![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
12 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the hallmarks of membranous nephropathy?
|
Adults with protenuria. edema (due to the protinuria), possibly coagulation problems.
|
|
|
What is unique about the deposition of Ig in membranous nephropathy?
|
They deposit in the subepethelal space.
Since this is remote from the plasma (where the compliment is), the actual glomerulus isn't dramatically altered and appears normal on microscopy. |
|
|
List four groups of secondary causes for membranous nephropathy.
|
Cancers (lung, lymphomas, colon)
Infections (malaria, hep B and C) Drugs (Penicillamine, gold) Immunologic (SLE) |
|
|
A child presents with edema and protinuria. What is the most likely disease?
|
Minimal change disease.
I bet there's minimal change in the disease. |
|
|
What is the only real change in minimal change disorder?
|
Podocyte effacement (only seen on SEM)
|
|
|
This was seen in a child with protinuria. What is it?
|
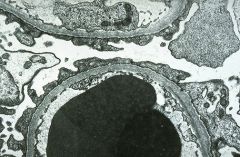
Minimal change disease. You don't actually biopsy these kids.
|
|
|
What is used to treat MCD?
|
Roids
|
|
|
What is the most common cause of nephrotic syndrome in African Americans?
|
Focal and Segmenting Glomerular Sclerosis (FSGS)
|
|
|
How does FSGS progress?
|
It starts in the medulary glomerulus and progresses in a random pattern throughout the kidney with tubular atrophy and interstitial fibrosis.
|
|
|
What causes are there for FSGS?
|
Idiopathic
AIDS (Collapsing FSGS) Genetic (seen in children) Adaptive response to renal damage |
|
|
Of the big three nephrotic syndromes which are most common in adults?
|
Membranous Nephtopathy
FSGS |
|
|
What lesions are typical in the kidney of diabetic nephropathy?
|
Diffuse and nodular glomerular lesions
Atherosclerotic vessels Pylonephritis lesions |

