![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
63 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Looks at shape and size, it can show stones or obstructions. It is the X-ray of kidneys, ureter, bladder studies |
KUB |
|
|
|
Uses sound waves to detect abnormalities in tissues and organs / it measures urine In the bladder ( residual) bladder needs to be |
Ultrasonography measured Full bladder |
|
|
|
Measures the renal excretion of urea nitrogen, a by product of protein metabolism of the liver |
BUN Normal. 7-20 Decreased renal failure, excessive protein intake, dehydration Increase means malnourished, over hydration, and liver damage |
|
|
|
Abnormally high levels of waste products in blood |
Uremia |
|
|
|
Restrict sodium and protein and give diuretics and carbohydrates?? |
Acute glomerulonephritis |
|
|
|
Abnormally high levels of waste products in blood |
Uremia |
|
|
|
Restrict sodium and protein and give diuretics and carbohydrates?? |
Acute glomerulonephritis |
|
|
|
This disease is characterized by proteinuria |
Chronic glomerulonephritis |
|
|
|
A kidney disorder that causes the body to excrete too much protein in the urine. It is a cluster of clinical findings that reflect underlying organ damage |
Nephrotic syndrome |
|
|
|
Disorder that causes structural changes in the glomerulus resulting in Renal loss of protein resulting in a Edema |
Nephrotic syndrome |
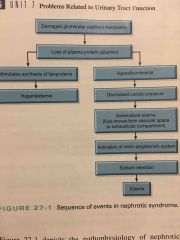
|
|
|
This disease is diagnosed with a needle biopsy of the kidney |
Nephrotic syndrome |
|
|
|
This lab test increases at a rate dependent on the degree of protein catabolism and Renal perfusion and fluid and protein intake |
BUN |
|
|
|
This lab test is more sensitive indicator of renal function then be you and it increases with glomerular damage and is used to monitor kidney function and disease progression |
Serum creatinine |
|
|
|
This lab test increases at a rate dependent on the degree of protein catabolism and Renal perfusion and fluid and protein intake |
BUN |
|
|
|
This lab test is more sensitive indicator of renal function then be you and it increases with glomerular damage and is used to monitor kidney function and disease progression |
Serum creatinine |
|
|
|
With Burns and crash injuries Myoglobin a protein released from the muscles when Injury occurs and hemoglobin are liberated causing obstruction Renal toxicity and in ischemia |
Myoglobinuria Or rhabdomyolysis |
|
|
|
Hyperkalemia may be reduced by administering this via orally, NG tube or retention enema |
Kayexalate (polystyrene sulfonate) exchanged sodium ions for potassium ions in the intestinal tract |
|
|
|
Foods containing potassium |
Bananas, citrus, tomatoes, melons |
|
|
|
Rising this can lead to confusion and lethargy |
Bun |
|
|
|
Why do seizures occur in esrf? |
Azotemia |
|
|
|
Why does someone with renal disease develop ulcers in the G.I. Tract |
Because chronic kidney disease places the body in stress |
|
|
|
Why does chronic kidney disease cause metabolic acidosis |
Because The G.I. track is unable to excrete acids excrete hydrogen ions and reabsorb bicarbonate |
|
|
|
Why does chronic kidney disease cause metabolic acidosis |
Because The G.I. track is unable to excrete acids excrete hydrogen ions and reabsorb bicarbonate |
|
|
|
Pain renal colic hematuria master swelling in the flank Ecchymosis and lacerations of the lateral and and Frank |
Renal trauma |
|
|
|
Why does chronic kidney disease cause metabolic acidosis |
Because The G.I. track is unable to excrete acids excrete hydrogen ions and reabsorb bicarbonate |
|
|
|
Why does chronic kidney disease cause metabolic acidosis |
Because The G.I. track is unable to excrete acids excrete hydrogen ions and reabsorb bicarbonate |
|
|
|
Pain renal colic hematuria master swelling in the flank Ecchymosis and lacerations of the lateral and and Frank |
Renal trauma |
|
|
|
What is the most common manifestation of renal trauma |
Hematuria |
|
|
|
Ecchymosis over the flank area |
Grey turners signs |
|
|
|
Why does chronic kidney disease cause metabolic acidosis |
Because The G.I. track is unable to excrete acids excrete hydrogen ions and reabsorb bicarbonate |
|
|
|
Pain renal colic hematuria master swelling in the flank Ecchymosis and lacerations of the lateral and and Frank |
Renal trauma |
|
|
|
What is the most common manifestation of renal trauma |
Hematuria |
|
|
|
Ecchymosis over the flank area |
Grey turners signs |
|
|
|
Ecchymosis over the Periumbilical area |
Cullen's sign |
|
|
|
Urine is. Formed here |
In the nephrons |
|
|
|
Urine is. Formed here |
In the nephrons |
|
|
|
Three step process to make Urine |
Glomerular filtration, tubular reabsorption, and tubular secretion |
|
|
|
Proteinuria greater than ----- is indicative of nephrotic syndrome and glomerular disease |
3.5 |
|
|
|
Proteinuria greater than ----- is indicative of nephrotic syndrome and glomerular disease |
3.5 |
|
|
|
The most life threatening effect of renal failure |
Retention of potassium |
|
|
|
This test refers to the kidneys ability to clear solutes from the plasma it is a 24 hour collection of urine it's factors include how quickly the substance is filtered across the glomerulus how much of the substance is reabsorbed along the two tubules and how much of the substance secreted into the tubules |
Renal clearance |
|
|
|
Endogenous waste product of skeletal muscle that is filtered at the glomerulus pass through the tubules with minimal change, and excreted in the urine! making it a good measure of the glomerular filtration rate |
Creatinine |
|
|
|
Urge to void starts at and it definitely feels at |
150-250 350 |
|
|
|
If residual urine is more that 100 |
It is increased risk for infection |
|
|
|
Why does diabetes increase risk for uti |
Increase glucose in urine = +environment for bacteria |
|
|
|
Bacteria entered the urinary Tract by three ways |
Ascending ( moving up urethra) Hematogenous spread (through blood stream) Direct extension ( fistula or hole in the intestines where batería are rampant) |
|
|
|
Which route is more common |
Ascending route E. Coli |
|
|
|
This confirms a UTI |
UA |

|
|
|
What can cause pyelonephritis |
Ureterovesical valve If chronic will need dialysis or transplant |
|
|
|
What does an IVP diagnose |
Stones, cyst, and obstructions |
|
|
|
Wilmors tumor favors what kidney |
L kidney Do not palpate de abd |
|
|
|
Neurological changes respiratory changes cardiovascular changes nausea vomiting anorexia hickups uremic frost anemia sexual dysfunction Fetor |
Chronic kidney failure |
|
|
|
End stage renal failure is characterized by a GFR of |
Less than 15 mL per minute |
|
|
|
When blood glucose leves rose about 220 mg/dl renal threshold for reabsorption is exceeded and |
Glucose is found in urine |
|
|
|
When fluid intake decreases the specific gravity |
Increases and vice versa |
|
|
|
The end product of muscle and protein metabolism |
Creatinine |
|
|
|
Normal GFR Is |
60 or greater |
|
|
|
Normal GFR Is |
60 or greater |
|
|
|
What is the best indicator of overall kidney function? |
Creatinine clearance Calculates measure of GFR filtration rate |
|
|
|
Measures the renal excretion of urine nitrogen a byproduct of protein metabolism in the liver however it is not the best indicator for kidney function |
BUN Normal range is 10-20 |
|
|
|
Best test to diagnose bladder ca |
Cystoscopy |
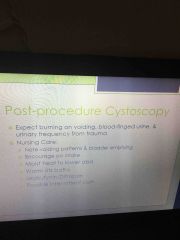
|
|
|
Proteins secreted by damaged kidney tubules |
Cast ( urinary cast) |
|
|
|
Why mental changes with acute glomerulonephritis? |
Due to build up of nitrogenous waste |
|

