![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
28 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
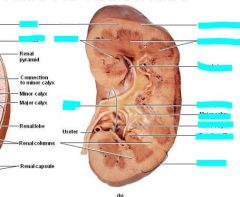
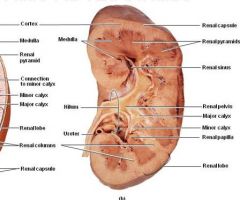
Medulla includes the ____ |
medullary (renal) pyramids and the renal columns |
|
|
Renal papilla |
Tip of the renal pyramid |
|
|
Each pyramid/papilla drains into a ____ |
minor calyx |
|
|
Two or more minor calyces join to form a _____ |
major calyx |
|
|
Major calyces ultimately join to form the ____ |
renal pelvis |
|
|
The ____ is the space created when the fat between the calyces and the renal vessels is dissected away |
Renal sinus |
|
|
|
|
|
Renal lobe includes as _____ as well as _____. All of the nephrons in each lobe drain into ____. |
A renal lobe includes a renal pyramid, as wellas it’s associated cortex (includes portions of the renal columns). All thenephrons in each lobe drain into the associated minor calyx. |
|
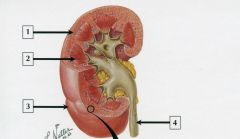
ID 1-4 |
1) Cortex 2) Medulla (pyramid) 3) Fibrous capsule 4) Ureter |
|
|
Blood is filtered by the _____ to produce _____ AKA _____ |
renal corpuscle provisional urine (AKA ultrafiltrate) |
|
|
Order of fluid flow in the kidneys? |
Renal corpuscle Proximal convoluted tubule Loop of Henle - thick descending limb, thin limb (ascending + descending), thick ascending limb Distal convoluted tubule Collecting duct |
|
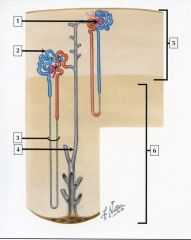
ID 1-6 |
1) Renal corpuscle 2) Proximal convoluted tubule 3) Loop of Henle 4) Collecting duct 5) Renal cortex 6) Renal medulla |
|
|
All renal papillae are directed toward the _____ |
renal pelvis |
|
|
Nephrons are oriented so that the tips of the loops of Henle are closest to the ____ and all collecting ducts are directed toward the ______ |
Nephrons around the kidney are oriented so that the tips of theloops of Henle are closest to theminor calyx, and all collecting ducts are directed toward the minor calyx thatdrains that lobe |
|
|
Organization of the nephrons |
-Coiled parts of the nephron (corpuscle, proximal and distal convoluted tubules) are entirely in the cortex -Straight parts of the nephron (loop of Henle, collecting ducts) fill up the medulla and extend into the cortex |
|
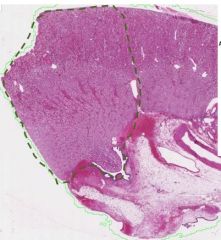
What structure is outlined here |
Renal lobe |
|
|
The cortex of each lobe can be broken down into ____ |
lobules |
|
|
The core of each lobule is composed of _____ and is called the _____. |
straight portions of the nephrone (loops of Henle, collecting duct) pars radiata or medullary rays |
|
|
The periphery of each lobule is composed of the _____ and is called the _____ |
coiled parts of the nephron (corpuscle, PCT, DCT) pars convoluta |
|
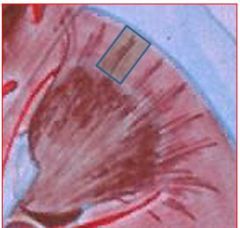
What is outlined? What is the dark part? The light part? |
Outline = lobule (part of the cortex of each kidney lobe) Dark part = straight portions of nephron (loops of Henle, collecting duct) and is called the pars radiata or medullary rays Light part = composed of coiled parts of the nephron (corpuscle, PCT, DCT) and is called the pars convoluta |
|
|
Blood vessels enter and leave the kidney at the ____ |
hilus |
|
|
The renal artery branches into ______ within the _____ |
segmental arteries within the renal sinus |
|
|
Segmental arteries give rise to ______ which run in the _____ between the _____ |
interlobar arteries renal columns renal pyramids |
|
|
At the junction of the medulla and cortex, the interlobar arteries branch at right angles to form the _____ that run ______ |
arcuate arteries between the cortex + medulla |
|
|
Coming off of the arcuate arteries at right angles are ______ which run in the _____ |
interlobular arteries cortex |
|
|
Where are the following arteries found? 1) Renal and segmental vessels 2) Interlobar vessels 3) Arcuate vessels 4) Interlobular vessels 5) Afferent and efferent arterioles 6) Peritbular vessels 7) Vasa recta |
|
|
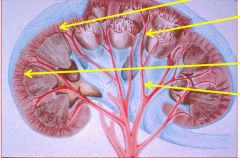
|
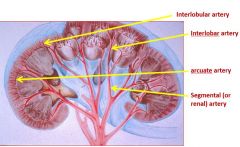
|
|
|
How are arteries and veins in the kidney identified? |
By their position not by their histologic appearance |

