![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
45 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
what is asexual reproduction how many parent organisms does it need example |
Reproduction that does not need sex one parent all body cells |
|
|
How does asexual reproduction work |
New cells are formed when old ones divide to create two identical copies called daughter cells |
|
|
what is the process called that cells divide by |
Mitosis |
|
|
When does sexual reproduction begin |
When the male and female sex cells (called gametes) fuse to form a new cell called a zygote |
|
|
What does the zygote do |
Divides over and over to produce the number and variety of cells needed to form a new organism |
|
|
What is the fusing of gametes called |
Fertilization |
|
|
why cant a gamete build a zygote by itself |
because it only carries half the number of chromosomes |
|
|
What are advantages to sexual reproduction (3) |
- Evolution (mutation) - variation (if there is little variation then a small change in the environment could wipe out a species) - produces offspring that are similar but different to parents |
|
|

|
|
|

|
|
|
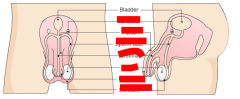
1. Ureter: 2. Prostategland: 3. Cowper'sglad: 4. Seminalvesicle: 5. Urethra |
1. delivers urine from the kidneys to the bladder. 2. add fluids to sperm to make semen. 3. neutralize the urethra 4. secretesfluids that are in it 5. tube running the length of the penis. It empties the bladder of urine and allows the passage of semen |
|
|
1. Testicle or testis: 2. Epidermis: 3. Penis: |
1. where the sperm is made or formed. They are also responsible for theproduction of testosterone. 2. coiled tubes at the top of the testis in which sperm are stored 3. contains sponge like tissue that fills with blood when the male is sexuallyaroused. The tissue expands and is harder than before, causing an erection. |
|
|
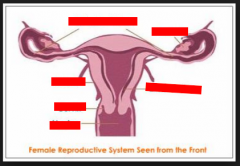
1. Ovary 2. Cervix 3. Fallopian tube |
1. releaseseggs (ova) and produces the female sex hormone estrogen and progesterone. 2. thesmall opening to the uterus. The cervix stretches during child birth. Duringsexual intercourse the penis foes not enter the cervix or the uterus. 3. thetube connecting ovaries to the uterus. Fertilization can occur there. |
|
|
1. Uterus 2. vagina |
1. thefertilized egg implants itself in the lining of the uterus to continue growing.The baby develops and grows here for the nine months of pregnancy. 2. thepenis is inserted here during sexual intercourse. Sperm must swim from here tothe fallopian tubes if fertilization is to occur. |
|
|
what is the menstrual cycle controlled by? |
Hormones from the ovaries and the pituitary gland |
|
|
what is mensturation |
The uterus lining breaking down caused by FSH (follicle stimulating hormone) |
|
|
what will a fertilized egg do |
it will bury itself in the uterus lining |
|
|
whats the difference between mitosis and meiosis |
mitosis is cell division which results in two daughter cells with the same number of chromosomes. (used for cell growth and repair) meiosis is the production of four daughter cells (divided in two divisions: meiosis 1 and meiosis 2) (used for sexual reproduction and produces haploid cells different to each other |
|
|
what are chromosomes and their genes made of |
DNA (deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) |
|
|
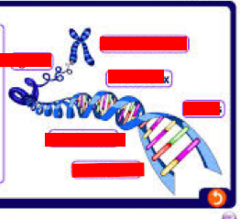
How does DNA form chromosomes |
They are long molecule of tightly coiled DNA |
|
|
What does DNA do? |
Carry code that controls what cells are made of and what they do |
|
|

|
|
|
what is a DNA ladder held together by |
held together by rungs made from pairs of chemicals called basas |
|
|
4 types of bases DNA |
A-adenine C-cytosine G-guanine T-thymine |
|
|
difference between homozygous and heterozygosis |
An organism can be homozygous dominant, if it carries two copies of the same dominant allele, or homozygous recessive, if it carries two copies of the same recessive allele. Heterozygous means that an organism has two different alleles of a gene. |
|
|
how are characteristics passed on to offspring |
Through chromosomes |
|
|
where are chromosomes located |
in the nucleus of cells |
|
|
What are homologous chromosomes |
chromosomes in matching pairs. They contain one chromosome that is inherited from each parent |
|
|
What X and Y combination makes: 1. girl 2. boy what chance do you have of having a girl |
1. XX 2. XY 50:50 |
|
|
what are sex linked traits |
traits that are linked by the X and Y chromosome eg red/green colour blindness or hemophilia |
|
|
when deos crossing over occur |
When the chromatids line up in the first cell division of meiosis. |
|
|
what is crossing over |
when the chromatids line up in pairs and parts of the chromosome can cross over to the other. This can happen randomly leading to large variations within offspring |
|
|
two examples of how gene technology has been used to benefit humans |
Crops can be larger taste better or stored better can detect disorders |
|
|
what is gene technology |
Gene technology alters particular characteristics of an organism by manipulating its genes |
|
|
Genetically modified plants |
Organisms that have their gene sequences altered are called genetically modified plants or animals |
|
|
what are transgenic animals |
An animal that has modified genes directly injected into it |
|
|
what is genetic engineering |
is about changing the DNA of a living thing to change its characteristic |
|
|
what are GM crops and 7 examples |
Crops that have been genetically modified - pest resistant - more nutricious - frost resistant - disease resistant - herbicide resistant - drought resistant - longer shelf life |
|
|
4 advantages of genetically modified crops |
- GM crops would need fewer chemical sprays -GM crops could grow in harsher conditions - GM crops could give bigger yields - GM crops could result in cheaper food |
|
|
4 disadvantages of genetically modified crops |
- The new proteins in GM crops could cause allergies - GM crops could reduce biodiversity - Accidental transfer of new genes to other plants - GM seeds are expensive |
|
|
advantages of genetic modifications (4) |
1. fix genes with diseases 2. genes can be used to show desirable characteristics 3.reduce cost of food production 4. better resistance to weeds pests and disease |
|
|
disadvantages of genetic modifications (3) |
1. unnatural 2. scientists playing god tampering with nature 3. couple food companies controlling food production |
|
|
What did Gregor Mendel discover |
Gregor Mendel, through his work on pea plants, discovered the fundamental laws of inheritance. He deduced that genes come in pairs and are inherited from each parent. Mendel tracked the segregation of parental genes and their appearance in the offspring as dominant or recessive traits. |
|
|
what are the symptoms of cystic fibrosis (5) |
-Persistent coughing, at times with phlegm -Frequent lung infections including pneumonia or bronchitis - Wheezing or shortness of breath -Poor growth or weight gain in spite of a good appetite -Male infertility |
|
|
is cystic fibrosis recessive or dominant |
recessive |

