![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
24 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
what is the difference between sex determination and differentiation?
|
Sex Determination: genetic makeup driving development of the bipotential gonad into an ovary or a testis
Sexual Differentation: Functional gonad driving development of internal and external reproductive structures |
|
|
what are the key genes on the X chromosome that leads to sexual development?
on the Y? |
two on the X chromosome: DAX-1 & the androgen receptor (AR)
one on the Y chromosome: SRY |
|
|
what are pseudoautosomal regions?
|
pairing of chromosomes during meiosis, crossing over occurs here
|
|
|
invagination of coelomic epithelium gives rise to what?
|
Paramesonephric ducts (female/mullerian)
|
|
|
if you have a developmental steroid problem in your gonads, where else might you have problems?
|
in the adrenal...
shared development |
|
|
what leads to regression of the mullerian ducts in men?
|
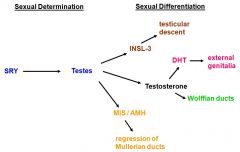
|
|
|
what leads to the development of Wolffian ducts (int genitalia)
|
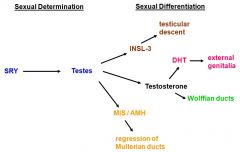
|
|
|
what leads to the external genitalia in males
|
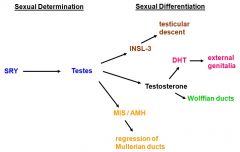
|
|
|
what leads to testicular descent?
|
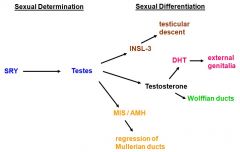
|
|
|
what 3 genes change the urogenital ridge to the bipotential gonad?
** |
Wt1 (Wilm's Tumor)
SF-1 DAX-1 |
|
|
Cells that express the SRY gene will develop into what kind of cells? what is necessary for this?
* |
SRY-->Sox 9-->Sertoli cells
|
|
|
in development, what releases AMH (anti Mullerian hormone) to cause the regression?
|
Sertoli cells
note: AMH also plays a role in testicular descent |
|
|
What stimulates the development of Leydig cells? what is a gene that is necessary for this
|
Sertoli-->Desert Hedge Hog-->Leydig
|
|
|
Starting with the urogenital ridge, go through XY sexual differentiation (include genes leading to the bipotential gonad, what is the important cell that leads to 3 important actions, etc)
|
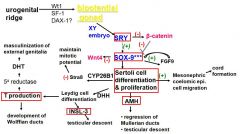
|
|
|
what allows for the maintenance of mitotic potential?
|
Sertoli-->CYP26B1-->(-)Stra8-->maintain mitotic potential
|
|
|
in a XX individual, after the bipotential gonad, what is a key gene that needs to be expressed to lead to further downstream events?
|
R-SPONDIN
|
|
|
R-Spondin leads to what gene activation? what does this do?
|
R-spondin-->Wnt 4--> B-catenin
B-cateinin inhibits Sox 9 and FGF9 (genes that would promote male development) it also inhibits expression of steroidogenic enzymes |
|
|
What activates Dax 1? What does Dax 1 then do (after you have already developed bipotential gonad)
|
Wnt4 stimulates the expression of Dax-1 (inhibits AMH, activates Estrogen)
|
|
|
starting with the urogenital ridge, please map out female sexual differentiation
|
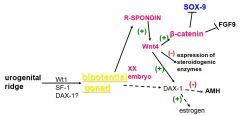
|
|
|
fusion of what structures lead to the development of the uterus, cervix, and upper portion of vagina?
|
paramesonephric ducts
|
|
|
what gives rise to the lower portion of the vagina?
|
urogenital sinus
|
|
|
in development, delay of expression is going to have a larger effect on males or females?
|
males, it starts earlier
|
|
|
what role do androgens play in testicular decent?
|
they increase the regression of the cranial suspensory ligament, leading to the gubernaculum being able to start pull the testes down
|
|
|
Why is hypospadias?
|
- Abnormal opening of penile urethra on ventral side of penis due to incomplete fusion of urethral folds
|

