![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
55 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Heteroscedasticity |
-Refers to the circumstance in which the variability of a variable is unequal across the range of values of a second variable that predicts it.
-errors for different response variables have difference variances |
|
|
Homoscedasticity |
Random variables in the sequence have the same finite variance |
|
|
Kurtosis |
Measure of peakedness of the probability distribution |
|
|
High kurtosis is called... |
Leptokurtic (>3) |
|
|
Low kurtosis |
Platykurtic (<3) |
|
|
Kurtosis with a normal distribution... |
Mesokurtic (=3) |
|
|
Residuals |
Errors of variation unexplained by the fitted model |
|
|
Root Mean Square Error (MSE) |
SD of the data about the regression line |
|
|
Assumptions of linear regression: |
1) relationship between X and Y is linear 2) residuals/errors are normally distributed 3) independence of residuals 4) homoskedascity |
|
|
Regression |
A method of estimating a numerical relationship between two variables |
|
|
Adjusted Rsquared |
Like Rsquared but does not increase when new variables are added to a model unless they have additional predictive capability |
|
|
Beta (standardised regression coefficient) |
Measure of how strongly each predictor variable influences the DV. Measured in units of SD. |
|
|
What are the two ways to identify predictor variables? |
1. Confirmatory approach - variables are chosen a priori
2. Exploratory approach - variables chosen automatically from what is available |
|
|
Error |
Part of the variability of Y which is not explained by the relationship with X. |
|
|
Does X or Y equal IV/DV |
Y = DV X = IV |
|
|
Does X or Y equal IV/DV |
Y = DV X = IV |
|
|
When is the least sum of squares the best method? |
The method of least squares is the best method if the deviations from the line are Normally distributed with uniform variance along the line. |
|
|
Why do we minimise variation only for one variable (y axis)? |
There are two reasons for this: 1. We are finding the best prediction of Y from the observed values of X, not from the the TRUE values of x and is included in these deviations measured in the Y direction. 2. The line found in this way depends on the units in which the variables are measured. |
|
|
Exponential |
When a quantity grows or decays at a rate proportional to its current value |
|
|
A logistic cruve |
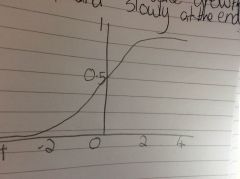
Back (Definition) |
|
|
IRR Incidence rate ratio |
Used in poisson regression |
|
|
IRR Incidence rate ratio |
Used in poisson regression |
|
|
Assumptions of poisson regression: |
1. DV is count 2. DV not over dispersed and not too many zeros 3. Each subject has the same length of observation (or can be adjusted) |
|
|
Can check Poisson distribution before and after regression |
BEFORE fit predicted probabilities to observed probabilities (prcounts)
AFTER test null hypothesis that data are poisson distributed (estaf gof)
|
|
|
Exposure time |
Term used in poisson regression to refer to where subjects are not followed for the same time. (Exposure(variable)) |
|
|
What do you do when poisson has overdispersion (variance > mean) |
Use negative binomial regression |
|
|
What do you do when poisson has overdispersion (variance > mean) |
Use negative binomial regression |
|
|
What to do when there are more zeros count variables than expected from poisson model? |
Use zero inflated poisson model |
|
|
What other methods can be used instead of new models to improve poisson regression? |
Change categories of exposure or introduce new exposures |
|
|
Vuong test |
Used to test, after running a zero inflated poisson, whether a poisson would be a better fit (p<0.00001, use ZIP) |
|
|
Continuous outcome, what type of regression? |
Linear |
|
|
Binary outcome, what type of regression? |
Logistic |
|
|
Count data, what type of regression? |
Poisson |
|
|
Categorical outcome, what type of regression? |
Ordered or multinomial |
|
|
Time to event data, what type of Regression? |
Survival analysis |
|
|
What does censored mean? |
Data is described as censored if it is incomplete.
Observations in survival analysis are 'right censored', which presumes that subjects that are censored did not experience an event during time of study |
|
|
What does the survival function show? |
The survival function gives, for every time, the probability of surviving (or not experiencing the event) up to that time. |
|
|
What does the survival function show? |
The survival function gives, for every time, the probability of surviving (or not experiencing the event) up to that time. |
|
|
What does the hazard function show? |
The hazard function gives the potential that the event will occur, per time unit, given that an individual has survived up to the specified time. |
|
|
What type of regression is also called log linear regression? |
Poisson regression |
|
|
How do you explain the change in coeffiecient in a poisson model? |
For every 1 unit change in the exposure, the log difference of the outcome is expected to change by the expected coefficient holding the other variables in the model constant |
|
|
What is a hazard rate at a time point? |
The hazard rate at a time point is the propensity to develop the event at that instant in time given the event not yet occurred
It represents the instantaneous failure rate at time t |
|
|
What is a hazard ratio? |
When you compare the hazard rate in two groups |
|
|
What is the proportional hazards assumption? |
The cox proportional hazards model relies on the hazards to be proportional I.e. That the effect of a given covariate does not change over time |
|
|
xi: stcox i.empgrade, basesurv(s) basehc(h) basech(ch)
What does basesurv do? |
stores estimate of baseline survival function:estimated probability of surviving till time t for all covariates equal to 0 |
|
|
xi: stcox i.empgrade, basesurv(s) basehc(h) basech(ch)
What does Basech do? |
Basech stores estimate of cumulative hazard function for all covariates equal to 0 |
|
|
xi: stcox i.empgrade, basesurv(s) basehc(h) basech(ch) |
Estimates of baseline Hazard function |
|
|
What is non-informative censoring? |
Censoring that is independent of event of interest (an assumption in Cox) |
|
|
Does the Cox model make any underlying assumptions about the shape of the underlying hazard function? |
No |
|
|
What is a wald test? |
The Wald test is a way of testing the significance of particular explanatory variables in a statistical model. Eg test parm |
|
|
Why is the likelihood ratio test favoured over the Wald test? |
1. No dependence on the scale used for the parameters of interest 2. the ease with which the calculation and interpretation of likelihood ratio statistics can be carried out in more complex situations, as well as simple situations 3.in contrast, although Wald tests are directly interpretable for exposure variables which are represented by a single parameter in the regression model, they are less useful for a categorical variable, which is represented by a serious of indicator variables in the regression model. |
|
|
What type of variable has less power to detect non-linearity in an Likelihood ratio test? Ordinal or continuous? |
Continuous |
|
|
What type of variable has less power to detect non-linearity in an Likelihood ratio test? Ordinal or continuous? |
Continuous |
|
|
What does the term interaction mean? |
The term interaction is used to describe situations in which the relationship between X and Y differs according to the level of one or more other variables |
|
|
For which type of regressions is the coefficient the log odds? |
Logistic, bottom of ZIP.
Coefficient of poisson is the log of the expected counts |

