![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
32 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the normal Intracellular pH?
|
6.9-7.1
|
|
|
What is the normal Extracellular pH?
|
7.35-7.45
|
|
|
How does pH affect protein function?
|
A change in pH can rapidly change protein function and lead to Disorder or Death
|
|
|
What buffers against pH change Both Inside & Outside cells?
|
Weak Acids
|
|
|
What is the primary Extracellular buffer?
|
HCO3- is the primary extracellular buffer
|
|
|
What is the 1st line of defense against pH change?
|
Circulating weak acids
|
|
|
What is the slowest response to buffer pH?
|
Kidneys producing acidic/alkaline urine (via H+ transport)
|
|
|
What are the 3 primary contributors to Extracellular Fluid pH Regulation?
|
1. Weak Acids circulating
2. Lungs for retaining/removing CO2 (respiratory center controls this) 3. Kidneys for producing acidic/alkaline urine (via H+ transport) |
|
|
What allows the lungs and CO2 to buffer the pH?
|
Carbonic Anhydrase
|
|
|
How does CO2 alter the blood pH?
|
C.A. allows CO2 to be thought of as an acid. If CO2 increase pH decreases.
|
|
|
What is another good buffer besides the big 3?
|
Phosphate (H2PO4- -> HPO4-2; pK = 6.8)
|
|
|
Why isn't phosphate as important as HCO3-?
|
Because it is not as abundant (1.4 mM vs 24 mM)
|
|
|
Where is phosphate considered an important buffer?
|
in Urine (because most HCO3- is reabsorbed)
|
|
|
What is especially important as Intracellular Buffers?
|
Proteins (hemoglobin is an H+ buffer)
|
|
|
What are the 3 minor buffers?
|
1. Phosphate
2. Proteins 3. Other weak acids in solution |
|
|
What are examples of metabolic acids?
|
Lactacidosis and GI secretions (stomach secreting acid also adds HCO3- into blood)
|
|
|
What 2 things can we regulate in regards to extracellular pH?
|
1. Respiratory (CO2)
2. Metabolic Acids |
|
|
In response to Acidification the body Compensates w/ _____________ to bring pH back to Normal
|
Alkalinization
|
|
|
What causes Metabolic Alkalosis?
|
Acidic Urine (increased ammonia)or Vomitting
|
|
|
What causes metabolic acidosis?
|
Alkaline Urine or Diarrhea
|
|
|
What causes Respiratory Alkalosis?
|
Hyperventilation
|
|
|
What causes Respiratory acidosis?
|
Hold Breath
|
|
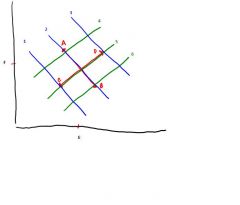
What is happening at point A?
|
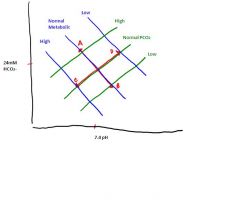
Respiratory Acidosis
(increased PCO2) |
|
What is happening at point B?
|
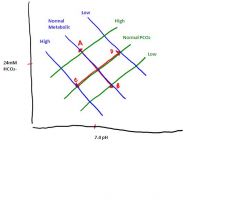
Respiratory Alkalosis
(Alkalosis because decreased PCO2) |
|
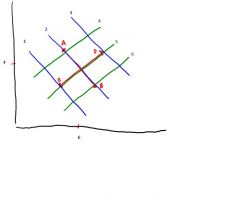
What is happening at point C?
|
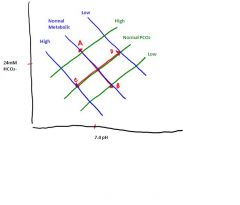
Metabolic Acidosis
(Acidosis because increased metabolic acid) |
|
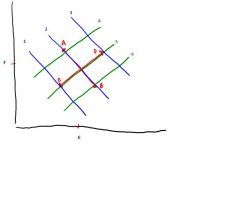
What is happening at point D?
|
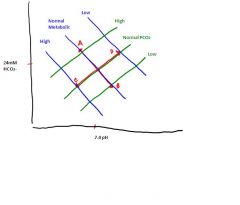
Metabolic Alkalosis
(alkalosis because decreased metabolic acid) |
|
What is happening at point C?
|
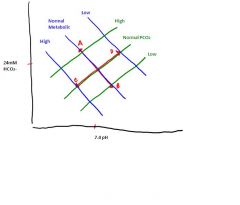
Metabolic Acidosis
(Acidosis because increased metabolic acid) |
|
|
How many ml/min of plasma enters Bowman's Capsule and proceeds into the Proximal Convoluted Tubule (PCT)?
|
125 ml/min
|
|
|
How many ml/min exits the collecting duct and leaves the body as urine?
|
2-3 ml/min
|
|
|
Edema will be "promoted" by any situation which either increases net loss of fluid from the _____________ or by something blockinge the __________ from the area.
|
Capillary (increased CHP, decreased COP, increased TOP or decreased THP)
Lymphatic Drainage (parasites invading the lymph nodes in elephantiasis, or lymph node removal w/radical mastectomy) |
|
|
Sometimes we want to produce edema, such as in Bowman's capsule during urine formation. We can regulate this process by regulating the ________. This is done through the presence of a second __________ associated w/each capillary bed. Therefore, the capillary tuft (glomerulus) present in Bowman's Capsule in each nephron has both an afferent and efferent arteriole. Constriction of the efferent or dilation of an afferent arteriole will increase _____ and increase _______________.
|
CHP (capillary hydrostatic pressure)
Metarteriole CHP Filtration Pressure |
|
|
How is the loss of water from the capillaries reabsorbed?
|
Lymphatic System collects the water and protein in the tissues
|

