![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
95 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the first signs of puberty for males and females?
|
males testis, girls breast buds
|
|
|
1. For both males and females, graphically demonstrate the temporal relationship between the different aspects of puberty development (hint, thing ranges and relative relationships)
2. Give average ages for these milestones |
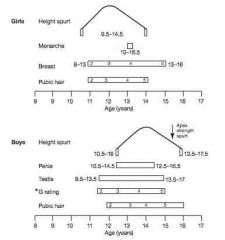
Male pubertal growth
• 11.5 testicular development • 12.9 adrenarche • 13.4 penile enlargement • 14 PHV(growth spurt) Female pubertal growth • 9.8 years thelarche • 10.5 adrenarche • 12 PHV (growth spurt) • 12.8 menarche |
|
|
Where is earlier menarche not seen?
|
poor rural areas and higher altitudes
|
|
|
What is the average age of breast budding? What is the range of age for breast budding? What is the duration of breast development?
|
avagerage age of breast dev: 10.5 yrs… Age range for budding= 8 yr, 6 mo - 13 yrs… Duration= 4 yrs
|
|
|
1. What is the average age (range) of onset of pubertal development in males and females?
2. What are the first signs of puberty for boys and gilrs? 3. When will pubic hair begin? 4. At what age is the PHV in boys and girls |
1. What is the average age (range) of onset of pubertal development in males and females? Males: >9-<14… Females: >8 <13
2. What are the first signs of puberty for boys and gilrs? Girls=breast budding... Boys= testicular enlargement/scrotal thinning 3. When will pubic hair begin? Six months after start of puberty *Note: For BOTH Boys and Girls, pubic hair may be the heralding sign of puberty, where breast budding or testicular enlargement will begin 6 months later. 4. PHV: a) Girls=12 (9 cm/yr) b) Boys=14 yrs |
|
|
What is the mean duration of pubert?
|
4.2 yrs = mean duration of puberty
|
|
|
what is the mean age of menarche?
|
what is the mean age of menarche? 12.8 y (12.5 - 12.75 m)
|
|
|
T/F breat and pubic hair do not show discordance.
|
false, normal girls may be B4 and P1 for example... in other words they don't progress evenly
|
|
|
What is the age (range) of onset of puberty age in boys… what is the mean age on onset of puberty in boys?
|
Range of onset 9-14 yrs… mean age of onset of puberty = 11.5 yrs
|
|
|
1. What stimulates leydig cells? and what percentage of testicular volume do the leydig cells account for?
2. What stimulates Sertoli cells? and what percentage of testicular volume do the sertoli cells (in tubules) account for? |
1. LH stimulation of Ledig cells (10% volume)
2. FSH/T stimulation of tubules (90% volume) |
|
|
For boys, in terms of Genital Development (G2-G5) what is PHV most closely related to? Give an example.
|
PHV in boys is associated with gonadal development… between G4-G5 --> @ 14y with ~10.3 cm/yr
|
|
|
In pubic hair dev in boys, what is the Tanner range and what is the duration in years? When does axillary hair develop. When does adult distribution of hair occur?
|
In pubic hair dev in boys, what is the Tanner range and what is the duration in years? P2-P5, 4yrs… When does axillary hair develop? 1-2 yrs after pubic hair development onset… When does adult distribution of hair occur? Usually no sooner than 20 y/o
|
|
|
What 4 things explain the difference in male and female height?
|
1) > prespurt growth in boys… 2)Boys are abouty 10 cm taller than girls when they begin their growth spurt… 3) > puberty gain during growth spurts in males… 4) > postspurt growth in GIRLS… SHORT ANSWER: BOYS START PUBERTY LATER… and GREATER OVERALL GROWTH DURING PUBERTY
|
|
|
During puberty there is an increase of GH by 2-3 times compared to prepuberty. (1) what is believed to cause this increase… (2) What is primarily responsible for growth spurts?
|
During puberty there is an increase of GH by 2-3 times compared to prepuberty. (1) what is believed to cause this increase? T and E. (2) What is primarily responsible for growth spurts? GH and Gonadal Steroids
|
|
|
With respect to menarche, when do girls do most of their growth?
|
Girls do most of their growth before menarche
|
|
|
What hormone do girls have more of at the start of puberty, which may explain why girls grow more at the start of puberty as compared to boys?
|
Girls have higher levels of GH at the beginning of puberty as compared to boys.
|
|
|
When do girls have PHV?
|
1.3 years before menarche at B3
|
|
|
When do boys have their PHV?
|
Boys increase in height velocity by G3 with a peak between G4-5… in other words after testicular development
|
|
|
What effect do PURE androgens have on GH?
|
Pure androgens have less of a stimulating effect that T or E and may even inhibit GH.
|
|
|
What is required for epiphyseal plate closure in both girls and boys?
|
Estrogen is required for epiphyseal plate closure
|
|
|
Which 5 hormones are required for growth for both boys and girls? (hint: not just gonadal hormones)
|
T, E, GH, IGF-1 and thyroid hormone are required for growth
|
|
|
What meant by the biphasic effects of Estrogen in terms of growth?
|
Low doses --> growth… high dose --> epiphyseal plate closure
|
|
|
what may explain growth spurts in androgen insensitive males?
|
T -(aromatization)--> E
|
|
|
Where do the GnRH neurons originate from? Where do they go? What do they become?
|
The GnRH neurons originate from the Olfactory placode (which will eventually become the nasal septum and cribiform plate) --> to the basal hypothalamus and arcuate region… where they become LHRH pulse generator
|
|
|
What guides the LHRH cells to the site of the LHRH pulse generator?
|
NCAM guides the LHRH cells
|
|
|
What causes Kallman's syndrome?
|
What causes Kallman's syndrome? Failure of LHRH cells to migrate (defect in gene at Xp22.3)
|
|
|
T/F Kallman's syndrome is autosomal recessive?
|
False, Kallman's syndrome is X-linked; related to a migration protein
|
|
|
In which week is LHRH migration complete? 2, 3, 4, 5, 6?
|
4.5 weeks
|
|
|
What is required for the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal unit to function?
|
What is required for the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal unit to function? Blood flow
|
|
|
T/F pulsative LHRH are detectable in the fetus, but in the absence of negative feedback.
|
True: LHRH is seen in the fetus with corresponding rises in FSH and LH… false: there is negative feedback of the GnRH pulse by 120 days and carries on thru late pregnancy
|
|
|
T/F fetal LH is higher in females than in males, which corresponds to low testosterone production in male fetuses.
|
True: LH is higher in the female fetus… but by week 7-16 male fetus testosterone is producing its highest levels of the pregnancy
|
|
|
In which infant, male or female, do you see a marked increase in LH within minutes of birth? What consequence does this have?
|
Male infants have an increase in LH within minutes of birth --> leading to a 10x increase in testosterone within hours of birth.
|
|
|
Both male and female infants undergo a 'mini-puberty", what is the time line and how long does it last?
|
Females: have an increase in estrogen at the second week --> lasting for 1-2 years… Males: lasts for 6 months
|
|
|
In which infant does estrogen enter the brain, what is the effect of this?
|
In Males: T -(aromatization)--> E --> crosses BBB --> masculinization of brain.
|
|
|
What two mechanism are believed to account for the suppression of the LHRH generator in the prepubertal child?
|
LHRH generator suppression in childhood: (1) highly sensitive steroid hormone DEPENDENT negative feedback (since there are very low levels of FSH/LH)… (2) Steroid INDEPENDENT intrinsic CNS inhibition of the LHRH pulse generator
|
|
|
What do gonadal dysgenesis in Turners children (or suppressed adrenal steroids) in the absence of low levels of FSH/LH suggest about the control of the LHRH pulse generator?
|
What do gonadal dysgenesis in Turners children (or suppressed adrenal steroids) in the absence of low levels of FSH/LH suggests that the LHRH pulse generator is under the intrinsic control of CNS
|
|
|
What does precocious puberty seen in children with hypothalamic neoplasms (and Hypothalamic Hamartomas) support?
|
Intrinsic control of the CNS over the pulse generator: (1) in hypothalamic neoplasms the neural pathways are blocked thus leading to activation of the the LHRH pulse generator… (2) hypothalamic Hamartomas are ectopic LHRH pulse generators, which are not inhibited by the CNS --> precocious puberty.
|
|
|
What is the significance of 48 kg for young women?
|
48 kg is the invariant mean weight needed to initiate puberty in young women
|
|
|
When is CNS control of the LHRH pulse generator first decreased in the onset of puberty? What effect does this have on Neg Feedback?
|
(1) CNS suppression of the LHRH pulse generator is decreased in NON-REM sleep during the onset of puberty, (2) making the pulse generator less sensitive to gonadal steroid negative FB.
|
|
|
What is the average LH peak (Peak/?min) pattern?
|
LH peak every 120 minutes
|
|
|
What is the rate of LH peaks (per hour) in mid follicular phase of adult women?
|
1/LH peak every hour during mid-follicular phase
|
|
|
what is the difference between FSH and LH between prepubertal boys and girls? What female pathology does this explain?
|
(1) FSH is stored in greater quantity in girls. Girls are more sensitive to LHRH release of FSH. LH is the same in boys and girls… (2) this explains why precocious puberty is seen more often in girls than in boys
|
|
|
Why are 55-90% of cycles anovulatory in first two years after menarche?
|
immature LHRH pulse generator in resonse to high levels of estrogen. Mature LHRH pulse generator is inhibited by low levels of estrogen, but stimulated by high levels of estrogen --> LH surge --> ovulation
|
|
|
Which occurs first, adrenarche or gonadarche?
|
adrenarche occurs before gonadarche
|
|
|
Name 3 enzymes of the ZR precipitate onset of adrenarche? What do they produce?
|
enzymes such as 17, 20 desmolase, 17 hydroxylase, 3ß hydrodrosteroid dehyrogenase in the ZR --> DHEAS and DHEA --> adrenarche
|
|
|
Pubic hair development at what age determines premature adrenarche?
|
Males: B/4 age of 9 yrs. Females: B/4 age of 8 yrs = premature adrenarche
|
|
|
Is sexual development seen in premature adrenarche?
|
Is sexual development seen in premature adrenarche? NO
|
|
|
In which sex is premature adrenarche seen more often?
|
In which sex is premature adrenarche seen more often? Females
|
|
|
Which enzymes are implicated in classic and nonclassic forms of CAH cause premature adrenarche?
|
21, 11ß and 3ß are implicated in the premature adrenarche related to CAH
|
|
|
What can carbohydrate intolerance lead to?
|
Carbohydrate intolerance lead to premature adrenarch
|
|
|
What effect does premature adrenarche have on the following? Bone age (before adulthood), average height (before adulthood), average final height.
|
What effect does premature adrenarche have on the following? Bone age (before adulthood) ADVANCED , average height (before adulthood) ABOVE AVERAGE, average final height NORMAL
|
|
|
What effect does premature adrenarche have on ovarian androgen?
|
premature adrenarche may lead to OVARIAN HYPERANDROGENISM.
|
|
|
When should an ACTH be given to children suspected of premature adrenarche?
|
When should an ACTH be given to children suspected of premature adrenarche? Increased bone age, virilization, cystic acne, cliteral hypertrophy, or have an elevated 17 hydroxyprogesterone and DHEA levels
|
|
|
T/F premature thelarche is followed by an abnormal puberty.
|
T/F premature thelarche is followed by an abnormal puberty. FALSE
|
|
|
Is premature thelarch bilateral or unilateral? When is premature thelarche usually seen (what age)?
|
Bilateral… usually seen at 2, not normally seen after 4 years old.
|
|
|
Which product is implicated in premature thelarche?
|
estrogen containing hair creams is implicated in premature thelarche
|
|
|
What happens to the FSH/LH ratio in premature thelarche? What happens to estrodiol levels? Prolactin?
|
What happens to the FSH/LH ratio in premature thelarche? it is reversed LH high, with FSH low… (2) What happens to estrodiol levels? Normal or elevated… (3) Prolactin NORMAL
|
|
|
Where does "inhibin" have its effect and where is it released from?
|
Gonads --> inhibin --> at level of pituitary
|
|
|
T/F HPG axis is stimulated by stress, emotion, visual/olfactory stimuli.
|
T/F HPG axis is stimulated by stress, emotion, visual/olfactory stimuli… TRUE
|
|
|
At what age does GABA have a greater GnRH inhibitory effect?
|
At what age does GABA have a greater GnRH inhibitory effect? PREPUBERTY
|
|
|
Where are granules of GnRH stored?
|
Where are granules of GnRH stored? GnRH secreting neurons w/in the arcuate nucleus of the Medial basal hypothalamus (MBH)
|
|
|
What is the rate of GnRH pulsative secretions?
|
What is the rate of GnRH pulsative secretions? 70-90 min intervals
|
|
|
which is true of FSH and LH: both are amino acids, they share a common beta subunit.
|
Both FALSE: FSH and LH are GLYCOPROTEINS, they share a common ∂ unit, but have a different ß subunit
|
|
|
Which of the following are inhibitory to the GnRH pulse? Estrogen, androgens, progestogens, activin, inhibin, follistatin
|
Which of the following are inhibitory to the GnRH pulse? Estrogen (has both neg & pos)… / androgens, progestogens, inhibin, follistatin --> INHIBITIORY… Activin --> STIMULATORY
|
|
|
T/F GABA inhibits the onset of puberty
|
TRUE
|
|
|
T/F Skeletal maturation effects onset of puberty and the exact trigger of puberty is well known.
|
TRUE: Skeletal maturation effects onset of puberty… FALSE: exact trigger of puberty is well known.
|
|
|
Which is pulsative, LH or FSH? When?
|
FSH is pulsative in early infancy in girls. LH is pulsative early infancy in males… LH is pulsative in both males and females in puberty
|
|
|
Which of the following is true of changes HPG changes at puberty: (1) increased sensitivity to Neg FB --> decreased pulsative GnRH… (2) increased sensitivity of pituitary gonadotrophs --> decreased LH/FSH secretions… (3) increased responsiveness of gonads to LH/FSH --> increased gonaldal steroid production
|
Which of the following is true: (1)FALSE: DECREASED sensitivity to Neg FB --> INCREASED pulsative GnRH… (2) FALSE: increased sensitivity of pituitary gonadotrophs --> INCREASED LH/FSH secretions… (3) TRUE: increased responsiveness of gonads to LH/FSH --> increased gonadal steroid production
|
|
|
What effect does leptin have on the LHRH pulse generator? Why does this make sense?
|
What effect does leptin have on the LHRH pulse generator? STIMULATES… Why does this make sense? Obesity hastens puberty
|
|
|
What is gonadarche and what does it result from?
|
Gonadarche is a rise in gonadal steroids that result from the HPG axis activation
|
|
|
T/F adrenarche is dependent upon gonadal steroid production
|
T/F adrenarche is dependent upon gonadal steroid production FALSE
|
|
|
What 3 things influence secondary sexual development?
|
What 3 things influence secondary sexual development? Gonadarche, adrenarche and physical changes caused by exposure to E and A
|
|
|
T/F estrogen causes breast development only in girls
|
T/F estrogen causes breast development in boys and girls. FALSE… BOTH BOYS AND GIRLS
|
|
|
T/F Androgens cause body hair, body odor, and acne in both boys and girls.
|
T/F Androgens cause body hair, body odor, and acne in both boys and girls. TRUE
|
|
|
What is the average height gain for girls during puberty?
|
What is the average height gain for girls during puberty? 9 inches
|
|
|
How long after the onset of puberty does Menarche begin?
|
How long after the onset of puberty does Menarche begin? 2-2-1/2 years
|
|
|
What is the average height gains for boys during puberty?
|
What is the average height gains for boys during puberty? 11 inches
|
|
|
in the Tanner stages, what does 1 equate to?
|
1= no puberty… (there is no zero)
|
|
|
Does gynacomastia usually regress in young boys?
|
Does gynacomastia usually regress in young boys? YES
|
|
|
What is used to cause the regression of breast development in gynacomasty seen in young men?
|
What is used to cause the regression of breast development in gynacomasty seen in young men? Surgery or an aromatase inhibitor
|
|
|
T/F it can take up to 6-8 months for the first growth spurt to occur in young men after the onset of puberty.
|
T/F it can take up to 6-8 months for the first growth spurt to occur in young men after the onset of puberty. TRUE
|
|
|
Name two normal variants of normal puberty
|
Name two normal variants of normal puberty: 1) constitutional delay… 2) familial early or rapid maturation
|
|
|
Which results in normal final height 1) constitutional delay… 2) familial early or rapid maturation
|
Which results in normal final height 1) constitutional delay… 2) familial early or rapid maturation… BOTH
|
|
|
What is anosmia? What can it result from?
|
What is anosmia? LACK OF SMELL... What can it result from? KALLMAN SYNDROME
|
|
|
T/F Kallman syndrom results in eucoidism because there is no puberty and no fusing of growth plates.
|
T/F Kallman syndrome results in eucoidism because there is no puberty and no fusing of growth plates. TRUE
|
|
|
Which of the following is not true of HYPOTHALAMIC HAMARTOMA? Presents at 2-4 years old, heteropic mass of GNRh secreting neurons, acts as ectopic pulse generator, activation of HPG axis in central precocious puberty, does not resond to Rx.
|
Which of the following is not true of HYPOTHALAMIC HAMARTOMA? TRUE: heteropic mass of GNRh secreting neurons, acts as ectopic pulse generator, activation of HPG axis in central precocious puberty… FALSE: Presents at 2-4 years old, does not resond to Rx.... PRESENT AT BIRTH... RESPONDS TO RX
|
|
|
Which results in delayed puberty, hyperpituitarism or hypo?
|
Which results in delayed puberty, hyperpituitarism or hypo? HYPOPITUITARISM
|
|
|
What is a sign of hypopituitarism in male infants?
|
What is a sign of hypopituitarism in male infants? Micro-penis as well as midline structural abnormalities
|
|
|
What is the effect on final height in central precocious puberty?
|
severe short stature
|
|
|
What are included in the work up for CPP?
|
GnRH stimulation test (to check for effects on LH and FSH… should be little increase) and MRI scan
|
|
|
Name 2 syndromes of gonadal abnormal puberty.
|
Name 2 causes of gonadal abnormal puberty: Turner syndrome (delayed puberty) and McCune-Albright syndrome (precocious puberty)
|
|
|
T/F in Turner syndrome, ovaries start out normal but undergo atresia.
|
T/F in Turner syndrome, ovaries start out normal but undergo atresia. TRUE
|
|
|
Why do ovaries undergo atresia in Turner syndrome?
|
Why do ovaries undergo atresia in Turner syndrome? Two x chromosomes are required to maintain normal ovaries
|
|
|
What is the triad for McCune-Albright syndrome?
|
What is the triad for McCune-Albright syndrome? Café au lait skin pigmentation (mosaic distribution), fibrous bone dysplasia and precocious puberty
|
|
|
What is the etiology behind the McCune-Albright syndrome?
|
What is the etiology behind the McCune-Albright syndrome? Activating mutation in Gs∂ --> hyperfx of endocrine tissue --> large ovarian cysts in girls
|

