![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
37 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What's the measure we use for acute renal failure?
|
BUN/Creatinine ratio
|
|
|
What is the response of the kidney to BUN?
|
Reabsorbed within the nephron for the countercurrent multiplier
Creatinine isn't. |
|
|
What's the definition of acute renal failure?
|
Abrupt decline in renal function with increased creatinine and increased BUN over a period of several days
|
|
|
What's the cause of prerenal azotemia?
|
Decreased renal blood flow-->decrased GFR
|
|
|
What are the different kinds of acute kidney injury?
|
Prerenal azotemia
Intrinsic renal failure Postrenal azotemia |
|
|
What's the response of the kidney to prerenal azotemia?
|
Retention of Na/H2O and urea in an attempt to conserve volume
|
|
|
What happens to the BUN/creatinine ratio in prerenal azotemia?
|
BUN/creatinine increases
|
|
|
What are the causes of intrinsic renal failure?
|
Acute tubular necrosis
Ischemia/toxins Acute glomerulonephritis |
|
|
What is the pathologic process that occurs during intrinsic renal failure?
|
Patchy necrosis --> debris obstructing the tubules
Backflow results across the necrotic tubule, decreasing GFR. |
|
|
What are the findings in the urine of intrinsic renal failure?
|
Epithelial/granular casts
|
|
|
What happens to the BUN/creatinine ratio in intrinsic renal failure?
|
Decreased BUN/creatinine ratio
|
|
|
What's the cause of postrenal azotemia?
|
Outflow obstruction:
Stones BPH Neoplasia Congenital anomalies Develops only with bilateral obstruction |
|
|
What are the changes in the urine during prerenal azotemia?
|
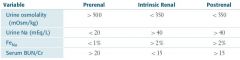
|
|
|
What are the changes in the urine during intrinsic renal failure?
|
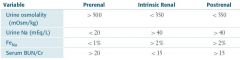
|
|
|
What are the changes in the urine during postrenal azotemia?
|
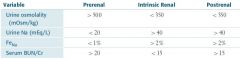
|
|
|
What are the consequences of renal failure?
|
Na/H2O retention
Hyperkalemia Metabolic acidosis Uremia Anemia Renal osteodystrophy Dyslipidemia Growth retardation and developmental delay (kids) |
|
|
What are the two different forms of renal failure/
|
Acute (ATN)
Chronic (HTN, diabetes) |
|
|
What are the consequences of Na/H2O retention following renal failure?
|
CHF
Pulmonary edema HTn |
|
|
What are the symptoms of uremia?
|
Nausea and anorexia
Pericarditis Asterixis Encephalopathy Platelet dysfunction |
|
|
Why is someone anemic during renal failure?
|
no EPO
|
|
|
What are the defects related to vitamin D in renal osteodystrophy?
|
Failure of vitamin D hydroxylation
Hypocalcemia Hyperphosphatemia |
|
|
What is a problem secondary to renal osteodystrophy?
|
Secondary hyperparathyroidism
|
|
|
What's a consequence of hyperphosphatemia in renal osteodystrophy?
|
Independent decrease in serum Ca by causing tissue calcifications
|
|
|
What's a consequence of decreased serum vitamin D in renal osteodystrophy?
|
Decreased intestinal Ca2+ absorption
|
|
|
Grossly, what is a sign of renal osteodystrophy?
|
Subperiosteal thinning of bones on plainfilms
|
|
|
What happens in autosomal dominant polyscystic kidney disease (ADPKD)?
|
Multiple, large, bilateral cysts destroy the kidney parenzyma
|
|
|
What's the presentation of ADPKD?
|
Flank pain
Hematura Hypertension Urinary infection Progressive renal failure |
|
|
What's the mutation in ADPKD?
|
PKD1
PKD2 |
|
|
What's the cause of death in ADPKD?
|
Complications of chronic kidney disease
HTN (increased renin) |
|
|
What are some other things that are associated with ADPKD?
|
Berry aneurysms
Mitral valve prolapse Benign hepatic cysts |
|
|
Who presents with autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease?
|
Infants
|
|
|
What's associated with ARPKD?
|
Congenital hepatic fibrosis
|
|
|
What's an in-utero complication of ARPKD?
|
Potter's syndrome
|
|
|
What are concerns for a baby with ARPKD past the neonatal period?
|
HTN
Portal hypertension Progressive renal insufficiency |
|
|
What pathology occurs in medullary cystic disease?
|
Tubulointerstitial fibrosis
Progressive renal insufficiency Inability to concentrate urine |
|
|
What's the appearance of medullary cystic disease on ultrasound?
|
Shrunken kidneys!
|
|
|
What's the prognosis of medullary cystic disease?
|
Poor.
|

