![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
52 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
pH =
|
Negative log of free hydrogen ion concentration (usually 40 mmol)
|
|
|
Acidemia and Alkalemia pH?
|
Acidemia = pH < 7.4
Alkalemia = pH > 7.4 |
|
|
Draw out the chart for primary disorders in metabolic and resp disturbances...NOW
|
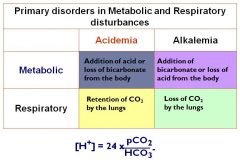
|
|
|
draw the A/B chart with pCO2 and pH
|
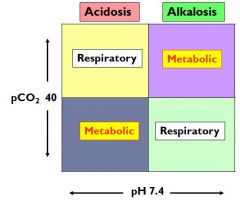
|
|
|
pH: 7.3 pCO2 30
|
Metabolic acidosis
|
|
|
pH: 7.3
PCO2: 47 |
Respiratory acidosis
|
|
|
pH: 7.45
PCO2: 47 |
Metabolic alkalosis
|
|
|
pH 7.45
PCO2: 30 |
Respiratory alkalosis
|
|
|
pH: 7.24
PCO2: 60 primary disorder? HCO3: 20, secondary disorder? |
Primary: Resp acidosis
Secondary: metabolic acidosis (norm is 22-30, so it was low) |
|
|
when do you calculate an anion gap?
|
metabolic acidosis
Cations=anions Na - (Cl + HCO3) |
|
|
normal anion gap?
|
12-16
|
|
|
An increase in the Anion Gap indicates the presence of other unmeasured
anions. This is usually (but not always) associated with.... |
a fall in serum bicarbonate – as in metabolic acidosis.
|
|
|
normal anion gap with metabolic acidosis
|
hyperchloremic
|
|
|
wide anion gap with metabolic acidosis
|
normochloremic
|
|
|
delta delta =
|
change in the anion gap and the change in the plasma HCO3 concentration or
Δ AG/ Δ HCO3 |
|
|
if delta ratio is 1-2
what do you have? |
Pure High AG
Metabolic Acidosis |
|
|
if delta ratio is <1
what do you have? |
High AG acidosis +
Hyperchloremic Metabolic Acidosis |
|
|
if delta ratio is >2
what do you have? |
High AG acidosis +
Metabolic Alkalosis |
|
|
Na+ = 140
Cl- = 102 HCO3 = 16 AG = 22 Δ AG=? Δ HCO3 (if 24 is normal) = D/D ratio? Dx? |
Δ AG = 10
Δ HCO3= 8 Δ Δ = 10/8 = 1.2 Dx: Pure High AG Metabolic Acidosis |
|
|
Example # 2
Na+ = 132 Cl- = 104 HCO3 = 8 AG = 20 AG=? change in HCO3 (if 24 is normal) = D/D ratio? Dx? |
Δ AG = 8
Δ HCO3= 16 Δ Δ = 8/16 = 0.5 Dx: High AG + Hyperchloremic Metabolic Acidosis |
|
|
Na+ = 144
Cl- = 96 HCO3 = 14 AG = 34 AG=? change in HCO3 (if 24 is normal) = D/D ratio? Dx? |
Δ AG = 22
Δ HCO3= 10 Δ Δ = 22/10 = 2.2 Dx: High AG + Metabolic Alkalosis |
|
|
Causes of high AG metabolic acidosis
|
Methanol
Uremia DKA Paraldehyde INH Lactic Acidosis Ethylene glycol Salicylates |
|
|
list 3 major causes of normal AG metabolic acidosis
|
GI loss of HCO3 (diarrhea)
Renal loss of HCO3 (RCAs) HCL/HCL precursor ingestion |
|
|
Cl levels can be a cause of metabolic alkalosis... there are 2 types...
chloride responsive has what level of urinary Cl? what about unresponsive? |
<20 mEq/L --> chloride responsive
>20 mEq/L -->chloride unresponsive |
|
|
Diuretics (remote)
Vomiting Gastrointestinal suction Status post chronic hypercarbia are causes of what |
chloride responsive metabolic alkalosis
|
|
|
Diuretics (recent)
High blood pressure low BP are causes of what? |
chloride UNponsive metabolic alkalosis
|
|
|
CNS depression
Neuromuscular disorders Thoracic cage restriction Impaired lung motion Acute obstructive pulmonary disease COPD causes of? |
respiratory acidosis
|
|
|
Anxiety
Stroke Hormones Drugs Sepsis Hyperthyroidism Pregnancy causes of ? |
respiratory alkalosis
|
|
|
a decrease in anion gap means what?
|
we have a decrease in Na (due to lab error)
or decreased unmeasured anions increased unmeasured cations because UA-UC=anion gap |
|
|
what does Decreased Unmeasured Cations do to the AG?
|
UA - UC =
Serum Anion Gap so increases anion gap |
|
|
what does increased unmeasured cations do to AG?
|
UA - UC =
Serum Anion Gap Decreased Anion Gap |
|
|
what do Decreased Unmeasured Anions do to the AG
|
UA - UC =
Serum Anion Gap Decreased Anion Gap |
|
|
For each Gram drop in serum albumin, the anion gap decreases by a factor of ___
|
2.5
|
|
|
what is your anion gap if your serum albumin is 4.5?
|
12
|
|
|
what is your anion gap if your serum albumin is 3.5?
|
9.5
|
|
|
what is your anion gap if your serum albumin is 2.5?
|
7
|
|
|
what is your anion gap if your serum albumin is 1.5?
|
4.5
|
|
|
true AG = ?
when do you calculate it? |
True AG = [(4.5 – Serum Alb) X 2.5] + AG
when albumin drops below 3 (4 is normal) |
|
|
normal urinary anion gap?
|
-10 to 10
|
|
|
As NH4 excretion increases, what happens to urinary chloride excretion?
|
it must increase as well
|
|
|
Cl excretion does what to the urine anion gap?
|
As chloride excretion increases, urinary anion gap becomes more negative
|
|
|
when you lose bicarb from the kidney, what happens to NH4 excretion? what happens to the urine anion gap?
|
Ammonium excretion decreased
Urine anion gap becomes positive |
|
|
when you lose bicarb from the GI, what happens to NH4 excretion? what happens to the urine anion gap?
|
Ammonium excretion increased
Urine anion gap becomes negative |
|
|
what is the osmolar gap?
|
The difference between the measured and calculated serum osmolality
Calculated Posm = 2 x[plasma Na] + [BUN]/2.8 + [Glucose]/18 measured when you have a met acidosis that is not caused by lactic acid or ketones |
|
|
if you have a metabolic acidosis with a high anion gap, and it is not due to ketones or lactic acid, what do you have to do?
|
calculate the osmolar gap
Calculated Posm = 2 x[plasma Na] + [BUN]/2.8 + [Glucose]/18 |
|
|
An osmolar gap of over ____ indicates the presence of other osmolarly
active substances in the blood |
20
|
|
|
what will the urine pH be like in Type I-III in RTA?
|
Type II: acid
Type I: alkaline Type II: Acid |
|
|
in what type RTA will kidney stones be present?
|
only in type I
|
|
|
In what RTA is Fanconi syndrome present?
|
Type II
|
|
|
what is the urine anion Gap for type I, II, IV
|
positive
|
|
|
please draw out the overall chart for how to figure out an acid base disturbance
|
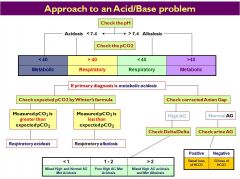
|
|
|
how do you calculate urinary ion gap
|
Na + K - Cl = Urinary Anion Gap
|

