|
When do fetal blood cells and vessels form?
|
3rd week
|
|
|
When does fetal circulation start?
|
4th week
|
|
|
What supplies maternal blood to the intervillous spaces?
|
Sprial arterioles supply maternal blood to the intervillous spaces
|
|
|
What converts Spiral arterioles? And what is the effect of this conversion?
|
Syncytotrophoblasts & intermediate trophoblasts cause PHYSIOLOGIC CONVERSION of spiral arterioles → specialized blood vessels that nurish growing fetus.
|
|
|
Why are chorionic villi so important?
|
1) Chorionic villi must be bathed by maternal blood for normal growth & dev… 2) Exhange occurs in elaborate capillary of the chorionic villi: nutrients, gas exhange, waste excretion.
|
|
|
What vessels feed the umbilical vein and what fx does the umbilical vein serve?
|
Chorionic vessel → form umbilical vein: carry oxygenated blood.
|
|
|
What do umbilical arteries carrie and where do they lead to?
|
deoxygenated blood… Two – Umbilical arteries carry deoxygenated blood → to chorionic villi → waste products enter intervillous space → exit maternal endometrial veins.
|
|
|
What function does the Placental membrane serve… (2) what three structures is it composed from?
|
Placental Barrier: fetal tissue separating fetal and maternal blood: components: trophoblast, connective tissue core of the villi, endothelium of the fetal capillaries
|
|
|
What are the two components of the placenta?
|
1) Maternal surface separate from deciduas basalis when expelled… 2) Fetal surface: direct toward amnionic cavity → attached to umbilical cord
|
|
|
Where are the fetal membranes? What are it's components?
|
1. Extend from margins of placenta. 2. Amnion, Chorion, Thin layer of decidua
|
|
|
Where does the umbilical cord connect, 2) what are its 3 contents?
|
1) two ends: fetal skin & amnion… 2) two umbilical arteries, 1 umbilical vein, Stroma (Whartons Jelly)
|
|
|
Which twins come from 1 fertilized and and which come from 2 fertilized eggs?
|
Monzygotic: 1 fertilized egg… Dizygotic: 2 fertilzed eggs
|
|
|
What type of twin will result from monchorionic/monoamnionic combination?
|
monchorionic/monoamnionic --> always monzygotic tiwns
|
|
|
What type of twin will result from monchorionic/diamnionic combination?
|
monchorionic/diamnionic --> always monozygotic twins
|
|
|
What type of twin will result from dichorionic/diamnionic combination?
|
either monozygotic or dizygotic twins
|
|
|
What type of twin will result from dichorionic/monoamnionic combination?
|
Can't happen has to be diamnionic
|
|
|
Which twins result from two morulas --> two blastocysts?
|
dizygotic twins
|
|
|
You're looking at a sample from the membrane dividing one fetus from the other: you see no dividing membrane. What types of twins are these and how do you know?
|
No dividing membrane --> single amnionic cavity --> monochorioinic/monoamnionic --> monozygotic twins
|
|
|
You're looking at a sample from the membrane dividing one fetus from the other: you see a dividing membrane, with two amnions. What types of twins are these and how do you know?
|
Not enough information…
|
|
|
You're looking at a sample from the membrane dividing one fetus from the other: you see a dividing membrane, with two amnions and chorion in the dividing membrane. What types of twins are these and how do you know?
|
dizygotic twins or monozygotic twins… dividning membrane --> two amnions --> 2 chorion in dividing membrane --> two chorions --> could be either
|
|
|
If there is no dividing membrane can you rule a twin type out?
|
yes… no dividing membrane --> monozygotic
|
|
|
If there is a dividing membrane, when can you rule out dizygotic twins: w/ chorion in dividing membrane or w/o chorion in the divding membrane?
|
dividing membran without chorion in the dividing membrane --> monozygotic only
|
|
|
What is a Placental Vascular Anastomosis? What are it's complications?
|
1) shunting of blood between fetuses… 2) Donor twin: hypovolemic and poorly developed… Recipient twin: hypervolemic and hydramniotic
|
|
|
Where does the blastocyst normally implant/
|
lateral wall of the uterine fundus
|
|
|
Match the following to either Placenta Previa, Placenta Accreta, or Abruptio Placenta: Caused by insufficient deciduas → leading trophoblast invastion of myometrium
|
PLACENTA ACCRETA: Caused by insufficient deciduas → leading trophoblast invastion of myometrium
|
|
|
Match the following to either Placenta Previa, Placenta Accreta, or Abruptio Placenta: complete ________ _________ --> Placental destruction → fetal exsanguinations… require cesarean section
|
complete PLACENTA PREVIA--> Placental destruction → fetal exsanguinations… require cesarean section
|
|
|
Match the following to either Placenta Previa, Placenta Accreta, or Abruptio Placenta: bordering or covering os (in the lower part of the uterus)
|
PLACENTA PREVIA: bordering or covering os (in the lower part of the uterus)
|
|
|
Match the following to either Placenta Previa, Placenta Accreta, or Abruptio Placenta: Premature separation of normally implanted placenta
|
ABRUPTIO PLACENTA: Premature separation of normally implanted placenta
|
|
|
Match the following to either Placenta Previa, Placenta Accreta, or Abruptio Placenta: has 3 different types of trophoblast penetration… (2) Which type is the worst? Why?
|
PLACENTA PERCRETA-TROPHOBLAST: has 3 different types of trophoblast penetration… (2) penetrates entire thickness --> leads to uterine rupture
|
|
|
Which type of placenta accreta invades the deep myometrium?
|
PLACENTA INCRETA: Trophoblast penetrates deep myometrium
|
|
|
Where does the trohoblast penetrate in Placenta Accreta?
|
the Trophoblast penetrates the superficial myometrium in placenta accreta
|
|
|
Match the following to either Placenta Previa, Placenta Accreta, or Abruptio Placenta: 3x Increased risk with pre-eclampsia
|
ABRUPTIO PLACENTA: Pre-eclampsia → 3x as likely to have abruptio placenta
|
|
|
Match the following to either Placenta Previa, Placenta Accreta, or Abruptio Placenta: Etiology: Previous surgery OR curettage (D&C) OR infection i. →Thin endometrium → thin deciduas → ?
|
Etiology: Previous surgery OR curettage (D&C) OR infection→Thin endometrium → thin deciduas → PLACENTA ACCRETA
|
|
|
Match the following to either Placenta Previa, Placenta Accreta, or Abruptio Placenta: Premature separation of the placenta caused by degeneration of deciduas w/ damage of decidual vessels
|
ABRUPTIO PLACENTA : Premature separation of normally implanted placenta… CAUSED BY degeneration of deciduas w/ damage of decidual vessels
|
|
|
Match the following to either Placenta Previa, Placenta Accreta, or Abruptio Placenta: Retroplacental hematoma → ischemia of placenta… associated with Couvellairs Uterus (extreme form of concealed type with symptoms of excessive bleeding and uterine rupture)
|
ABRUPTIO PLACENTA: Retroplacental hematoma → ischemia of placenta… associated with Couvellairs Uterus (extreme form of concealed type with symptoms of excessive bleeding and uterine rupture)
|
|
|
Match the following to either Placenta Previa, Placenta Accreta, or Abruptio Placenta: Placenta cannot separate normally after delivery → hemorrhage
|
PLACENTA PREVIA: Placenta cannot separate normally after delivery → hemorrhage
|
|
|
Match the following to eitherPlacenta Previa, Placenta Accreta, or Abruptio Placenta: Placental tissue remains postpartum --> leading to bleeding and infection
|
PLACENTA ACCRETA: Placental tissue remains postpartum --> leading to bleeding and infection
|
|
|
Match the following to eitherPlacenta Previa, Placenta Accreta, or Abruptio Placenta: Complications of excessive bleeding --> Associated with Maternal shock, fetal distress (or death), and DIC
|
APBRUPTIO PLACENTA: Complications of excessive bleeding --> Associated with Maternal shock, fetal distress (or death), and DIC
|
|
|
Match the following to eitherPlacenta Previa, Placenta Accreta, or Abruptio Placenta: Post partum bleeding because uterine contraction insufficient to cause tamponade (Normally minimal bleeding due to uterine contraction → tamponade)
|
ABRUPTIO PLACENTA: Post partum bleeding because uterine contraction insufficient to cause tamponade (Normally minimal bleeding due to uterine contraction → tamponade)
|
|
|
Match the following to eitherPlacenta Previa, Placenta Accreta, or Abruptio Placenta: Placenta penetrates myometrium
|
PLACENTA ACCRETA: Placenta penetrates myometrium
|
|
|
Match the following to eitherPlacenta Previa, Placenta Accreta, or Abruptio Placenta: Sheehan's syndrome and intraglomerular thrombi associated with kidney cortical necrosis (Irreversible lesion → death 95% of cases)
|
ABRUPTIO PLACENTA: (1) Sheehan's syndrome and (2) intraglomerular thrombi associated with kidney cortical necrosis (Irreversible lesion → death 95% of cases)
|
|
|
Which causes bleeding PLACENTA PREVIA, ACCRETA, or ABRUPTIO at the placental margin or distal to the placental margin?
|
In ABRUPTIO PLACENTA separation at the margin is associated with bleeding.
|
|
|
Match the following to eitherPlacenta Previa, Placenta Accreta, or Abruptio Placenta: Blastocyst implants in lateral wall of uterine fundus.
|
None: NORMAL PLACENTA:: Has blastocyst implants in lateral wall of uterine fundus
|
|
|
Match the following to eitherPlacenta Previa, Placenta Accreta, or Abruptio Placenta: Symptoms associated with bleeding after 7 months (due to placental separation)
|
PLACENTA PREVIA: Symptoms associated with bleeding after 7 months (due to placental separation)
|
|
|
Match the following to eitherPlacenta Previa, Placenta Accreta, or Abruptio Placenta: Premature separation of normally implanted placenta after 20th week, where the fetal blood supply decreases proportionally to the size of the separation
|
ABRUPTIO PLACENTA: Premature separation of normally implanted placenta after 20th week, where the fetal blood supply decreases proportionally to the size of the separation
|
|
|
Which type of cord knot is caused by the umbilical vein being longer than the umbilical artery? False or true
|
False knots are caused by the umbilical vein being longer than the umbilical artery
|
|
|
Which type of cord knot causes entanglements and impede blood flow in the umbilical vein? False or True?
|
TRUE KNOTS cause entanglements and impede blood flow in the umbilical vein… FALSE KNOTS have no clinical significance.
|
|
|
What type of umbilical cord abnormality is assoicated with Insertion of cord into membrane NOT Whartons Jelly (unprotected)? Velamentous, single umbilical or True knots?
|
Velamentous cord inserts into membrane, not Whartons jelly
|
|
|
What type of umbilical cord abnormality is assoicated with increased risk of fetal morbidity and mortality during labor (arteries are unprotected: Velamentous, Single umbilical artery, or True knots?
|
Velmentous insertion is associate with increased risk of fetal morbidity and mortality during labor (arteries are unprotected
|
|
|
What type of umbilical cord abnormality is assoicated with gestational diabetes: Velamentous, Single umbilical artery, or True knots?
|
Single umbilical artery is associated with gestational diabetes
|
|
|
What type of umbilical cord abnormality is 7x more common in twin pregnancy: Velamentous, Single umbilical artery, or True knots?
|
Velementous insertion are 7x more common in twin pregnancies
|
|
|
What type of umbilical cord abnormality is associate with congenital malformations: Velamentous, Single umbilical artery, or True knots?
|
Both Single Umbilical artery and Velamentous are associated with congenital malformations
|
|
|
What type of umbilical cord abnormality is associate with perinatal mortality and infants being small for delivery date: Velamentous, Single umbilical artery, or True knots?
|
Small size and increased perinatal mortality is associated with single umbilical artery.
|
|
|
What type of umbilical cord abnormality is associate with single umbilical artery: Velamentous or True knots?
|
Velamentous insertion is associated with single umbilical artery
|
|
|
What type of infection is ectopic pregnancy related to?
|
chronic tubal infection (especially gonococcus infection) is associated with ectopic pregnancy
|
|
|
What happens if an ectopic pregnancy is not diagnosed by the 4-5th week?
|
tubal rupture if ectopic pregnancy is not diagnosed by 4-5th week.
|
|
|
What are the two types of placental infection?
|
the two types of placental infection are chorioamniontitis and transplacental-Villitis
|
|
|
Which placental infection is associated with viral infections: Ascending Infection-chorioamniontitis or transplacental-Villitis
|
Viral infection is associated with transplacental-Villitis
|
|
|
Which placental infection is a major cause of premature births: Ascending Infection-chorioamniontitis or transplacental-Villitis
|
Ascending Infection-chorioamniontitis --> major cause of premature births
|
|
|
Which placental infection is associated with congenital abnormalities: Ascending Infection-chorioamniontitis or transplacental-Villitis
|
transplacental-Villitis associate with congenital abnormalities
|
|
|
Which placental infection is secondary to vaginal or cevix infection: Ascending Infection-chorioamniontitis or transplacental-Villitis
|
Is secondary to vaginal or cevix infection -->Ascending Infection-chorioamniontitis
|
|
|
Which placental infection is associated with Hx of reproductive failure: Ascending Infection-chorioamniontitis or transplacental-Villitis
|
Hx of reproductive failure: transplacental-Villitis
|
|
|
Which placental infection is secondary to hematogenous spread or extension from endometrium: Ascending Infection-chorioamniontitis or transplacental-Villitis
|
Which placental infection is secondary to hematogenous spread or extension from endometrium: transplacental-Villitis
|
|
|
Which placental infection is associated with intrauterine growth restriction: Ascending Infection-chorioamniontitis or transplacental-Villitis
|
Which placental infection is associated with intrauterine growth restriction -->transplacental-Villitis
|
|
|
Placenta Accreta:
Placenta penetrates myometrium a. Caused by insufficient deciduas → leading to trophoblast invastion of myometrium b. Etiology: Previous surgery OR curettage (D&C) OR infection →Thin endometrium → thin deciduas → placenta accreta |
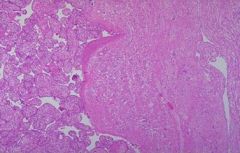
Which placenta pathology is seen in this image?
|
|
|
Abruptio Placenta:
1. Premature separation of normally implanted placenta a. Cause: degeneration of deciduas w/ damage of decidual vessels 2. Retroplacental hematoma → ischemia of placenta a. Couvellairs Uterus: extreme form of concealed type i. Excessive bleeding ii. Uterine rupture |
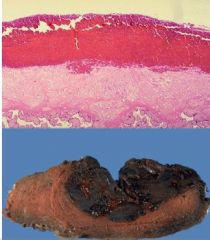
Name the placental abnormality associated with these two images
|
|
|
There is chorion in the center... thus its dichorionic... since there is no such thing as dichorionic monochorionic, this is DICHORIONIC-DIAMNIONIC
(2) Could be Faternal twins or Identical twins |
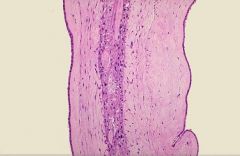
(1) Which type of twining is indictated by this image? Monochorionic-Monoamnioinic, Monochorionic-Diamnionic, Dichorionic-Monochorionic, or Dichorionic-Diamnionic
(2) Faternal twins or Identical twins? |
|
|
Since there is no chorion between the amnions, this is MONOCHORIONIC... since there are two amnioins this is DIAMNIONIC... thus MONOCHORIONIC-DIAMNIONIC
|
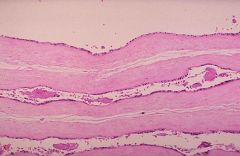
(1) Which type of twining is indictated by this image? Monochorionic-Monoamnioinic, Monochorionic-Diamnionic, Dichorionic-Monochorionic, or Dichorionic-Diamnionic
(2) Faternal twins or Identical twins? |

