![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
64 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
1)Annual incidence of kidney stones
2) peak onset? 3) more common in men or women |
1) 1:1000
2) third decade 3)Men |
|
|
What is he medical term for flank pain of kidney-stone origin?
|
Renal colic
|
|
|
4 Symptoms of nephrolithiasis
(2 are just in some cases) |
Renal Colic
hematuria UTI Renal falure in severe cases due to obstruction |
|
|
1) Describe the time course of renal colic
2) Where does it radiate |
1) abrupt in onset. lasts 30-60 minutes
2) down the path of the ureter to the groin/testicles/labia |
|
|
The basic DDx fr acute abdominal or flank pain (6 Things)
|
Ectopic pregnancy
Nephrolithiasis GI obstruction Appendicitis Testicular Torsion Diverticulitits |
|
|
Nephrolithiasis with a chief complaint of pain usually presents with other symptioms such as...
|
microscopic or macroscopic hematuria
Frequency Urgency Nausea Vomiting |
|
|
Can plain films see?
1) Calcium phosphate crystals 2) Cacium oxalate stones 3) Struvite (Maagnesium ammonium phosphate) 4) uric acid stones 5) cysteine stones |
1) yes
2) yes 3) yes 4) no 5) no |
|
|
What two imaging modalities an see all types of crystals?
|
US and CT
|
|
|
Frequency of Urinary Stones... given the frequency, name the stone
1) 80% 2)10% 3) 8% 2) 1% |
1) Calcium
2) Uric acid 3) struvite 4) Cysteine |
|
|
There are three kinds of Ca++ based stones. Name them and give their frequency (should add up to 80% because Ca++ stones are 80% of stones)
|
1) Calcium oxalate- 35%
2) Calcium oxalate and Calcium phosphate MIXED- 40% 3) Just Calcium phosphate- 5% |
|
|
Name a drug which can ppt. to cause stones
|
TRIAMTERENE (in lecture)
Acyclovir |
|
|
Three steps needed for stone formation
|
1) nidus formation
2) retention of nidus in tract 3)Growth of nidus to the size where it can be seen radiographicaly or symptoms |
|
|
The level of saturation where solid is in equilibrium with solute (liquid) is called the...
|
Solubility product
|
|
|
The level of supersaturation where a solute can no longer exist in the solute phae and spontaneously ppts. out is called the...
|
formation product
|
|
|
What is heterogenous nucleation?
|
Precipitation below saturation point due to seeding by a solid phase already present.
|
|
|
Do Calcium Oxalate crystals form by heterogenous nucleation?
|
Yes
|
|
|
Give a single explanation that accounts for these two facts
1) Calcium oxalate crystals often contain calcium phosphate 2) High urine uric acid (hyperuricosuria) favors Calcium oxalate stone formation |
Calcium oxalate crystals form by heterogenous nucleation on small nidus of Calcium phosphate of uric acid.
|
|
|
___ urine volume (concentrated urine) favors stone formation
|
low
|
|
|
Low urine pH lowers the solubility of ___1____
High Urine pH lower the solubility of ___2___ and ___3____ 4) Why is (1) true? |
1) Uric acid (is less soluble than H + Urate)
2) Calcium phosphate 3) Struvite 4) Favors H2PO4- over HPO4 (2-). The former forms more soluble Calcium complexes. |
|
|
low urine pH is a risk factor for 2 kinds of crystals. why?
|
Uric acis is less soluble when protonated, and these crystals are niduses for Calcium oxalate crystal formation. (Heterogeneous nucleation)
|
|
|
1)High pH cause the precipitation of crystals containing ____1____
2) two examples of these crystals are? |
1) Phosphate
2) Calcium oxalate and Struvite |
|
|
1) Calcium phosphate stones are most often seen in patients with what other condition?
2) Why? |
1) Distal renal tubular acdosis
2) persistently alkaline urine |
|
|
1) Struvite stones from in the presence of what other condition?
2) Why? |
1) UTI with a urease-positive bug
2) Urease splits urea to CO2 and ammonia which alkalinizes the urine, and then combines with phosphate and Mg++ to form struvite crystals. |
|
|
1) What is the main biogenic inhibitor of nephrolithiasis?
2) How does it work? |
1) Citrate
2) Because it bins Ca++ to a soluble complex |
|
|
1) Hypocitraturia can be caused by what systemic phenomenon?
2) This same sytemic phenomenon can be caused by ______kalemia. Why? |
1) Metabolic Acidosis
2) Hypokalemia, because K+ conservation drags H+ with it and causes an acidosis |
|
|
What is aggregation?
|
Smaller crystals form to make a larger symptomatic one
|
|
|
Hypercalcemia can cause hypercalciuria by overflow. How do these conditions cause hypercalcemia?
2) TB and sarcoidosis 3) tumor 4) Immobilization 5) PTH secreting parathyroid adenoma |
2) increased D3 synthesis leading to Ca++ uptake from gut
3) eats away bone, liberating Ca++ 4) Bone reabsorption 5) Bone reabsorption |
|
|
1) Hypocalciuria not caused by hypocalcemia is caused by?
2) How do we think it is mediated |
1) idiopathic
2) Increase Ca++ reabsorption from gut |
|
|
1) Mainstay Tx of Calium oxalate nephrolithiasis?
2) how do they work? 3) Why not lasix? |
1) Thiazide Diuretics
2) The mainly work by decreasing ECFV which results in PCT reabsorption of Ca++ 3) Loop diuretics cause hypercalciuria |
|
|
high protein intake predisposes you to calcium stones in two ways. Name them.
|
1) Acidifies urine, favoring formation of uric acid nidus
2) Hypocitraturia |
|
|
How does sodium intake effect stone formation?
|
High sodium intake expands the ECFV which halts PCT uptake of Ca++. This favors hypercalciuria and promotes nephrolithiasis.
|
|
|
Hyperoxaluria promotes Calcium oxalate stone formation.
What foods promote dietary hyperoxaluria? |
nuts
sunflower seeds spinach rhubarb chocolate lime peel star fruit peppers |
|
|
1) Name some surgicalcauses of enteric hyperoxaluria
2) What natural product increases the permeability of the colonic mucosa to oxalate? 3) FIrst Tx for hyperoxaluria? (twofold) 4) Second Tx of hyperoxaluria? |
1) Small bowel resection
jejunal bypass inflammatory bowel 2) Detergent bile acids 3) Dietary restriction and Calciu carbonate which binds oxalate in gut. 4) Cholestyramine which binds bile acids in the gut. 5) |
|
|
1) Primary hyperoxaluria is hereditary ovrproduction of oxalate by the _______
2) Symptoms? |
1) liver
2) Childhood onset of Calium oxalate stones in the kidney, heart, joints, and eyes |
|
|
How does diarrhea cause uric acid stone formation? (two ways)
|
1) wastes bicarb, acidifying urine
2) reduces urinary volume, increases concentration. |
|
|
1)Under what situations can one have high uric acid in the urine?
2) Uric acid is a metabolite of what essential molecules? |
1) Tumor lysis after chemo
hematologic malignanacies Anythign which causes lots of purine turnover. 2) Purines |
|
|
Tx of uric acid stone? (3 things)
|
replete volume
alkalinize urine >6.5 with Potassium citrate Allopurinol which inhibits xanthine oxidase conversio of xanthine to uric acid. |
|
|
What should I use to alkalinize the urine in the case of a uric acid stone?
|
Potassium citrate
Citrate will help favor Ca++ excretion so Ca++ stones dont form. Basic pH deprotonates urate and makes it more soluble |
|
|
What does allopurinol do?
|
Inhibits xanthine oxidase from converting xanthine to uric acid
|
|
|
Magnesium ammonium phosphste
ureas stones infection stones triple stones all refer to? |
Struvite stones
|
|
|
Proteus spp., Providencia spp, enterococci, and Pseudomonas spp. all ____1____ the urine by producing ____2___ which splits __3__ to ___4__ and ___5___. This favors formation of ____6___ stones
|
1) alklainize
2) urease 3) urea 4) CO2 5) Ammonia 6) Struvite |
|
|
How do mixed struvite/ Ca++ oxalate stones evolve?
|
Primary Ca++ oxalate stones cause UTI with a urease positive bug which then favors struvite ppt.
|
|
|
Struvite stones do or do not pass spontaneously?
|
Do not
|
|
|
Which two kinds of stones grow to be the largest, often making staghorn shaped and obstructing the whole renal pelvis
|
Struvite
Cysteine |
|
|
If you see coffin-lid shaped stones in the urine, what is the Dx?
|
Struvite stones
|
|
|
1) What is the Tx for struvite stones?
2) Why do Antibiotics not work? |
1) Surgical removal
2) Incorporation of bacteria into stone, cannot get urine sterile |
|
|
Cystinuria is a genetic defect of....
|
dibasic amino acid transport in the PCT
|
|
|
What 4 AAs are wasted in cystinuria?
|
COAL
Cysteine Ornithine Arginine Lysine |
|
|
Can cysteins stones be seen on abdominal radiograph?
|
NO
|
|
|
Preventative Rx for cysteinuria, besides dietary restriction? How do they work?
|
Penicillamine
Tiopronin By formine disulfide bonds with cysteine, it is solublized. |
|
|
How do we treat alrady developed bad cysteine stones?
|
Surgical removal.
|
|
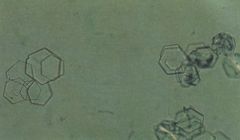
heaxagonal stones in urine. Dx?
|
Cytsteinuria
|
|

Rhomboid, football shaped stones in urine. dx?
|
Uric acid stone
|
|

Ditetrahedral stones in urine. Dx?
|
Calcium oxalate crystals
|
|

coffin lid crystals in urine. Dx?
|
Struvite stones
|
|
|
For patients with Calcium-oxate stones, and high urine oxalate. Rx? Why?
|
It will bind oxalate in the GUT and increase intestinal excretion of oxlate.
|
|
|
Does E. Coli (common cause of UTI) have urease and case struvite stones??
|
Nope
|
|
|
When giving citrate for stone, why do we use the K+ salt and not the Na+ salt?
|
Na+ addition may cause reduced Na+ reabsorption and hence less Ca++ reabsorption.
|
|
|
stones under what size will usually pass on own
|
4-5 mm
|
|
|
Urological interventions for stones...
|
US breakup
ureteroscopy to grab it. |
|

what stone. coffin lid.
|
Struvite
|
|
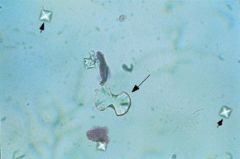
what kind of stone
bitetrahedral or dumbbell |
Ca-ox
|
|
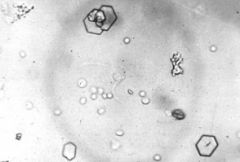
what kind of stone. hexagons.
|
cysteine
|
|

What kind of stone.... footballs
|
Uric acid
|

