![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
29 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
hydroureter
|
obstruction (probably congenital) at the ureteral orifice
|
|
|
Hydronephrosis
|
abnormal collection of urine within the renal pelvis
|
|
|
Hydronephrosis
|
no echos on ultrasound
|
|
|
Type I RTA
|
the serum is acidic but the urine is alkaline, secondary to an inability to secrete protons into the urine.
|
|
|
Type II (Proximal) RTA
|
inability to reabsorb bicarbonate.
|
|
|
Gross, painless hematauria
|
Bladder tumor
|
|
|
invade into the renal vein
RCC |
Renal Cell Carcinoma
|
|
|
Urinary Tract Infection
|
acute cystitis
painful bladder interstitital cystitits acute/chronic pylonephritis |
|
|
Most common UTI pathogen
|
E. Coli
|
|
|
Inflammation of the bladder
|
acute cystitis
|
|
|
Hyperemia of the mucosa
|
Acute cystitis
|
|
|
Acute infection of the renal pelvis interstitum
Vesicoureteral reflux |
Acute pyelonephritis
|
|
|
Abnormal flow of urine back to the ureters
|
Vesicoureteral reflux
|
|
|
Persistent or recurring episodes of acute pyelonephritis that leads to scarring
|
Chronic pyelonephritis
|
|
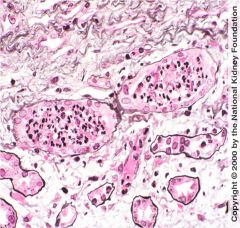
|
Intratubular aggregations of polymorphonuclear neutrophils (PMNs).
|
|
|
Pathogenesis of pathogens
|
1. attachment to epithelium and causes inflammation
2. PMNS cross over epithelial wall into urine |
|
|
Signs of glomerular damage
|
Decreased glomerular membrane surface area
Glomerular capillary blood flow Blood hydrostatic pressure |
|
|
Glomerularnephritis
|
Inflammation of the glomerulus
|
|
|
Mechanisms of Injury
|
Depositions of circulating soluble antigen-antibody complexes
Formation of antibodies against the glomerular basement membrane streptococcal release of NA |
|
|
Goodpasture Syndrome
|
Rapidly progressing glomerularnephritis (antibodies)
|
|
|
Minimal change disease
|
effacement of epithelial cells (podocytes) foot processes and loss of normal charge barrier
|
|
|
Minimal change disease
|
albumin leaks out and proteinemia ensues
|
|
|
Focal glomeruloscelerosis
|
Area of collagenous sclerosis runs across the middle of the glomerulus.
|
|
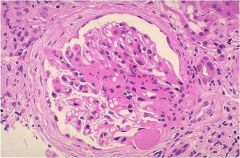
|
Focal Glomerulosclerosis
|
|
|
Chronic Kidney Failure
|
Irreversible loss of renal function that affects nearly all organ systems
|
|
|
Stages of chronic renal failure
|
1. chronic renal insufficiency
2. chronic renal failure 3. end-stage renal failure |
|
|
Hypospadias
|
Chordee - phallus is completely separated from perineum or still tethered downwards from connective tissue or with undescended tissues
|
|
|
Epispadias
|
failure of midline penile fusion much earlier in embrogenesis
|
|
|
Extrophy of the bladder
|
malformation of the bladder and urethra in which bladder is "inside out"
|

